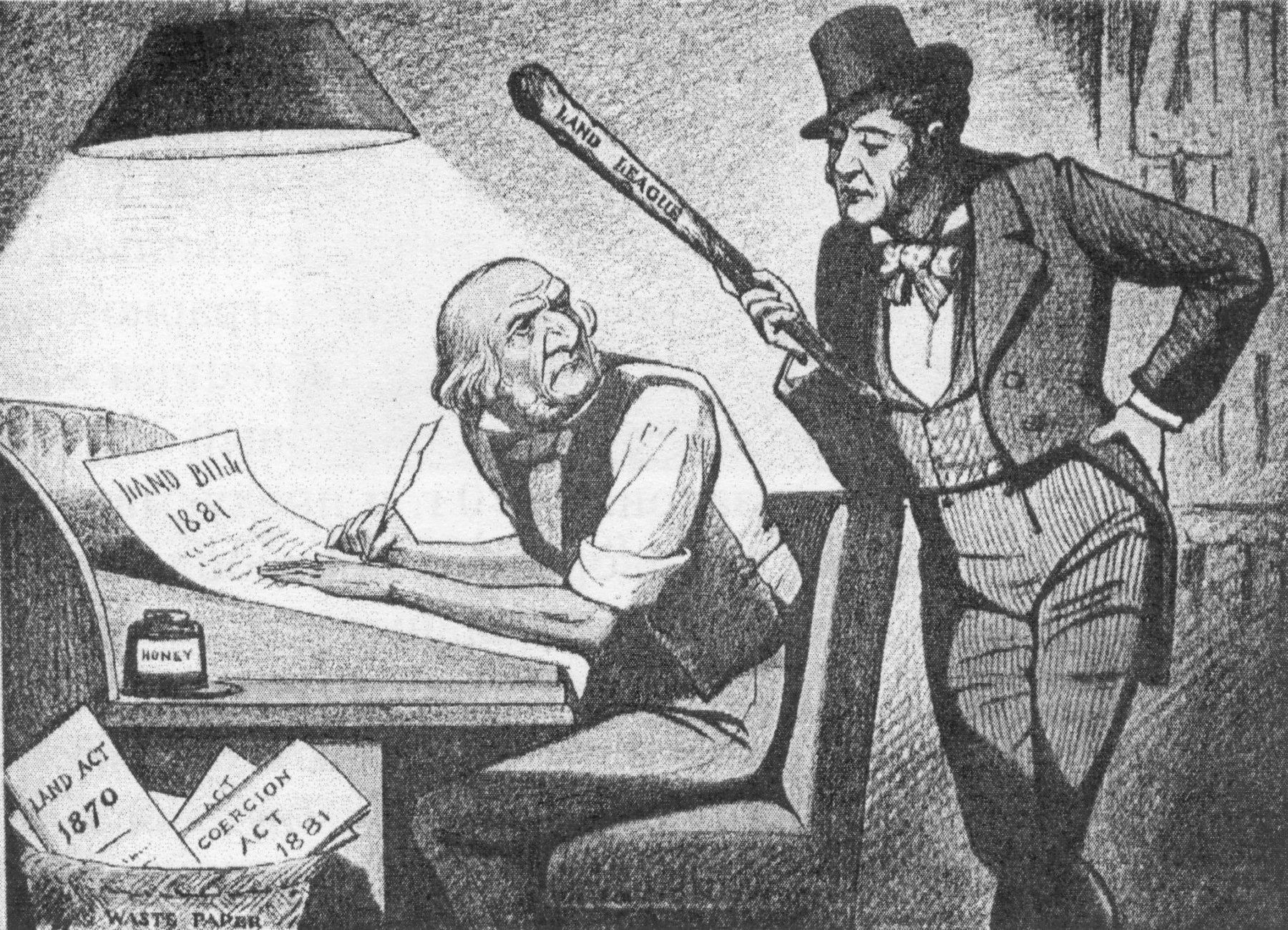|
Irish Coercion Act
A Coercion Act was an Act of Parliament that gave a legal basis for increased state powers to suppress popular discontent and disorder. The label was applied, especially in Ireland, to acts passed from the 18th to the early 20th century by the Irish, British, and Northern Irish parliaments. London In December 1816, a mass meeting took place at Spa Fields near London. The Coercion Act 1817 was an act of Parliament that suspended habeas corpus and extended existing laws against seditious gatherings in Britain. The Coercion Act 1817 was the result of this mass meeting. Ireland The total number of "Coercion Acts" relating to Ireland is a matter of definition, including whether to count separately an act which continues an expiring act. Michael Farrell in 1986 put the total from 1801 to 1921 at 105. John Spencer, 5th Earl Spencer said in the House of Lords that 87 such acts had been passed between the Acts of Union 1801 and 1887, a rate of one per year. The figure was repeated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
3 & 4 Will
3 (three) is a number, numeral (linguistics), numeral and numerical digit, digit. It is the natural number following 2 and preceding 4, and is the smallest odd prime number and the only prime preceding a square number. It has religious and cultural significance in many societies. Evolution of the Arabic digit The use of three lines to denote the number 3 occurred in many writing systems, including some (like Roman and Chinese numerals) that are still in use. That was also the original representation of 3 in the Brahmic numerals, Brahmic (Indian) numerical notation, its earliest forms aligned vertically. However, during the Gupta Empire the sign was modified by the addition of a curve on each line. The Nāgarī script rotated the lines clockwise, so they appeared horizontally, and ended each line with a short downward stroke on the right. In cursive script, the three strokes were eventually connected to form a glyph resembling a with an additional stroke at the bottom: ३. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Times
''The Times'' is a British Newspaper#Daily, daily Newspaper#National, national newspaper based in London. It began in 1785 under the title ''The Daily Universal Register'', adopting its modern name on 1 January 1788. ''The Times'' and its sister paper ''The Sunday Times'' (founded in 1821), are published by Times Media, since 1981 a subsidiary of News UK, in turn wholly owned by News Corp. ''The Times'' and ''The Sunday Times'' were founded independently and have had common ownership only since 1966. It is considered a newspaper of record in the UK. ''The Times'' was the first newspaper to bear that name, inspiring numerous other papers around the world. In countries where these other titles are popular, the newspaper is often referred to as or , although the newspaper is of national scope and distribution. ''The Times'' had an average daily circulation of 365,880 in March 2020; in the same period, ''The Sunday Times'' had an average weekly circulation of 647,622. The two ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Land Law (Ireland) Act 1881
The Land Law (Ireland) Act 1881 (44 & 45 Vict. c. 49) was the second Land Acts (Ireland), Irish land act passed by the Parliament of the United Kingdom. Background The Liberal Party (UK), Liberal government of William Ewart Gladstone had previously passed the Landlord and Tenant (Ireland) Act 1870 in an attempt to solve the problem of tenant-landlord relations in Ireland. However, the Act was seen to have failed in its purpose. The Home Rule League, Home Rule Party had been formed in 1873 and was rapidly turning previously Liberal seats into Home Rule seats. Gladstone visited Ireland in autumn 1877, spending almost a month in County Wicklow and Dublin. Gladstone wrote in his diary that he ensured he visited "farms, cottages & people", including conversing with Irishmen and "turning my small opportunities to account as well as I could". When he had to spend a day in Dublin amongst the English establishment there, he lamented: "...not enough of ''Ireland''". The Liberals were 18 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United Ireland (newspaper)
The Irish National Land League ( Irish: ''Conradh na Talún''), also known as the Land League, was an Irish political organisation of the late 19th century which organised tenant farmers in their resistance to exactions of landowners. Its primary aim was to abolish landlordism in Ireland and enable tenant farmers to own the land they worked on. The period of the Land League's agitation is known as the Land War. Historian R. F. Foster argues that in the countryside the Land League "reinforced the politicization of rural Catholic nationalist Ireland, partly by defining that identity against urbanization, landlordism, Englishness and—implicitly—Protestantism." Foster adds that about a third of the activists were Catholic priests, and Archbishop Thomas Croke was one of its most influential champions. Background Following the founding meeting of the Mayo Tenants Defence Association in Castlebar, County Mayo on 26 October 1878 the demand for ''The Land of Ireland for the peo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
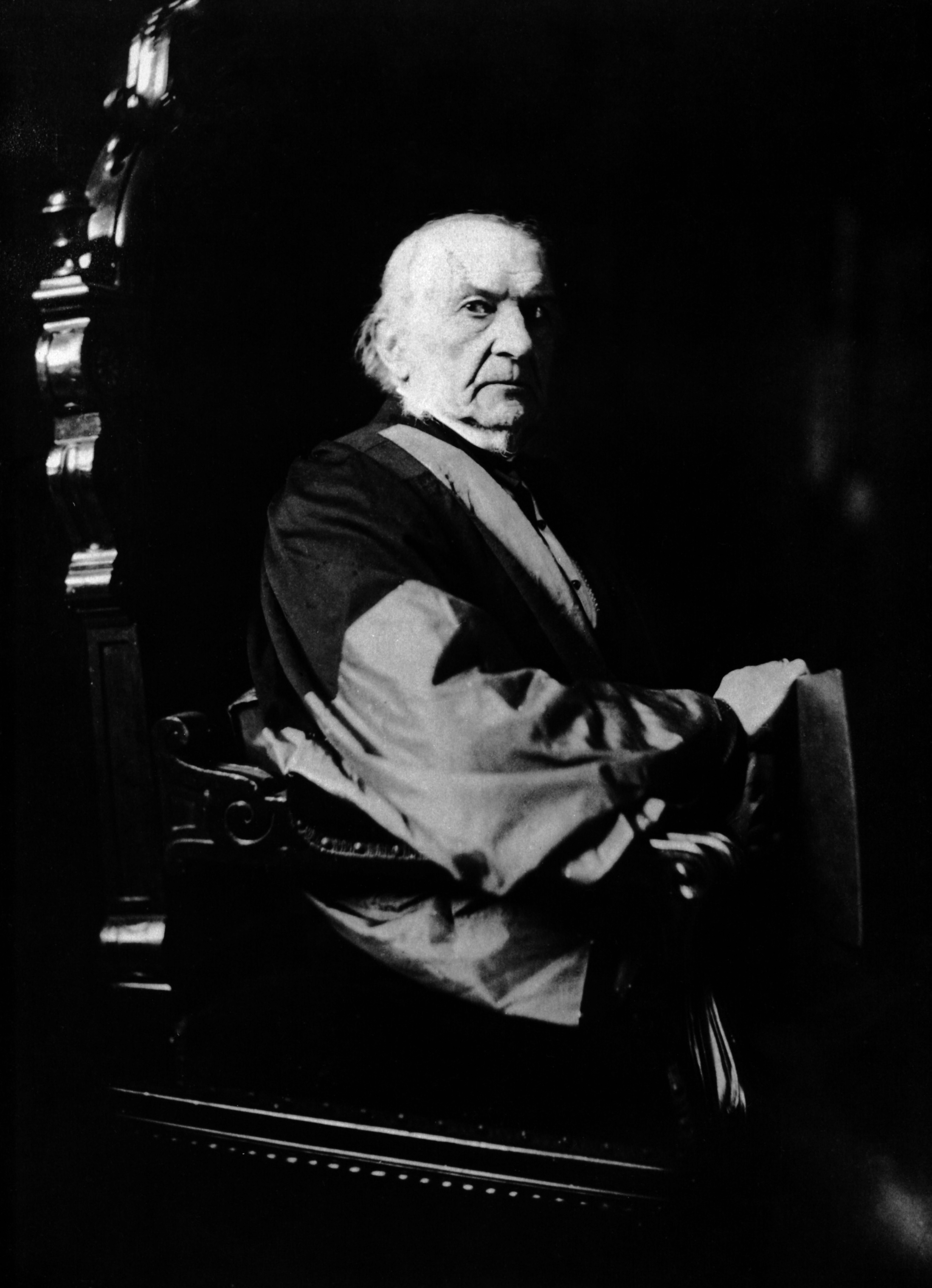
Charles Stewart Parnell
Charles Stewart Parnell (27 June 1846 – 6 October 1891) was an Irish nationalist politician who served as a Member of Parliament (United Kingdom), Member of Parliament (MP) in the United Kingdom from 1875 to 1891, Leader of the Home Rule League from 1880 to 1882, and then of the Irish Parliamentary Party from 1882 to 1891, who held the balance of power in the House of Commons of the United Kingdom, House of Commons during the Home Rule debates of 1885–1886. He fell from power following revelations of a long-term affair, and died at age 45. Born into a powerful Anglo-Irish people, Anglo-Irish Church of Ireland, Protestant landowning family in County Wicklow, he was a land reform agitator and founder of the Irish National Land League in 1879. He became leader of the Home Rule League, operating independently of the Liberal Party (UK), Liberal Party, winning great influence by his balancing of constitutional, radical, and economic issues, and by his skilful use of parliamentary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Irish National Land League
The Irish National Land League ( Irish: ''Conradh na Talún''), also known as the Land League, was an Irish political organisation of the late 19th century which organised tenant farmers in their resistance to exactions of landowners. Its primary aim was to abolish landlordism in Ireland and enable tenant farmers to own the land they worked on. The period of the Land League's agitation is known as the Land War. Historian R. F. Foster argues that in the countryside the Land League "reinforced the politicization of rural Catholic nationalist Ireland, partly by defining that identity against urbanization, landlordism, Englishness and—implicitly—Protestantism." Foster adds that about a third of the activists were Catholic priests, and Archbishop Thomas Croke was one of its most influential champions. Background Following the founding meeting of the Mayo Tenants Defence Association in Castlebar, County Mayo on 26 October 1878 the demand for ''The Land of Ireland for the pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protection Of Persons And Property (Ireland) Act 1881
The Protection of Persons and Property (Ireland) Act 1881,The Act had no official short title. It was referred to as ''Protection of Persons and Property (Ireland) Act'', or with ''Person'' in the singular, and/or with ''(Ireland)'' omitted. ( 44 & 45 Vict. c. 4) also called the Coercion Act 1881 or the Crimes Act 1881, was an act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom which allowed for internment without trial of those suspected of involvement in the Land War in Ireland. The provisions could be introduced by proclamation of the Lord Lieutenant of Ireland in any area of the island. Lists of internees had to be laid before Parliament. Enactment The 1881 act was one of more than 100 Coercion Acts applied to Ireland under the Union. W. E. Gladstone was returned to office in 1880, during the agrarian violence and civil disturbance of the Land War in Ireland. William Edward Forster was made Chief Secretary for Ireland. He carried the Compensation for Disturbance Bill through ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
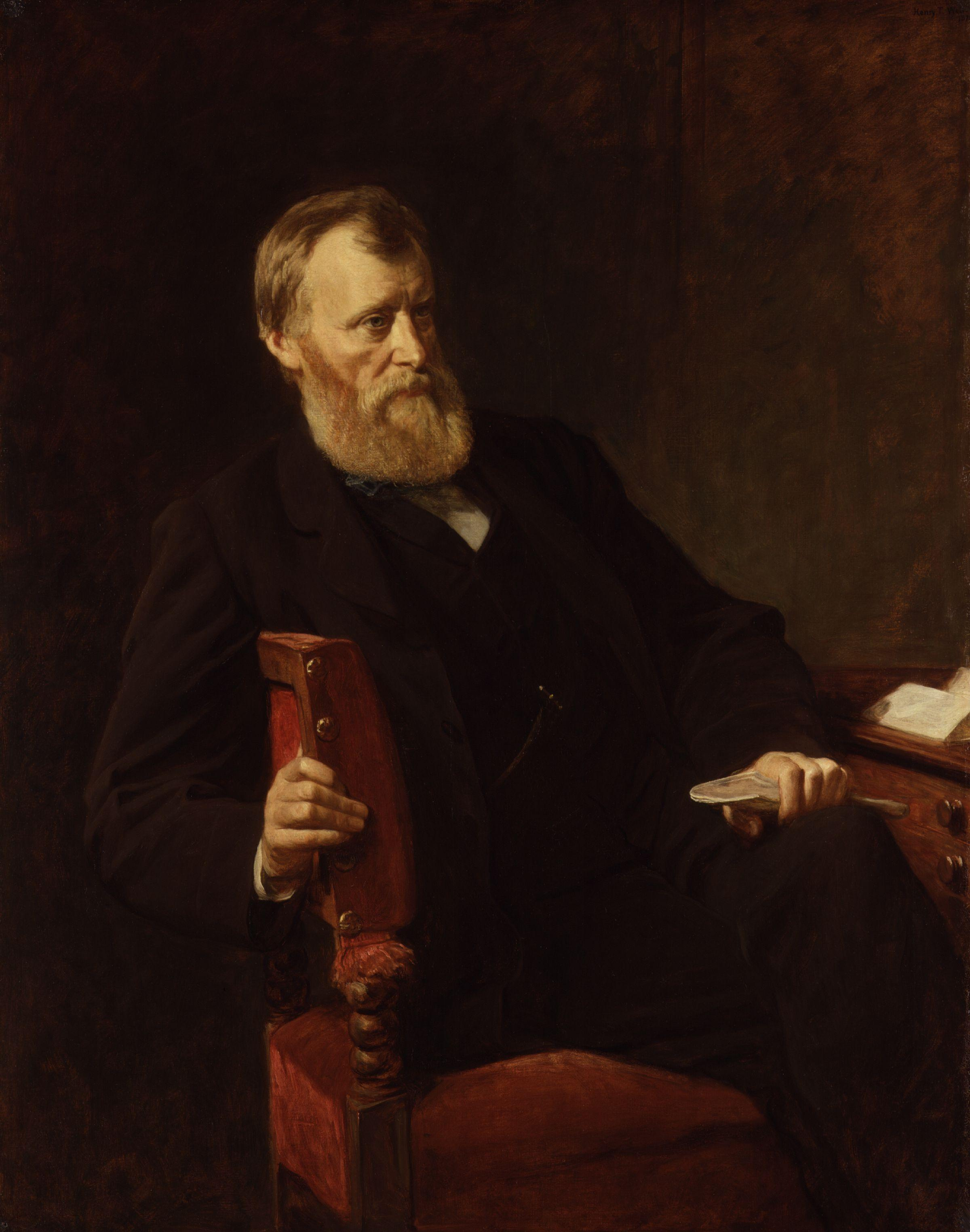
Joseph Biggar
Joseph Gillis Biggar (c. 1828 – 19 February 1890), commonly known as Joe Biggar D.D. Sheehan, Ireland Since Parnell', London: Daniel O'Connor, 1921. or J. G. Biggar, was an Irish nationalist politician from Belfast. He served as an MP in the House of Commons of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland as member of the Home Rule League and later Irish Parliamentary Party for Cavan from 1874 to 1885 and West Cavan from 1885 to his death in 1890. Origins He was the eldest son of Joseph Bigger, merchant and chairman of the Ulster bank, by Isabella, daughter of William Houston of Ballyearl, Antrim. He was educated at the Belfast Academy, and, entering his father's business of a provision merchant, became head of the firm in 1861, and carried it on till 1880. His surname was originally spelled Bigger, but he changed the spelling upon conversion and taking up his political career; which caused some confusion about his namesake (also a Protestant nationalist from Belfast, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Famine (Ireland)
The Great Famine, also known as the Great Hunger ( ), the Famine and the Irish Potato Famine, was a period of mass starvation and disease in Ireland lasting from 1845 to 1852 that constituted a historical social crisis and had a major impact on Irish society and history as a whole. The most severely affected areas were in the western and southern parts of Ireland—where the Irish language was dominant—hence the period was contemporaneously known in Irish as , which literally translates to "the bad life" and loosely translates to "the hard times". The worst year of the famine was 1847, which became known as "Black '47".Éamon Ó Cuív – the impact and legacy of the Great Irish Famine The population of Ireland on the eve of the famine was about 8.5 million; by 1901, it was just 4.4 million. During the Great Hunger, roughly 1 million people died and more than 1 million more Irish diaspora, fled the country, causing the country's population to fall by 20–25% between 18 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Peel
Sir Robert Peel, 2nd Baronet (5 February 1788 – 2 July 1850), was a British Conservative statesman who twice was Prime Minister of the United Kingdom (1834–1835, 1841–1846), and simultaneously was Chancellor of the Exchequer (1834–1835). He previously was Home Secretary twice (1822–1827, 1828–1830). He is regarded as the father of modern British policing, owing to his founding of the Metropolitan Police while he was Home Secretary. Peel was one of the founders of the modern Conservative Party. The son of a wealthy textile manufacturer and politician, Peel was the first prime minister from an industrial business background. He earned a double first in classics and mathematics from Christ Church, Oxford. He entered the House of Commons in 1809 and became a rising star in the Tory Party. Peel entered the Cabinet as home secretary (1822–1827), where he reformed and liberalised the criminal law and created the modern police force, leading to a new type of officer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
44 & 45 Vict
44 may refer to: * 44 (number) * one of the years 44 BC, AD 44, 1944, 2044 Military *44M Tas, a Hungarian medium/heavy tank design of World War II *44M Tas Rohamlöveg, a Hungarian tank destroyer design of World War II, derived from the 44M Tas tank * 44th Regiment of Foot a British Infantry Regiment(East Essex). Other uses *"Forty-Four", a blues standard *Forty-Fours, a group of islands in the Chatham Archipelago *Forty Four, Arkansas, an unincorporated community in Izard County, Arkansas * ''44'' (album), a 2020 quadruple album by Joel Plaskett *"44", a song by Bad Gyal featuring Rema from '' Warm Up'' *"Forty Four", a song by Karma to Burn from ''Appalachian Incantation'' * .44 caliber, a family of firearms and firearm cartridges ** .44 Special, a revolver cartridge ** .44 Magnum, a large revolver cartridge evolved from the .44 special *44 Nysa, a main-belt asteroid *DAF 44, a small family car *The international calling code for United Kingdom * Barack Obama, the 44th Presiden ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |