|
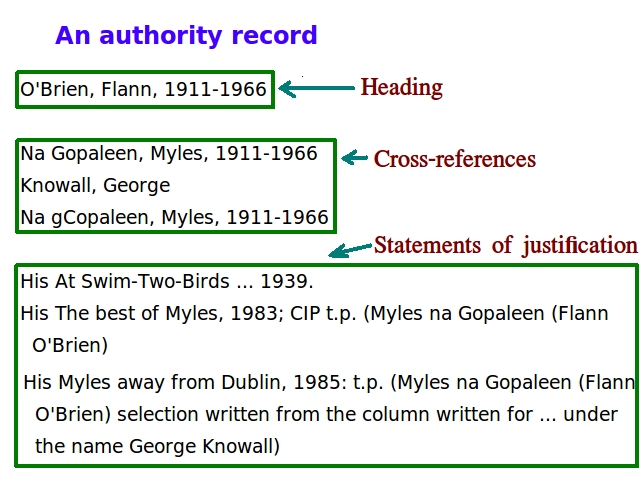
International Standard Archival Authority Record
An International Standard Archival Authority Record (ISAAR) is a form of authority control record, standardized by the Committee of Descriptive Standards of the International Council on Archives. ISAAR (CPF) is the ''International Standard Archival Authority Record For Corporate Bodies, Persons and Families''; its first edition was adopted by the committee in 1996, with a revised edition in 2003. See also * ISAD(G) * Records in Contexts * Describing Archives: A Content Standard * Encoded Archival Description * Manual of Archival Description * Archival processing * Finding aid References Library cataloging and classification Metadata Index (publishing) {{library-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Authority Control
In information science, authority control is a process that organizes information, for example in library catalogs, by using a single, distinct spelling of a name (heading) or an identifier (generally persistent and alphanumeric) for each topic or concept. The word ''authority'' in ''authority control'' derives from the idea that the names of people, places, things, and concepts are ''authorized,'' i.e., they are established in one particular form. Note: root words for both ''author'' and ''authority'' are words such as ''auctor'' or ''autor'' and ''autorite'' from the 13th century. These one-of-a-kind headings or identifiers are applied consistently throughout catalogs which make use of the respective authority file, and are applied for other methods of organizing data such as linkages and cross references. Each controlled entry is described in an authority ''record'' in terms of its scope and usage, and this organization helps the library staff maintain the catalog and make ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Council On Archives
The International Council on Archives (ICA; French: ''Conseil international des archives'') is an international non-governmental organization which exists to promote international cooperation for archives and archivists. It was set up in 1948, with Charles Samaran, the then director of the Archives nationales (France), Archives nationales de France, as chairman, and membership is open to national and international organisations, professional groups and individuals. In 2015, it grouped together about 1400 institutional members in 199 countries and territories. Its mission is to promote the conservation, development and use of the world's archives. ICA has close partnership links with UNESCO, and is a founding member of Blue Shield International, the Blue Shield, which works to protect the world's cultural heritage threatened by wars and natural disasters, and which is based in The Hague. Mission statement ICA's mission statement reads: "The International Council on Archives (ICA) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ISAD(G)
ISAD(G) (General International Standard Archival Description) defines the elements that should be included in an archival finding aid. It was approved by the International Council on Archives (ICA/CIA) as an international framework standard to register archival documents produced by corporations, persons and families. Description ISAD(G) defines a list of elements and rules for the description of archives and describes the kinds of information that must and should be included in such descriptions. It creates a hierarchy of description that determines what information should be included at what level. Principles ISAD(G) follows four general principles: * Description from the general to the specific Multilevel description starts from a general level of description, which is usually the fonds, and proceeds to more detailed levels, such as the subfonds, the series, the file, the item, etc. This hierarchical structure must be represented and properly defined in the archival descr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Records In Contexts
Records in Contexts, or RiC, is a conceptual model and ontology for the archival description of records, designed by the Expert Group on Archival Description (EGAD) established by the International Council on Archives (ICA). The EGAD initially began work on the standard between 2012 and 2016, with a conceptual model (RiC-CM) and an ontology (RiC-O) released for comment during 2016. Version 0.2 was released in 2021, now featuring an independent introduction to archival description (RiC-IAD) and updates to the original RiC-CM and RiC-O. A fourth part of the standard covering Application Guidelines (RiC-AG) is also expected, prior to a completed RiC version 1.0 being released as an official ICA recommendation. Content The Conceptual Model aims to bring together the council's current descriptive standards, namely the General International Standard Archival Description (ISAD(G)), International Standard Archival Authority Records — Corporate Bodies, Persons, and Families (ISAAR(CPF ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
A Content Standard
A, or a, is the first letter and the first vowel letter of the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, and others worldwide. Its name in English is '' a'' (pronounced ), plural ''aes''. It is similar in shape to the Ancient Greek letter alpha, from which it derives. The uppercase version consists of the two slanting sides of a triangle, crossed in the middle by a horizontal bar. The lowercase version is often written in one of two forms: the double-storey and single-storey . The latter is commonly used in handwriting and fonts based on it, especially fonts intended to be read by children, and is also found in italic type. In English, '' a'' is the indefinite article, with the alternative form ''an''. Name In English, the name of the letter is the ''long A'' sound, pronounced . Its name in most other languages matches the letter's pronunciation in open syllables. History The earliest known ancestor of A is ''aleph''—the first letter of the Phoenician ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Encoded Archival Description
Encoded Archival Description (EAD) is a standard for encoding descriptive information regarding archival records.Pitti, D (2012). "Encoded Archival Description (EAD)". In Bates, Marcia J., (ed.) ''Understanding Information Retrieval Systems: Management, Types, and Standards.'' pp. 685–697. London: Auerbach Publications. Overview Archival records differ from the items in a library collection because they are unique, usually unpublished and unavailable elsewhere, and because they exist as part of a collection that unifies them.Eastwood, T. "A Contested Realm: The Nature of Archives and the Orientation of Archival Science". In ''Currents of Archival Thinking'', Terry Eastwood and Heather MacNeil, eds. (Libraries Unlimited, 2017): 3–23. For these reasons, archival description involves a hierarchical and progressive analysis that emphasizes the intellectual structure and content of the collection and does not always extend to the level of individual items within it. Following the de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manual Of Archival Description
The Society of Archivists (SoA), which was in existence from 1947 to 2010, was the principal professional body for archivists, archive conservators and records managers in the United Kingdom and Ireland. In 2010 the Society amalgamated with the National Council on Archives (NCA) and the Association of Chief Archivists in Local Government (ACALG) to become the Archives and Records Association (United Kingdom and Ireland), otherwise known as the ARA. Of the three bodies which merged, the Society was by far the largest, and many of its structures and activities were inherited by the new body with little obvious change. History The Society was founded in 1947 as the Society of Local Archivists, but changed its name to the Society of Archivists in 1954 due to its membership expanding beyond archivists working in local government. Aims The Society was constituted as a registered charity with the express aim to: * Foster the care and preservation of archives in the public interest and to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archival Processing
Archival processing is the act of surveying, arranging, describing, and performing basic preservation activities on the recorded material of an individual, family, or organization after they are permanently transferred to an archive. A person engaging in this activity is known as an ''archival processor, archival technician,'' or archivist. Ideally, when an archives receives a collection of papers or a group of records, they will have been arranged by the originator (the original person, persons, or organization that created or assembled the collection or records) and boxed up for the move to the archives in such a way that this order has been preserved. However, collections and record groups are often semi-organized, and sometimes lack any discernible organization. Observing the organization of delivered materials, imposing organization where it is lacking, then describing the organized material are tasks covered by the terms "archival processing", "arrangement and description", "a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Finding Aid
A finding aid, in the context of archival science and archival research, is an organization tool, a document containing detailed and processed metadata and other information about a specific collection of records within an archive. Finding aids often consist of a documentary inventory and description of the materials, their source, and their structure. The finding aid for a fonds is usually compiled by the collection's entity of origin, provenance, or by an archivist during archival processing, and may be considered the archival science equivalent of a library catalog or a museum collection catalog. The finding aid serves the purpose of locating specific information within the collection. The finding aid can also help the archival repository manage their materials and resources. The history of finding aids mirrors the history of information. Ancient Sumerians had their own systems of indexes to locate bureaucratic and administrative records. Finding aids in the 19th and 20th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Library Cataloging And Classification
A library is a collection of books, and possibly other materials and media, that is accessible for use by its members and members of allied institutions. Libraries provide physical (hard copies) or digital (soft copies) materials, and may be a physical location, a virtual space, or both. A library's collection normally includes printed materials which may be borrowed, and usually also includes a reference section of publications which may only be utilized inside the premises. Resources such as commercial releases of films, television programmes, other video recordings, radio, music and audio recordings may be available in many formats. These include DVDs, Blu-rays, CDs, cassettes, or other applicable formats such as microform. They may also provide access to information, music or other content held on bibliographic databases. In addition, some libraries offer creation stations for makers which offer access to a 3D printing station with a 3D scanner. Libraries can vary wid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metadata
Metadata (or metainformation) is "data that provides information about other data", but not the content of the data itself, such as the text of a message or the image itself. There are many distinct types of metadata, including: * Descriptive metadata – the descriptive information about a resource. It is used for discovery and identification. It includes elements such as title, abstract, author, and keywords. * Structural metadata – metadata about containers of data and indicates how compound objects are put together, for example, how pages are ordered to form chapters. It describes the types, versions, relationships, and other characteristics of digital materials. * Administrative metadata – the information to help manage a resource, like resource type, and permissions, and when and how it was created. * Reference metadata – the information about the contents and quality of Statistical data type, statistical data. * Statistical metadata – also called process data, may ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |