|
Inequality Of Arithmetic And Geometric Means
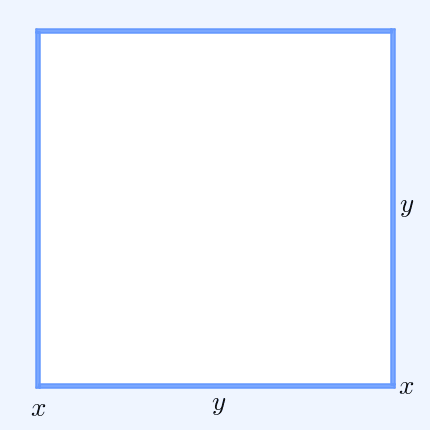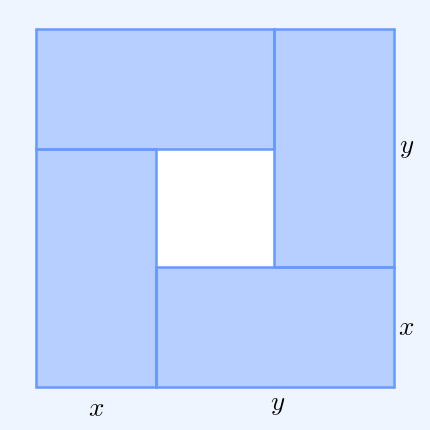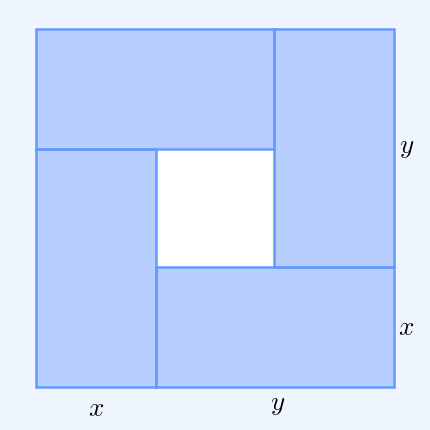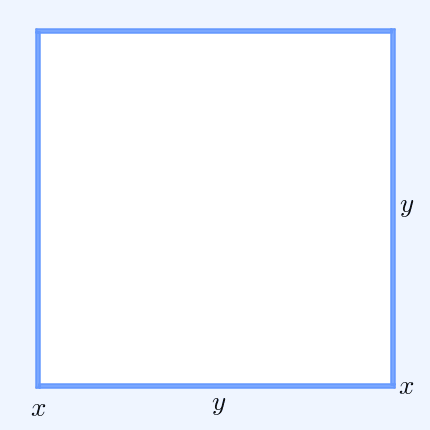
In mathematics, the inequality of arithmetic and geometric means, or more briefly the AM–GM inequality, states that the arithmetic mean of a list of non-negative real numbers is greater than or equal to the geometric mean of the same list; and further, that the two means are equal if and only if every number in the list is the same (in which case they are both that number). The simplest non-trivial case – i.e., with more than one variable – for two non-negative numbers and , is the statement that :\frac2 \ge \sqrt with equality if and only if . This case can be seen from the fact that the square of a real number is always non-negative (greater than or equal to zero) and from the elementary case of the binomial formula: :\begin 0 & \le (x-y)^2 \\ & = x^2-2xy+y^2 \\ & = x^2+2xy+y^2 - 4xy \\ & = (x+y)^2 - 4xy. \end Hence , with equality precisely when , i.e. . The AM–GM inequality then follows from taking the positive square root of both sides and then dividing both ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AM GM Inequality Animation
AM or Am may refer to: Arts and entertainment Music * A minor, a minor scale in music * A.M. (Chris Young album), ''A.M.'' (Chris Young album) * A.M. (Wilco album), ''A.M.'' (Wilco album) * AM (Abraham Mateo album), ''AM'' (Abraham Mateo album) * AM (Arctic Monkeys album), ''AM'' (Arctic Monkeys album) * AM (musician), American musician * Am, the Chord names and symbols (popular music), A minor chord symbol * ''Armeemarschsammlung'' (Army March Collection), catalog of German military march music * Andrew Moore (musician), Canadian musician known as A.M. * DJ AM, American DJ and producer * Skengdo & AM, British hip hop duo Television and radio * AM (ABC Radio), ''AM'' (ABC Radio), Australian current affairs radio program * ''American Morning'', American morning television news program * ''Am, Antes del Mediodía'', Argentine current affairs television program * Am, a character in the anthology ''Star Wars: Visions'' Other media * Allied Mastercomputer, the antagonist of the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Financial Mathematics
Mathematical finance, also known as quantitative finance and financial mathematics, is a field of applied mathematics, concerned with mathematical modeling of financial markets. In general, there exist two separate branches of finance that require advanced quantitative techniques: derivatives pricing on the one hand, and risk and portfolio management on the other. Mathematical finance overlaps heavily with the fields of computational finance and financial engineering. The latter focuses on applications and modeling, often by help of stochastic asset models, while the former focuses, in addition to analysis, on building tools of implementation for the models. Also related is quantitative investing, which relies on statistical and numerical models (and lately machine learning) as opposed to traditional fundamental analysis when managing portfolios. French mathematician Louis Bachelier's doctoral thesis, defended in 1900, is considered the first scholarly work on mathematical fina ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
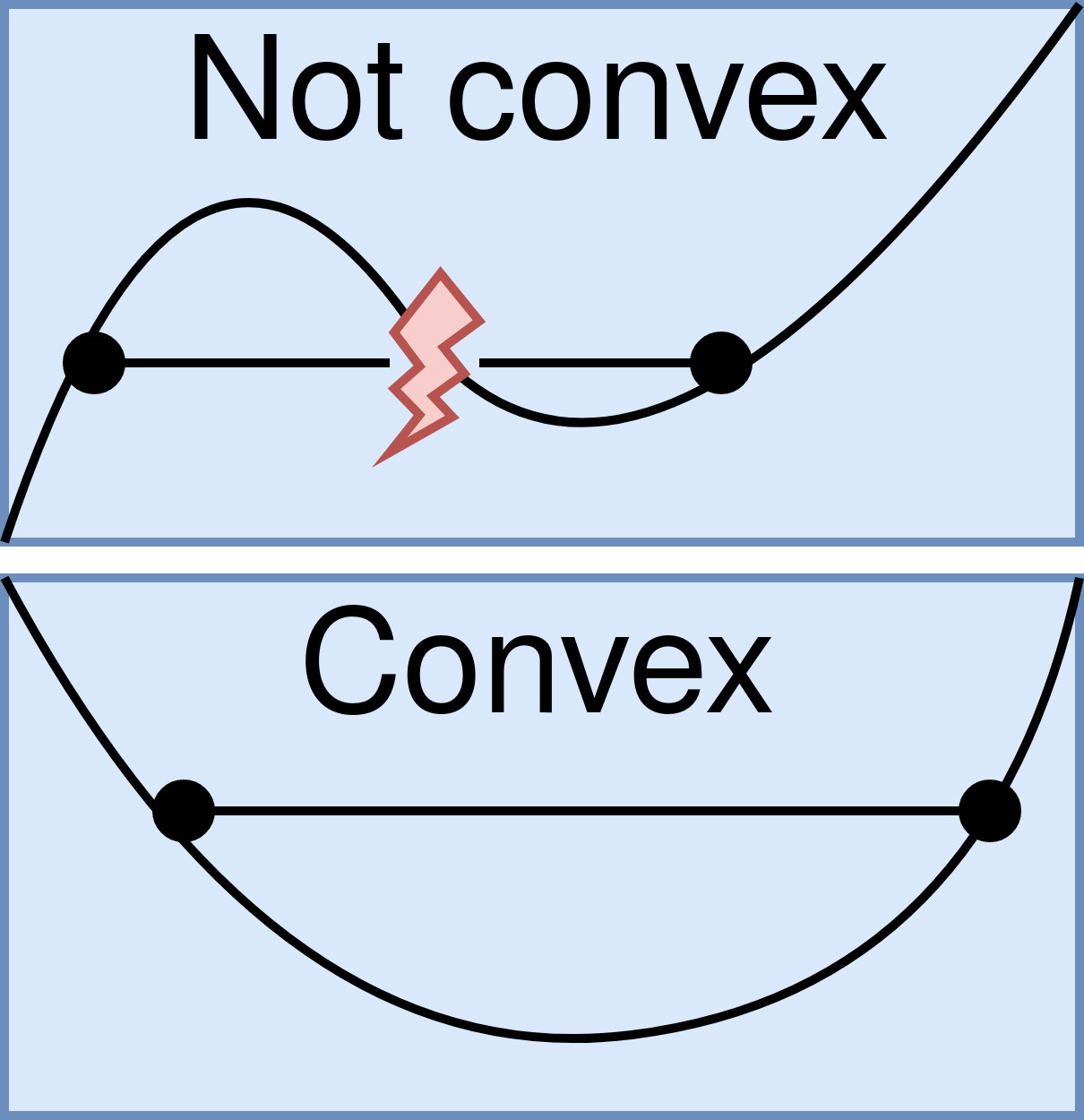
Strictly Convex Function
In mathematics, a real-valued function is called convex if the line segment between any two points on the graph of the function lies above the graph between the two points. Equivalently, a function is convex if its epigraph (the set of points on or above the graph of the function) is a convex set. A twice-differentiable function of a single variable is convex if and only if its second derivative is nonnegative on its entire domain. Well-known examples of convex functions of a single variable include the quadratic function x^2 and the exponential function e^x. In simple terms, a convex function refers to a function whose graph is shaped like a cup \cup, while a concave function's graph is shaped like a cap \cap. Convex functions play an important role in many areas of mathematics. They are especially important in the study of optimization problems where they are distinguished by a number of convenient properties. For instance, a strictly convex function on an open set has n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Derivative
In mathematics, the derivative of a function of a real variable measures the sensitivity to change of the function value (output value) with respect to a change in its argument (input value). Derivatives are a fundamental tool of calculus. For example, the derivative of the position of a moving object with respect to time is the object's velocity: this measures how quickly the position of the object changes when time advances. The derivative of a function of a single variable at a chosen input value, when it exists, is the slope of the tangent line to the graph of the function at that point. The tangent line is the best linear approximation of the function near that input value. For this reason, the derivative is often described as the "instantaneous rate of change", the ratio of the instantaneous change in the dependent variable to that of the independent variable. Derivatives can be generalized to functions of several real variables. In this generalization, the de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Critical Point (mathematics)
Critical point is a wide term used in many branches of mathematics. When dealing with functions of a real variable, a critical point is a point in the domain of the function where the function is either not differentiable or the derivative is equal to zero. When dealing with complex variables, a critical point is, similarly, a point in the function's domain where it is either not holomorphic or the derivative is equal to zero. Likewise, for a function of several real variables, a critical point is a value in its domain where the gradient is undefined or is equal to zero. The value of the function at a critical point is a critical value. This sort of definition extends to differentiable maps between and a critical point being, in this case, a point where the rank of the Jacobian matrix is not maximal. It extends further to differentiable maps between differentiable manifolds, as the points where the rank of the Jacobian matrix decreases. In this case, critical points ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Differential Calculus
In mathematics, differential calculus is a subfield of calculus that studies the rates at which quantities change. It is one of the two traditional divisions of calculus, the other being integral calculus—the study of the area beneath a curve. The primary objects of study in differential calculus are the derivative of a function, related notions such as the differential, and their applications. The derivative of a function at a chosen input value describes the rate of change of the function near that input value. The process of finding a derivative is called differentiation. Geometrically, the derivative at a point is the slope of the tangent line to the graph of the function at that point, provided that the derivative exists and is defined at that point. For a real-valued function of a single real variable, the derivative of a function at a point generally determines the best linear approximation to the function at that point. Differential calculus and integral calculu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Augustin Louis Cauchy
Baron Augustin-Louis Cauchy (, ; ; 21 August 178923 May 1857) was a French mathematician, engineer, and physicist who made pioneering contributions to several branches of mathematics, including mathematical analysis and continuum mechanics. He was one of the first to state and rigorously prove theorems of calculus, rejecting the heuristic principle of the generality of algebra of earlier authors. He almost singlehandedly founded complex analysis and the study of permutation groups in abstract algebra. A profound mathematician, Cauchy had a great influence over his contemporaries and successors; Hans Freudenthal stated: "More concepts and theorems have been named for Cauchy than for any other mathematician (in elasticity alone there are sixteen concepts and theorems named for Cauchy)." Cauchy was a prolific writer; he wrote approximately eight hundred research articles and five complete textbooks on a variety of topics in the fields of mathematics and mathematical physics. Biog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematical Induction
Mathematical induction is a method for proving that a statement ''P''(''n'') is true for every natural number ''n'', that is, that the infinitely many cases ''P''(0), ''P''(1), ''P''(2), ''P''(3), ... all hold. Informal metaphors help to explain this technique, such as falling dominoes or climbing a ladder: A proof by induction consists of two cases. The first, the base case, proves the statement for ''n'' = 0 without assuming any knowledge of other cases. The second case, the induction step, proves that ''if'' the statement holds for any given case ''n'' = ''k'', ''then'' it must also hold for the next case ''n'' = ''k'' + 1. These two steps establish that the statement holds for every natural number ''n''. The base case does not necessarily begin with ''n'' = 0, but often with ''n'' = 1, and possibly with any fixed natural number ''n'' = ''N'', establishing the truth of the statement for all natu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antilog
In mathematics, the logarithm is the inverse function to exponentiation. That means the logarithm of a number to the base is the exponent to which must be raised, to produce . For example, since , the ''logarithm base'' 10 of is , or . The logarithm of to ''base'' is denoted as , or without parentheses, , or even without the explicit base, , when no confusion is possible, or when the base does not matter such as in big O notation. The logarithm base is called the decimal or common logarithm and is commonly used in science and engineering. The natural logarithm has the number as its base; its use is widespread in mathematics and physics, because of its very simple derivative. The binary logarithm uses base and is frequently used in computer science. Logarithms were introduced by John Napier in 1614 as a means of simplifying calculations. They were rapidly adopted by navigators, scientists, engineers, surveyors and others to perform high-accu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Logarithm
In mathematics, the logarithm is the inverse function to exponentiation. That means the logarithm of a number to the base is the exponent to which must be raised, to produce . For example, since , the ''logarithm base'' 10 of is , or . The logarithm of to ''base'' is denoted as , or without parentheses, , or even without the explicit base, , when no confusion is possible, or when the base does not matter such as in big O notation. The logarithm base is called the decimal or common logarithm and is commonly used in science and engineering. The natural logarithm has the number e (mathematical constant), as its base; its use is widespread in mathematics and physics, because of its very simple derivative. The binary logarithm uses base and is frequently used in computer science. Logarithms were introduced by John Napier in 1614 as a means of simplifying calculations. They were rapidly adopted by navigators, scientists, engineers, surveyors and oth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Concave Function
In mathematics, a concave function is the negative of a convex function. A concave function is also synonymously called concave downwards, concave down, convex upwards, convex cap, or upper convex. Definition A real-valued function f on an interval (or, more generally, a convex set in vector space) is said to be ''concave'' if, for any x and y in the interval and for any \alpha \in ,1/math>, :f((1-\alpha )x+\alpha y)\geq (1-\alpha ) f(x)+\alpha f(y) A function is called ''strictly concave'' if :f((1-\alpha )x + \alpha y) > (1-\alpha) f(x) + \alpha f(y)\, for any \alpha \in (0,1) and x \neq y. For a function f: \mathbb \to \mathbb, this second definition merely states that for every z strictly between x and y, the point (z, f(z)) on the graph of f is above the straight line joining the points (x, f(x)) and (y, f(y)). A function f is quasiconcave if the upper contour sets of the function S(a)=\ are convex sets. Properties Functions of a single variable # A differentia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jensen's Inequality
In mathematics, Jensen's inequality, named after the Danish mathematician Johan Jensen, relates the value of a convex function of an integral to the integral of the convex function. It was proved by Jensen in 1906, building on an earlier proof of the same inequality for doubly-differentiable functions by Otto Hölder in 1889. Given its generality, the inequality appears in many forms depending on the context, some of which are presented below. In its simplest form the inequality states that the convex transformation of a mean is less than or equal to the mean applied after convex transformation; it is a simple corollary that the opposite is true of concave transformations. Jensen's inequality generalizes the statement that the secant line of a convex function lies ''above'' the graph of the function, which is Jensen's inequality for two points: the secant line consists of weighted means of the convex function (for ''t'' ∈ ,1, :t f(x_1) + (1-t) f(x_2), whil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |