|
Jacopo Da Varazze
Jacobus de Voragine (c. 123013/16 July 1298) was an Italian chronicler and archbishop of Genoa. He was the author, or more accurately the compiler, of the ''Golden Legend'', a collection of the legendary lives of the greater saints of the medieval church that was one of the most popular religious works of the Middle Ages. Biography Jacobus was born either in Varazze or in Genoa, where a family originally from Varazze and bearing that name is attested at the time. He entered the Dominican order in 1244, and became the prior at Como, Bologna and Asti in succession. Besides preaching with success in many parts of Italy, he also taught in the schools of his own fraternity. He was provincial of Lombardy from 1267 till 1286, when he was removed at the meeting of the order in Paris. He also represented his own province at the councils of Lucca (1288) and Ferrara (1290). On the last occasion he was one of the four delegates charged with signifying Pope Nicholas IV's desire for the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jacobus De Boragine
Jacobus de Boragine was one of the Glossators, and Four Doctors of Bologna. Also known as Jacobus, he was born in the early 12th century and was an Italian lawyer, one of four students of Irnerius called the ''Quattuor Doctores'', although Savigny disputes the general tradition of his inclusion in this list. The other doctors were Bulgarus, Martinus and Hugo. The legal philosophy of Bulgarus adhered closely to the letter of the law while their fellow, Martinus, took a more natural law and Equity approach. His time at Bologna was therefore one of the formative times in legal theory. He was an author of many parts of the Gloss of the ''Corpus juris civilis The ''Corpus Juris'' (or ''Iuris'') ''Civilis'' ("Body of Civil Law") is the modern name for a collection of fundamental works in jurisprudence, issued from 529 to 534 by order of Justinian I, Byzantine Emperor. It is also sometimes referred ...''. *The legal commentary ''De Regulis Juris'', which Savigny calle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dominican Order
The Order of Preachers ( la, Ordo Praedicatorum) abbreviated OP, also known as the Dominicans, is a Catholic mendicant order of Pontifical Right for men founded in Toulouse, France, by the Spanish priest, saint and mystic Dominic of Caleruega. It was approved by Pope Honorius III via the papal bull '' Religiosam vitam'' on 22 December 1216. Members of the order, who are referred to as ''Dominicans'', generally carry the letters ''OP'' after their names, standing for ''Ordinis Praedicatorum'', meaning ''of the Order of Preachers''. Membership in the order includes friars, nuns, active sisters, and lay or secular Dominicans (formerly known as tertiaries). More recently there has been a growing number of associates of the religious sisters who are unrelated to the tertiaries. Founded to preach the Gospel and to oppose heresy, the teaching activity of the order and its scholastic organisation placed the Preachers in the forefront of the intellectual life of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
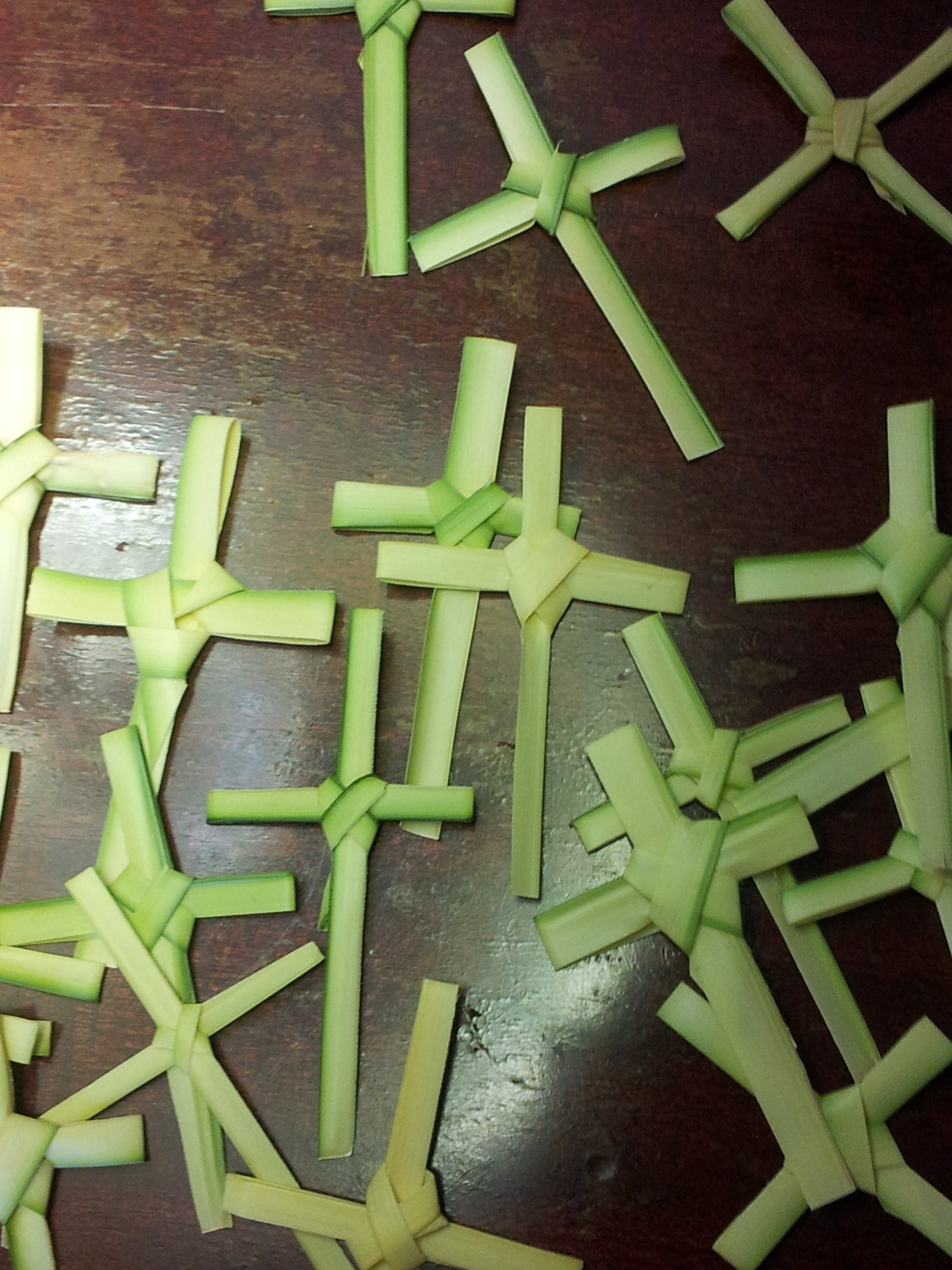
Palm Sunday
Palm Sunday is a Christian moveable feast that falls on the Sunday before Easter. The feast commemorates Christ's triumphal entry into Jerusalem, an event mentioned in each of the four canonical Gospels. Palm Sunday marks the first day of Holy Week. For adherents of mainstream Christianity, it is the last week of the Christian solemn season of Lent that precedes the arrival of Eastertide. In most liturgical churches, Palm Sunday is celebrated by the blessing and distribution of palm branches (or the branches of other native trees), representing the palm branches which the crowd scattered in front of Christ as he rode into Jerusalem; these palms are sometimes woven into crosses. The difficulty of procuring palms in unfavorable climates led to their substitution with branches of native trees, including box, olive, willow, and yew. The Sunday was often named after these substitute trees, as in Yew Sunday, or by the general term Branch Sunday. In Syriac Christianity it is ofte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Franciscan
, image = FrancescoCoA PioM.svg , image_size = 200px , caption = A cross, Christ's arm and Saint Francis's arm, a universal symbol of the Franciscans , abbreviation = OFM , predecessor = , merged = , formation = , founder = Francis of Assisi , founding_location = , extinction = , merger = , type = Mendicant Order of Pontifical Right for men , status = , purpose = , headquarters = Via S. Maria Mediatrice 25, 00165 Rome, Italy , location = , coords = , region = , services = , membership = 12,476 members (8,512 priests) as of 2020 , language = , sec_gen = , leader_title = Motto , leader_name = ''Pax et bonum'' ''Peace and llgood'' , leader_title2 = Minister General , leader_name2 = ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles II Of Naples
Charles II, also known as Charles the Lame (french: Charles le Boiteux; it, Carlo lo Zoppo; 1254 – 5 May 1309), was King of Naples, Count of Provence and Forcalquier (1285–1309), Prince of Achaea (1285–1289), and Count of Anjou and Maine (1285–1290); he also styled himself King of Albania and claimed the Kingdom of Jerusalem from 1285. He was the son of Charles I of Anjouone of the most powerful European monarchs in the second half of the 13th centuryand Beatrice of Provence. His father granted Charles the Principality of Salerno in the Kingdom of Sicily (or ''Regno'') in 1272 and made him regent in Provence and Forcalquier in 1279. After the uprising known as the Sicilian Vespers against Charles's father, the island of Sicily became an independent kingdom under the rule of Peter III of Aragon in 1282. A year later, his father made Charles regent in the mainland territories of the ''Regno'' (or the Kingdom of Naples). Charles held a general assembly where unpopular t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Munio De Zamora
Munio of Zamora, O.P., (1237 – 19 February 1300) was a Spanish Dominican friar who became the seventh Master General of the Dominican Order in 1285, and later a bishop. Life Spain No details of Munio's early life are recorded, but he is assumed to have been born in Zamora. What is known of him comes from diverse sources, of varying value, and giving contradictory judgments. It would appear that he had a reputation of being an excellent administrator, when he was appointed as Prior Provincial of his native country in 1281. He was also known as being an ascetic man, practicing perpetual abstinence, though he also came to be known for his leniency towards those under his authority. One notable difference he had from his predecessors was that he did not have the academic background which they did, never having studied at the great universities of Italy or France, and thus not having a Master's degree. Administration was his sole talent. Master General Munio, in his of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pope Nicholas IV
Pope Nicholas IV ( la, Nicolaus IV; 30 September 1227 – 4 April 1292), born Girolamo Masci, was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 22 February 1288 to his death on 4 April 1292. He was the first Franciscan to be elected pope.McBrien, Richard P., ''Live of the Popes'', p.226, Harper Collins, 2000 Early life Jerome Masci (Girolamo Masci) was born on 30 September 1227 at Lisciano, near Ascoli Piceno. He was a pious, peace-loving man whose goals as a Franciscan friar were to protect the Church, promote the crusades, and root out heresy. According to Heinrich of Rebdorf, he was a Doctor of Theology. As a Franciscan friar, he had been elected the Order's superior (minister) for Dalmatia during the Franciscan general chapter held at Pisa in 1272. Pope Gregory X (1271-1276), was sending a legate to the Byzantine emperor, Michael VIII Palaiologos, in 1272, to invite the participation of Byzantine prelates in the Second Council of Lyons. The pope's ambitio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ferrara
Ferrara (, ; egl, Fràra ) is a city and ''comune'' in Emilia-Romagna, northern Italy, capital of the Province of Ferrara. it had 132,009 inhabitants. It is situated northeast of Bologna, on the Po di Volano, a branch channel of the main stream of the Po River, located north. The town has broad streets and numerous palaces dating from the Renaissance, when it hosted the court of the House of Este. For its beauty and cultural importance, it has been designated by UNESCO as a World Heritage Site. History Antiquity and Middle Ages The first documented settlements in the area of the present-day Province of Ferrara date from the 6th century BC. The ruins of the Etruscan town of Spina, established along the lagoons at the ancient mouth of Po river, were lost until modern times, when drainage schemes in the Valli di Comacchio marshes in 1922 first officially revealed a necropolis with over 4,000 tombs, evidence of a population centre that in Antiquity must have played a majo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lucca
Lucca ( , ) is a city and ''comune'' in Tuscany, Central Italy, on the Serchio River, in a fertile plain near the Ligurian Sea. The city has a population of about 89,000, while its province has a population of 383,957. Lucca is known as one of the Italian's "Città d'arte" (Arts town), thanks to its intact Renaissance-era city walls and its very well preserved historic center, where, among other buildings and monuments, are located the Piazza dell'Anfiteatro, which has its origins in the second half of the 1st century A.D. and the Guinigi Tower, a tower that dates from the 1300s. The city is also the birthplace of numerous world-class composers, including Giacomo Puccini, Alfredo Catalani, and Luigi Boccherini. Toponymy By the Romans, Lucca was known as ''Luca''. From more recent and concrete toponymic studies, the name Lucca has references that lead to "sacred wood" (Latin: ''lucus''), "to cut" (Latin: ''lucare'') and "luminous space" (''leuk'', a term used by the f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lombardy
(man), (woman) lmo, lumbard, links=no (man), (woman) , population_note = , population_blank1_title = , population_blank1 = , demographics_type1 = , demographics1_footnotes = , demographics1_title1 = , demographics1_info1 = , demographics1_title2 = , demographics1_info2 = , demographics1_title3 = , demographics1_info3 = , timezone1 = CET , utc_offset1 = +1 , timezone1_DST = CEST , utc_offset1_DST = +2 , postal_code_type = , postal_code = , area_code_type = ISO 3166 code , area_code = IT-25 , blank_name_sec1 = GDP (PPS) , blank_info_sec1 = €401 billion (2019) , blank1_name_sec1 = GDP per capita , blank1_info_sec1 = €39,700 (2019) $51,666 (2016) (PPP) , blank2_name_sec1 = HDI (2019) , blank2_info_sec1 = 0.912 · 4th of 21 , blank_name ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |