|
Italian War In Soviet Union, 1941-1943
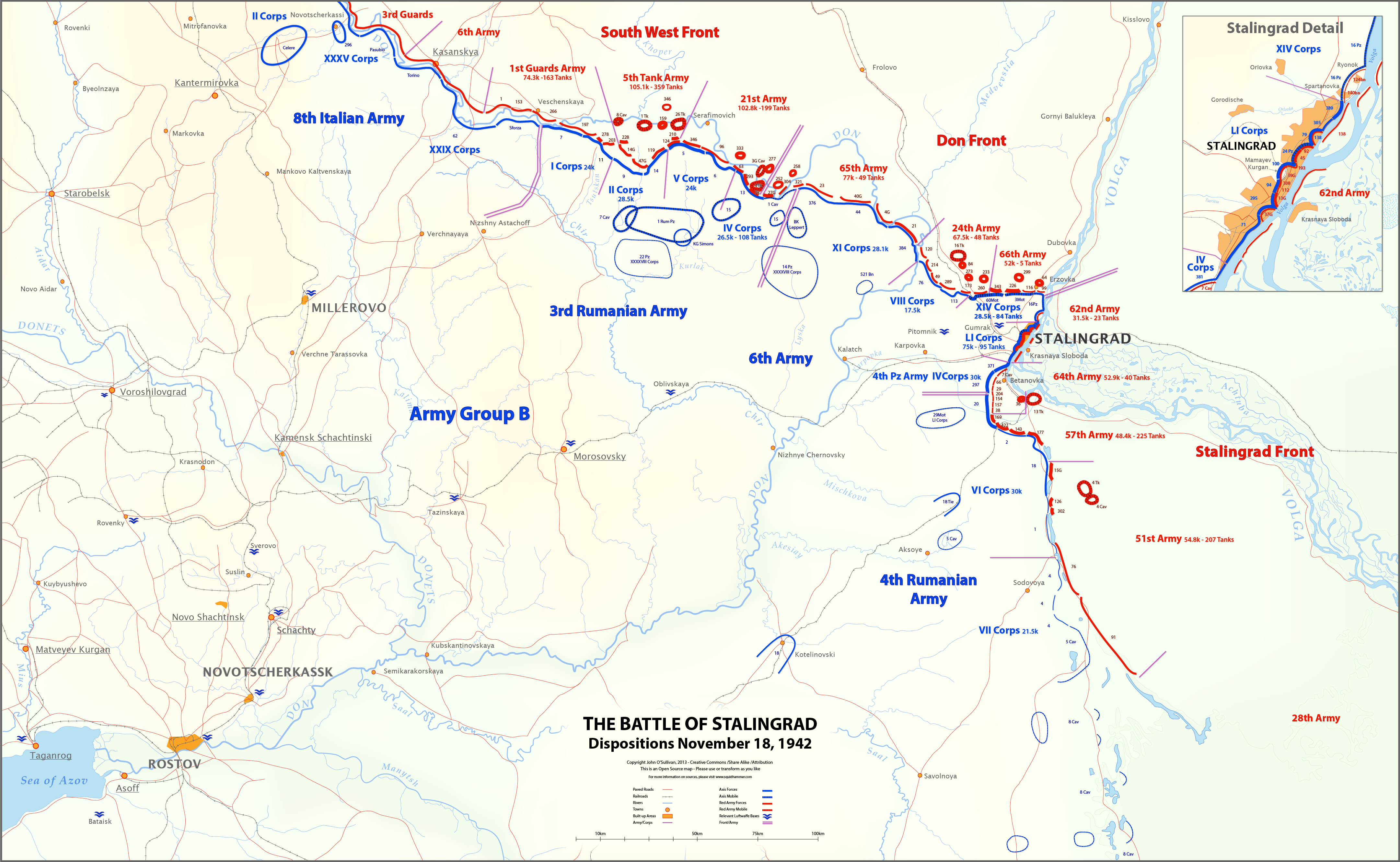
The Italian participation on the Eastern Front represented the military intervention of the Kingdom of Italy in the Operation Barbarossa, launched by Nazi Germany against the Soviet Union in 1941. The commitment to actively take part in the German offensive was decided by Benito Mussolini a few months before the beginning of the operation, when he became aware of Adolf Hitler's intention to invade, but it was confirmed only in the morning of 22 June 1941, as soon as the Italian dictator was informed that same day the German armies had given way to the invasion. An expeditionary force quickly became operational, with three divisions, previously put on alert: called the "Italian Expeditionary Corps in Russia" (''Corpo di Spedizione Italiano in Russia,'' CSIR), it arrived on the eastern front in mid-July 1941. Initially integrated into the 11th German Army and then in the 1st Panzer Army, the CSIR participated in the campaign until April 1942, when the needs of the front required the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastern Front (World War II)
The Eastern Front of World War II was a theatre of conflict between the European Axis powers against the Soviet Union (USSR), Poland and other Allies, which encompassed Central Europe, Eastern Europe, Northeast Europe ( Baltics), and Southeast Europe (Balkans) from 22 June 1941 to 9 May 1945. It was known as the Great Patriotic War in the Soviet Union – and still is in some of its successor states, while almost everywhere else it has been called the ''Eastern Front''. In present-day German and Ukrainian historiography the name German-Soviet War is typically used. The battles on the Eastern Front of the Second World War constituted the largest military confrontation in history. They were characterised by unprecedented ferocity and brutality, wholesale destruction, mass deportations, and immense loss of life due to combat, starvation, exposure, disease, and massacres. Of the estimated 70–85 million deaths attributed to World War II, around 30 million occurred on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benito Mussolini
Benito Amilcare Andrea Mussolini (; 29 July 188328 April 1945) was an Italian politician and journalist who founded and led the National Fascist Party. He was Prime Minister of Italy from the March on Rome in 1922 until his deposition in 1943, and " Duce" of Italian Fascism from the establishment of the Italian Fasces of Combat in 1919 until his execution in 1945 by Italian partisans. As dictator of Italy and principal founder of fascism, Mussolini inspired and supported the international spread of fascist movements during the inter-war period. Mussolini was originally a socialist politician and a journalist at the ''Avanti!'' newspaper. In 1912, he became a member of the National Directorate of the Italian Socialist Party (PSI), but he was expelled from the PSI for advocating military intervention in World War I, in opposition to the party's stance on neutrality. In 1914, Mussolini founded a new journal, ''Il Popolo d'Italia'', and served in the Royal Italian Arm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shebekino
Shebekino (russian: Шебе́кино) is a town in Belgorod Oblast, Russia, located on the Nezhegol River, southeast of Belgorod. Population: History It was founded in 1713 and was granted town status in 1938. Administrative and municipal status Within the framework of administrative divisions, Shebekino serves as the administrative center An administrative center is a seat of regional administration or local government, or a county town, or the place where the central administration of a commune is located. In countries with French as administrative language (such as Belgium, Lu ... of Shebekinsky District, even though it is not a part of it. As an administrative division, it is incorporated separately as the town of oblast significance of Shebekino—an administrative unit with the status equal to that of the districts.Law #248 As a municipal division, the town of oblast significance of Shebekino is incorporated within Shebekinsky Municipal District as Shebekino ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
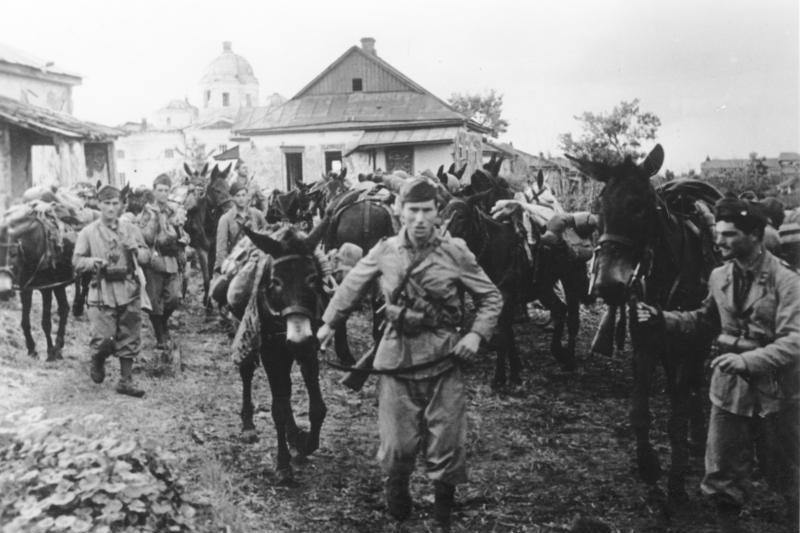
Alpini
The Alpini are the Italian Army's specialist mountain infantry. Part of the army's infantry corps, the speciality distinguished itself in combat during World War I and World War II. Currently the active Alpini units are organized in two operational brigades, which are subordinated to the Alpine Troops Headquarters. The Alpini's name comes from their inceptive association with the Alps, the mountain range that Italy shares with France, Switzerland, Austria, and Slovenia. An individual soldier of the Alpini is called Alpino. Established in 1872, the Alpini are the oldest active mountain infantry in the world. Their original mission was to protect Italy's border with France and Austria-Hungary. In 1888 the Alpini deployed on their first mission abroad, in Africa, a continent to which they returned on several occasions and during various wars of the Kingdom of Italy. During World War I they fought a three-year campaign on the Alps against Austro-Hungarian Kaiserjäger and the G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
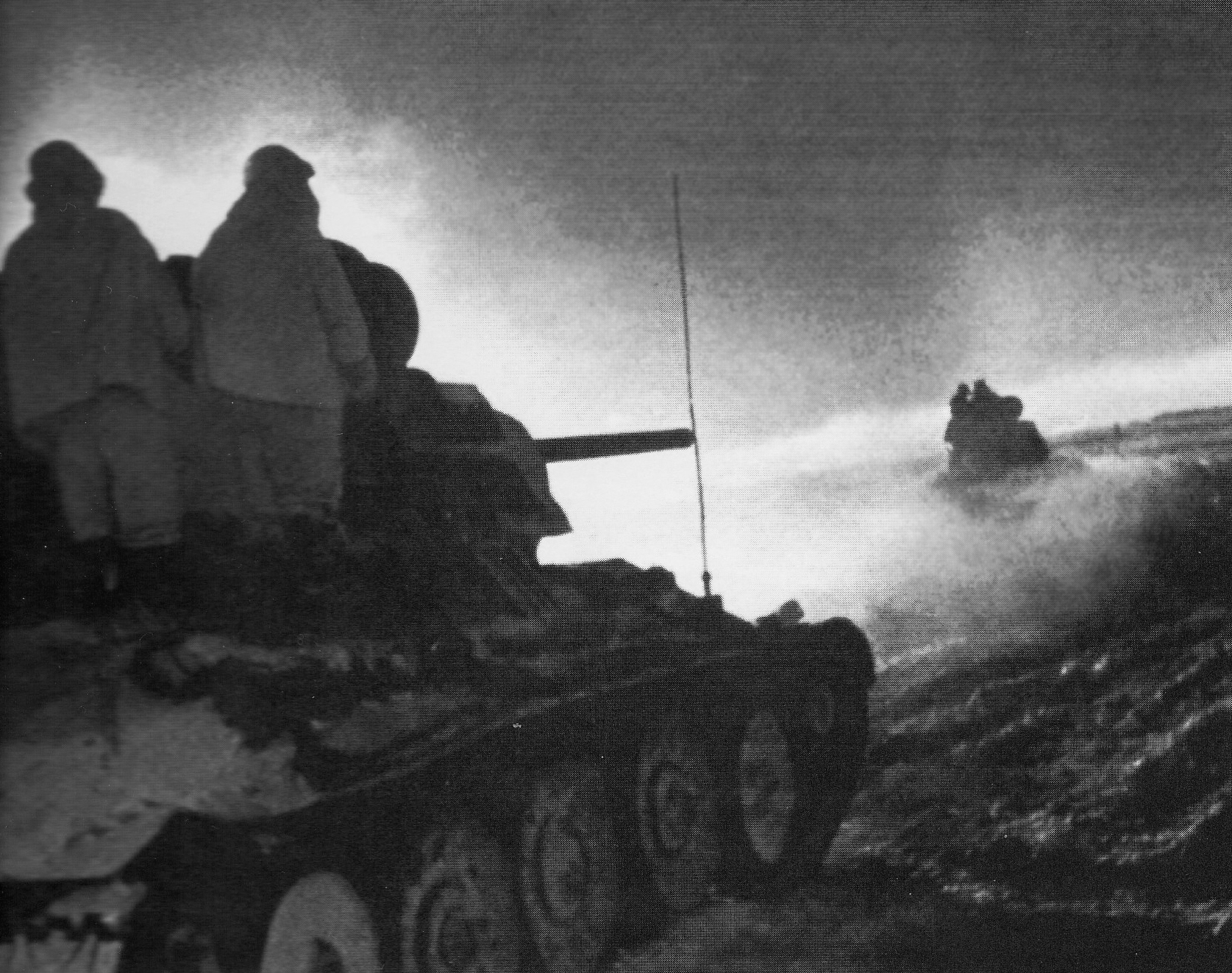
Operation Little Saturn
Operation Little Saturn was a Red Army offensive on the Eastern Front of World War II that led to battles in Don and Chir rivers region in German-occupied Soviet Union territory in 16–30 December 1942. The success of Operation Uranus, launched on 19 November 1942, had trapped 250,000 troops of General Friedrich Paulus' German 6th Army and parts of General Hoth's 4th Panzer Army in Stalingrad. To exploit this victory, the Soviet general staff planned an ambitious offensive with Rostov-on-Don as the ultimate objective, codenamed "Saturn". Later Joseph Stalin reduced his ambitious plans to a relatively smaller operation codenamed "Little Saturn". The offensive succeeded in smashing the Axis troops and applied pressure on the over-stretched German forces in Eastern Ukraine. Another counter-offensive south of the Don prevented further German advances to the relief of the entrapped forces at Stalingrad. With subsequent operations, in January and February 1943, the Soviet armies ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Operation Uranus
Operation Uranus (russian: Опера́ция «Ура́н», Operatsiya "Uran") was the codename of the Soviet Red Army's 19–23 November 1942 strategic operation on the Eastern Front of World War II which led to the encirclement of Axis forces in the vicinity of Stalingrad: the German Sixth Army, the Third and Fourth Romanian armies, and portions of the German Fourth Panzer Army. The Red Army carried out the operation at roughly the midpoint of the five-month long Battle of Stalingrad, aiming to destroy German forces in and around Stalingrad. Planning for Operation Uranus had commenced in September 1942, and developed simultaneously with plans to envelop and destroy German Army Group Center (Operation Mars) and German forces in the Caucasus. Due to the length of the front lines created by the German 1942 summer offensive, which had aimed at taking the Caucasus oil fields and the city of Stalingrad, German and other Axis forces were over-extended. The German de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Third Army (Romania)
The 3rd Army (Armata a 3-a Română) was a field army of the Romanian Land Forces active from the 19th century to the 1990s. It fought as part of the German Army Group B during World War II, in Ukraine, the Crimea, and the Caucasus. General Petre Dumitrescu commanded the 3rd Army for a period. World War I After Romania entered World War I in August 1916 on the side of the Allies, the Third Army defended the border with Bulgaria, while the rest of the Romanian Army engaged in the Battle of Transylvania. When a Bulgarian-German army under August von Mackensen invaded Romania in September 1916, the Third Army made attempts to withstand the enemy offensive at Silistra, Bazargic, Amzacea and Topraisar, but had to withdraw under the pressure of superior enemy forces after the Second Battle of Cobadin. After the Flămânda Offensive, the Third Army was disbanded. The commanders of the 3rd Army during that time were : * Divisional General Mihail Aslan: 27 August 1916 – 7 September 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Army (Hungary)
The Hungarian Second Army (''Második Magyar Hadsereg'') was one of three field armies (''hadsereg'') raised by the Kingdom of Hungary (''Magyar Királyság'') which saw action during World War II. All three armies were formed on March 1, 1940. The Second Army was the best-equipped Hungarian formation at the beginning of the war, but was virtually eliminated as an effective fighting unit by overwhelming Soviet force during the Battle of Stalingrad, suffering 84% casualties. Towards the end of the war, a reformed Second Army fought more successfully at the Battle of Debrecen, but, during the ensuing Siege of Budapest, it was destroyed completely and absorbed into the Hungarian Third Army. Commanders The Hungarian Second Army had four commanders from March 1, 1940 - November 13, 1944: * Colonel General Vitéz Gusztáv Jány (vitéz Jány Gusztáv) (March 1, 1940 - August 5, 1943; awarded the German Knight's Cross on March 31, 1943) * Colonel General Géza Lakatos (Lakatos G� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Italian Army In Russia
The Italian Army in Russia ( it, Armata Italiana in Russia; ARMIR) was an army-sized unit of the Royal Italian Army which fought on the Eastern Front during World War II between July 1942 and April 1943. The ARMIR was also known as the 8th Italian Army and initially had 235,000 soldiers. Formation In July 1942, the ARMIR was created when Italian dictator Benito Mussolini decided to scale up the Italian effort in the Soviet Union. The existing Italian Expeditionary Corps in Russia (''Corpo di Spedizione Italiano in Russia'', or CSIR) was expanded to become the ARMIR. Unlike the "mobile" CSIR which it replaced, the ARMIR was primarily an infantry army. A good portion of the ARMIR was made up of mountain troops ('' Alpini''), which were ill-suited to the vast, flat expanses of southern Russia. Like the CSIR, the ARMIR included an Aviation Command (''Comando Aereo'') with a limited number of fighters, bombers, and transport aircraft. This command was part of the '' Regia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1st Panzer Army
The 1st Panzer Army (german: 1. Panzerarmee) was a German tank army that was a large armoured formation of the Wehrmacht during World War II. When originally formed on 1 March 1940, the predecessor of the 1st Panzer Army was named Panzer Group Kleist (''Panzergruppe Kleist'') with Colonel General Ewald von Kleist in command. Service history Panzer Group Kleist was the first operational formation of several Panzer corps in the Wehrmacht. Created for the Battle of France on 1 March 1940; it was named after its commander Ewald von Kleist. Panzer Group Kleist played an important role in the Battle of Belgium. Panzer corps of the Group broke through the Ardennes and reached the sea, forming a huge pocket, containing several Belgian, British, and French armies. When the armistice was signed, the Group was deployed in occupied France, being renamed to Panzer Group 1 (''Panzergruppe 1'') in November. In April 1941, Panzer Group 1 took part in the invasion of Yugoslavia as part of Fie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.png)