|
Jendrassik Maneuver
The Jendrassik maneuver is a medical maneuver wherein the patient clenches the teeth, flexes both sets of fingers into a hook-like form, and interlocks those sets of fingers together. The tendon below the patient's knee is then hit with a reflex hammer to elicit the patellar reflex. The elicited response is compared with the reflex result of the same action when the maneuver is not in use. Often a larger reflex response will be observed when the patient is occupied with the maneuver: "A weak or apparently missing reflex could be triggered by afferent activity resulting from such muscle tension. This is the true explanation for the maneuver, not a diversion of the patient’s attention – a misconception that can be heard even today." This effect was first observed in the late 19th century by Hungarian physician Ernő Jendrassik, after whom it was named. This maneuver is particularly useful in that even if the patient is aware of the maneuver's purpose, it still functions prop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
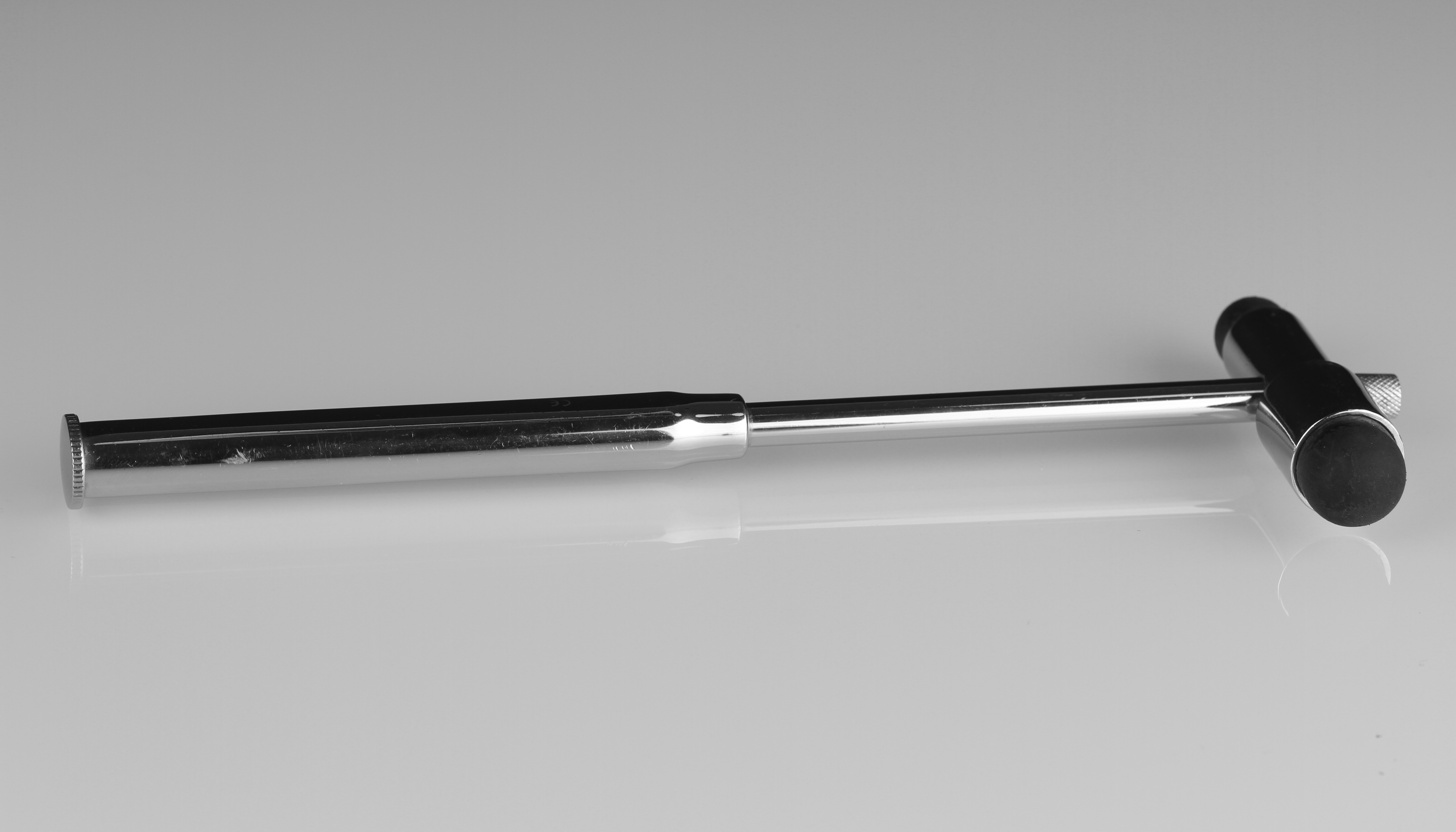
Reflex Hammer
A reflex hammer is a medical instrument used by practitioners to test deep tendon reflexes, the best known possibly being the patellar reflex. Testing for reflexes is an important part of the neurological examination, neurological physical examination in order to detect abnormalities in the central nervous system, central or peripheral nervous system, peripheral nervous system. Reflex hammers can also be used for chest percussion (medicine), percussion.Swartz MH. ''Textbook of Physical Diagnosis: History and Examination.'' Third edition. Philadelphia: WB Saunders; 1998 Models of reflex hammer Prior to the development of specialized reflex hammers, hammers specific for percussion of the chest were used to elicit reflexes.Lanska DJ. The history of reflex hammers. ''Neurology''. 1989 Nov;39(11):1542-9. However, this proved to be cumbersome, as the weight of the chest percussion hammer was insufficient to generate an adequate stimulus for a reflex. Starting in the late 19th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
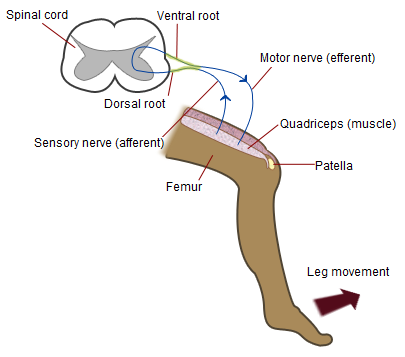
Patellar Reflex
The patellar reflex, also called the knee reflex or knee-jerk, is a stretch reflex which tests the L2, L3, and L4 segments of the spinal cord. Many animals, most significantly humans, have been seen to have the patellar reflex, including dogs, cats, horses, and other mammalian species. Mechanism Striking of the patellar tendon with a reflex hammer just below the patella stretches the muscle spindle in the quadriceps muscle. This produces a signal which travels back to the spinal cord and synapses (without interneurons) at the level of L3 or L4 in the spinal cord, completely independent of higher centres. From there, an alpha motor neuron conducts an efferent impulse back to the quadriceps femoris muscle, triggering contraction. This contraction, coordinated with the relaxation of the antagonistic flexor hamstring muscle causes the leg to kick. There is a latency of around 18 ms between stretch of the patellar tendon and the beginning of contraction of the quadriceps femori ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ernő Jendrassik
Jendrassik Ernő (7 June 1858 – 21 December 1921) was a Hungarian physician best known for his research on reflexes, in particular, the Jendrassik maneuver. He was born in Kolozsvár, Transylvania, Austrian Empire The Austrian Empire, officially known as the Empire of Austria, was a Multinational state, multinational European Great Powers, great power from 1804 to 1867, created by proclamation out of the Habsburg monarchy, realms of the Habsburgs. Duri ..., to Jendrassik Jenő, who was a famous physician and professor of physiology. Jendrassik graduated from the University of Budapest in medicine in 1880. His first paper, ''Beiträge zur Lehre von den Sehnenreflexen'', was published in 1883 and earned him local and international recognition. It was also the beginning of his research on reflexes. References * 1858 births 1921 deaths 19th-century Hungarian physicians 20th-century Hungarian physicians Physicians from Austria-Hungary {{Hungary-med-bio-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Romberg's Sign
Romberg's test, Romberg's sign, or the Romberg maneuver is a test used in an exam of neurological function for balance. The exam is based on the premise that a person requires at least two of the three following senses to maintain balance while standing: * proprioception (the ability to know one's body position in space) * vestibular function (the ability to know one's head position in space) * vision (which can be used to monitor and adjust for changes in body position). A patient who has a problem with proprioception can still maintain balance by using vestibular function and vision. In the Romberg test, the standing patient is asked to close their eyes. An increased loss of balance is interpreted as a positive Romberg's test. The Romberg test is a test of the body's sense of positioning (proprioception), which requires healthy functioning of the dorsal columns of the spinal cord. The Romberg test is used to investigate the cause of loss of motor coordination (ataxia). A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diagnostic Neurology
Diagnosis (: diagnoses) is the identification of the nature and cause of a certain phenomenon. Diagnosis is used in a lot of different disciplines, with variations in the use of logic, analytics, and experience, to determine " cause and effect". In systems engineering and computer science, it is typically used to determine the causes of symptoms, mitigations, and solutions. Computer science and networking * Bayesian network * Complex event processing * Diagnosis (artificial intelligence) * Event correlation * Fault management * Fault tree analysis * Grey problem * RPR problem diagnosis * Remote diagnostics * Root cause analysis * Troubleshooting * Unified Diagnostic Services Mathematics and logic * Bayesian probability * Block Hackam's dictum * Occam's razor * Regression diagnostics * Sutton's law Medicine * Medical diagnosis * Molecular diagnostics Methods * CDR computerized assessment system * Computer-aided diagnosis * Differential diagnosis * Retrospective diagno ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |