|
Jia Xian
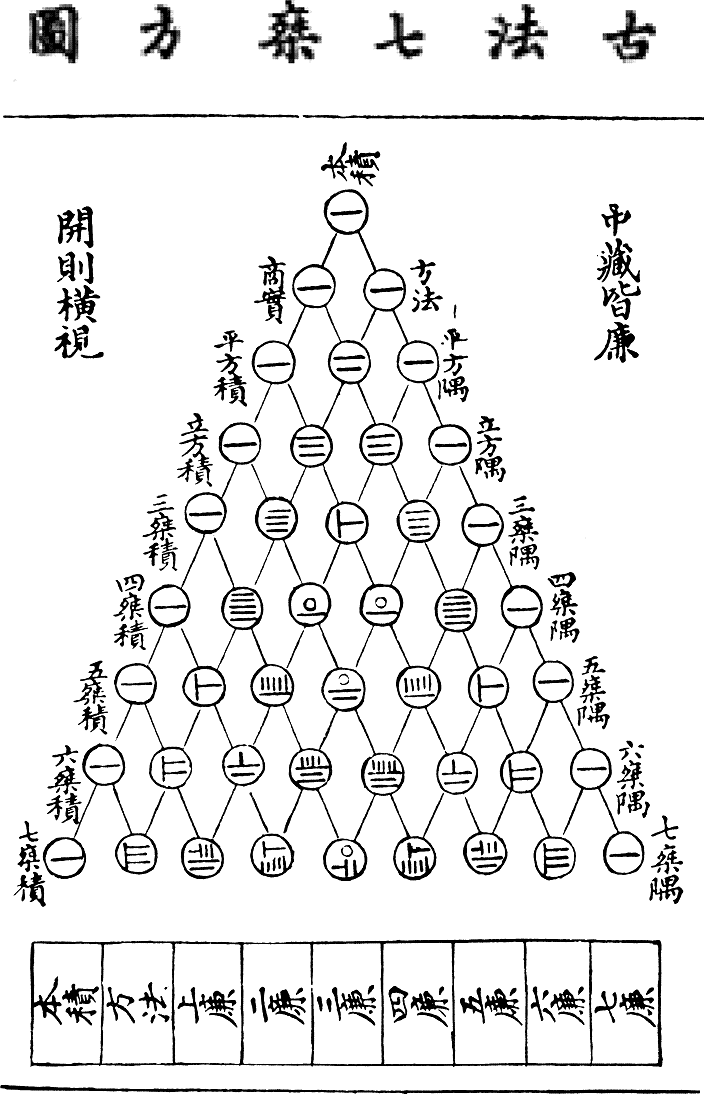
Jia Xian (; ca. 1010–1070) was a Chinese mathematician from Kaifeng of the Song dynasty. He described Pascal's triangle during the 11th century. Biography According to the history of the Song dynasty, Jia was a palace eunuch of the Left Duty Group. He studied under the mathematician Chu Yan, and was well versed in mathematics, writing many books on the subject. Jia Xian described the Pascal's triangle (Jia Xian triangle) around the middle of the 11th century, about six centuries before Pascal. Jia used it as a tool for extracting square and cubic roots. The original book by Jia entitled ''Shi Suo Suan Shu'' was lost; however, Jia's method was expounded in detail by Yang Hui, who explicitly acknowledged his source: "My method of finding square and cubic roots was based on the Jia Xian method in ''Shi Suo Suan Shu''." A page from the ''Yongle Encyclopedia The ''Yongle Encyclopedia'' () or ''Yongle Dadian'' () is a Chinese ''leishu'' encyclopedia commissioned by the Yongl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jia (surname)
Jiǎ () is a surname. Chia is the corresponding Wade-Giles romanization, which is commonly used in Taiwan. Ka is the corresponding Cantonese-based romanization, which is used in Hong Kong and other Cantonese-speaking regions. Notable people with Jia as a surname Historical figures * Jia Yi (賈誼; 200–169 BCE), official of the Han dynasty * Jia Kui (scholar) (賈逵; 30–101), scholar and astronomer of the Eastern Han dynasty * Jia Xu (賈詡; 147–223), official of the Cao Wei state * Jia Kui (general) (賈逵; 174–228), general of Cao Wei state ** Jia Chong (賈充; 217–282), general of the Jin dynasty ** Jia Nanfeng (賈南風; 257–300), empress of the Jin dynasty * Huiyuan (慧遠; 334–416), Buddhist teacher of the Jin dynasty * Jia Dan (賈耽; 730–805), official of the Tang dynasty * Jia Dao (賈島; 779–843), poet of the Tang dynasty * Jia Su (賈餗; died 835), official of the Tang dynasty * Jia Xian (贾宪; 1010–1070), mathematician of the S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yang Hui
Yang Hui (, ca. 1238–1298), courtesy name Qianguang (), was a Chinese mathematician and writer during the Song dynasty. Originally, from Qiantang (modern Hangzhou, Zhejiang), Yang worked on magic squares, magic circles and the binomial theorem, and is best known for his contribution of presenting Yang Hui's triangle. This triangle was the same as Pascal's triangle, discovered by Yang's predecessor Jia Xian. Yang was also a contemporary of Qin Jiushao, another well-known Chinese mathematician. Written work The earliest extant Chinese illustration of 'Pascal's triangle' is from Yang's book ''Xiángjiě Jiǔzhāng Suànfǎ '' () of 1261 AD, in which Yang acknowledged that his method of finding square roots and cubic roots using "Yang Hui's triangle" was invented by mathematician Jia XianNeedham, Volume 3, 134-137. who expounded it around 1100 AD, about 500 years before Pascal. His book (now lost), known as ''Rújī Shìsuǒ'' () or ''Piling-up Powers and Unlocking Coeffici ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Song Dynasty Science Writers
A song is a musical composition performed by the human voice. The voice often carries the melody (a series of distinct and fixed pitches) using patterns of sound and silence. Songs have a structure, such as the common ABA form, and are usually made of sections that are repeated or performed with variation later. A song without instruments is said to be a cappella. Written words created specifically for music, or for which music is specifically created, are called lyrics. If a pre-existing poem is set to composed music in the classical tradition, it is called an art song. Songs that are sung on repeated pitches without distinct contours and patterns that rise and fall are called chants. Songs composed in a simple style that are learned informally by ear are often referred to as folk songs. Songs composed for the mass market, designed to be sung by professional singers who sell their recordings or live shows, are called popular songs. These songs, which have broad appeal, are oft ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematicians From Imperial China
A mathematician is someone who uses an extensive knowledge of mathematics in their work, typically to solve mathematical problems. Mathematicians are concerned with numbers, data, quantity, structure, space, models, and change. History One of the earliest known mathematicians was Thales of Miletus (); he has been hailed as the first true mathematician and the first known individual to whom a mathematical discovery has been attributed. He is credited with the first use of deductive reasoning applied to geometry, by deriving four corollaries to Thales's theorem. The number of known mathematicians grew when Pythagoras of Samos () established the Pythagorean school, whose doctrine it was that mathematics ruled the universe and whose motto was "All is number". It was the Pythagoreans who coined the term "mathematics", and with whom the study of mathematics for its own sake begins. The first woman mathematician recorded by history was Hypatia of Alexandria ( – 415). She succeed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
11th-century Chinese Mathematicians
The 11th century is the period from 1001 (represented by the Roman numerals MI) through 1100 (MC) in accordance with the Julian calendar, and the 1st century of the 2nd millennium. In the history of Europe, this period is considered the early part of the High Middle Ages. There was, after a brief ascendancy, a sudden decline of Byzantine power and a rise of Norman domination over much of Europe, along with the prominent role in Europe of notably influential popes. Christendom experienced a formal schism in this century which had been developing over previous centuries between the Latin West and Byzantine East, causing a split in its two largest denominations to this day: Roman Catholicism and Eastern Orthodoxy. In Song dynasty China and the classical Islamic world, this century marked the high point for both classical Chinese civilization, science and technology, and classical Islamic science, philosophy, technology and literature. Rival political factions at the Song dynasty ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karine Chemla
Karine Chemla (born 8 February 1957) is a French historian of mathematics and sinologist who works as a director of research at the Centre national de la recherche scientifique (CNRS). She is also a senior fellow at the New York University Institute for the Study of the Ancient World. She was elected a Member of the American Philosophical Society in 2019. Education Chemla studied at Paris Diderot University and the École normale supérieure de jeunes filles, earning an agrégation in mathematics in 1978 and a diploma of advanced studies in 1979. At this time, her work was in pure mathematics. However, in 1980, influenced by the work of Ilya Prigogine, she won a Singer–Polignac scholarship to travel to China and study the history of Chinese mathematics.. Returning to France, she earned her Ph.D. in the history of mathematics from Paris 13 University in 1982, and began working for CNRS at that time.. Contributions Chemla's research interests include Chinese mathema ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jia Xian Cubic Root
JIA or Jia may refer to JIA * Japan Institute of Architects * Juína Airport IATA code * Jacksonville International Airport, a medium-to-large airport in the U.S. city of Jacksonville, Florida * Jetstream International Airlines, now known as PSA Airlines * Johannesburg International Airport, a large airport near the city of Johannesburg in South Africa * ''Journal of the Institute of Actuaries'', the former name of a peer-reviewed journal published by the Institute of Actuaries * Juvenile idiopathic arthritis, a disease of joints in young people * PSA Airlines ICAO code Jia * ''Jia'' (EP), by Jia, 2017 * ''Jia'' (short film), 2023 Australian short film * Jia (vessel), a type of ancient Chinese bronze or pottery vessel * ''Family'' (Ba Jin novel) (家, pinyin: Jiā), a 1931–1932 novel by Ba Jin * Jia (甲, Kah), a unit of land measurement used in Taiwan, equal to 0.9699 hectares * Jia (), the first of the ten Heavenly Stems Places * Jia County, Henan (郏县), of Pingdingsh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yongle Encyclopedia
The ''Yongle Encyclopedia'' () or ''Yongle Dadian'' () is a Chinese ''leishu'' encyclopedia commissioned by the Yongle Emperor (1402–1424) of the Ming dynasty in 1403 and completed by 1408. It comprised 22,937 manuscript rolls in 11,095 volumes. Fewer than 400 volumes survive today, comprising about 800 rolls, or 3.5% of the original work. Most of the text was lost during the latter half of the 19th century, in the midst of events including the Second Opium War and the Boxer Rebellion. Its sheer scope and size made it the world's largest general encyclopedia, until it was surpassed by Wikipedia in late 2007, nearly six centuries later. Background Although known for his military achievements, the Yongle Emperor (1402–1424) was an intellectual who enjoyed reading. His love for research led him to develop the idea of categorizing literary works into a reference encyclopedia to preserve rare books and simplify research.Jianying, Huo. "Emperor Yongle." ''China Today'', April ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cubic Root
In mathematics, a cube root of a number is a number that has the given number as its third power; that is y^3=x. The number of cube roots of a number depends on the number system that is considered. Every real number has exactly one real cube root that is denoted \sqrt /math> and called the ''real cube root'' of or simply ''the cube root'' of in contexts where complex numbers are not considered. For example, the real cube roots of and are respectively and . The real cube root of an integer or of a rational number is generally not a rational number, neither a constructible number. Every nonzero real or complex number has exactly three cube roots that are complex numbers. If the number is real, one of the cube roots is real and the two other are nonreal complex conjugate numbers. Otherwise, the three cube roots are all nonreal. For example, the real cube root of is and the other cube roots of are -1+i\sqrt 3 and -1-i\sqrt 3. The three cube roots of are 3i, \tfrac-\tf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yanghui Triangle
In mathematics, Pascal's triangle is an infinite triangular array of the binomial coefficients which play a crucial role in probability theory, combinatorics, and algebra. In much of the Western world, it is named after the French mathematician Blaise Pascal, although other mathematicians studied it centuries before him in Persia, India, China, Germany, and Italy. The rows of Pascal's triangle are conventionally enumerated starting with row n = 0 at the top (the 0th row). The entries in each row are numbered from the left beginning with k = 0 and are usually staggered relative to the numbers in the adjacent rows. The triangle may be constructed in the following manner: In row 0 (the topmost row), there is a unique nonzero entry 1. Each entry of each subsequent row is constructed by adding the number above and to the left with the number above and to the right, treating blank entries as 0. For example, the initial number of row 1 (or any other row) is 1 (the sum of 0 and 1), whereas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |