|
Index Librorum Prohibitorum
The (English: ''Index of Forbidden Books'') was a changing list of publications deemed heretical or contrary to morality by the Sacred Congregation of the Index (a former dicastery of the Roman Curia); Catholics were forbidden to print or read them, subject to the local bishop. The Holy Office justified that decision by referring to chapter 13 of Paul the Apostle's Epistle to the Romans regarding state authority coming from God. However, somewhat later, the Vatican criticized in the encyclical (March 1937) about the challenges of the church in Nazi Germany. Abolition (1966) On 7 December 1965, Pope Paul VI issued the that reorganized the Holy Office as the ''Sacred Congregation for the Doctrine of the Faith''. The Index was not listed as being a part of the newly constituted congregation's competence, leading to questioning whether it still was. This question was put to Cardinal Alfredo Ottaviani, pro-prefect of the congregation, who responded in the negative. The Cardinal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Index Librorum Prohibitorum 1
Index (: indexes or indices) may refer to: Arts, entertainment, and media Fictional entities * Index (A Certain Magical Index), Index (''A Certain Magical Index''), a character in the light novel series ''A Certain Magical Index'' * The Index, an item on the Halo Array in the ''Halo'' video game series Periodicals and news portals * ''Index Magazine'', a publication for art and culture * Index.hr, a Croatian online newspaper * index.hu, a Hungarian-language news and community portal * The Index (Kalamazoo College), ''The Index'' (Kalamazoo College), a student newspaper * ''The Index'', an 1860s European propaganda journal created by Henry Hotze to support the Confederate States of America * ''Truman State University Index'', a student newspaper Other arts, entertainment and media * The Index (band) * ''Indexed'', a Web cartoon by Jessica Hagy * ''Index'', album by Ana Mena Business enterprises and events * Index (retailer), a former UK catalogue retailer * INDEX, a market res ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Printing Press
A printing press is a mechanical device for applying pressure to an inked surface resting upon a printing, print medium (such as paper or cloth), thereby transferring the ink. It marked a dramatic improvement on earlier printing methods in which the cloth, paper, or other medium was brushed or rubbed repeatedly to achieve the transfer of ink and accelerated the process. Typically used for texts, the invention and global spread of the printing press was one of the most influential events in the second millennium. In Germany, around 1440, the goldsmith Johannes Gutenberg invented the movable type, movable-type printing press, which started the Printing Revolution. Modelled on the design of existing screw presses, a single Renaissance movable-type printing press could produce up to 3,600 pages per workday, compared to forty by History of typography in East Asia, hand-printing and a few by scribe, hand-copying. Gutenberg's newly devised hand mould made possible the precise and rapi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Cartesianism
Cartesianism is the philosophical and scientific system of René Descartes and its subsequent development by other seventeenth century thinkers, most notably François Poullain de la Barre, Nicolas Malebranche and Baruch Spinoza. Descartes is often regarded as the first thinker to emphasize the use of reason to develop the natural sciences. For him, philosophy was a thinking system that embodied all knowledge. Aristotle and St. Augustine's work influenced Descartes's cogito argument. Additionally, there is similarity between Descartes's work and that of Scottish philosopher George Campbell's 1776 publication, titled ''Philosophy of Rhetoric''. In his ''Meditations on First Philosophy'' he writes, " t what then am I? A thing which thinks. What is a thing which thinks? It is a thing which doubts, understands, onceives affirms, denies, wills, refuses, which also imagines and feels." Cartesians view the mind as being wholly separate from the corporeal body. Sensation and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
René Descartes
René Descartes ( , ; ; 31 March 1596 – 11 February 1650) was a French philosopher, scientist, and mathematician, widely considered a seminal figure in the emergence of modern philosophy and Modern science, science. Mathematics was paramount to his method of inquiry, and he connected the previously separate fields of geometry and algebra into analytic geometry. Descartes spent much of his working life in the Dutch Republic, initially serving the Dutch States Army, and later becoming a central intellectual of the Dutch Golden Age. Although he served a Dutch Reformed Church, Protestant state and was later counted as a Deism, deist by critics, Descartes was Roman Catholicism, Roman Catholic. Many elements of Descartes's philosophy have precedents in late Aristotelianism, the Neostoicism, revived Stoicism of the 16th century, or in earlier philosophers like Augustine of Hippo, Augustine. In his natural philosophy, he differed from the Scholasticism, schools on two major point ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
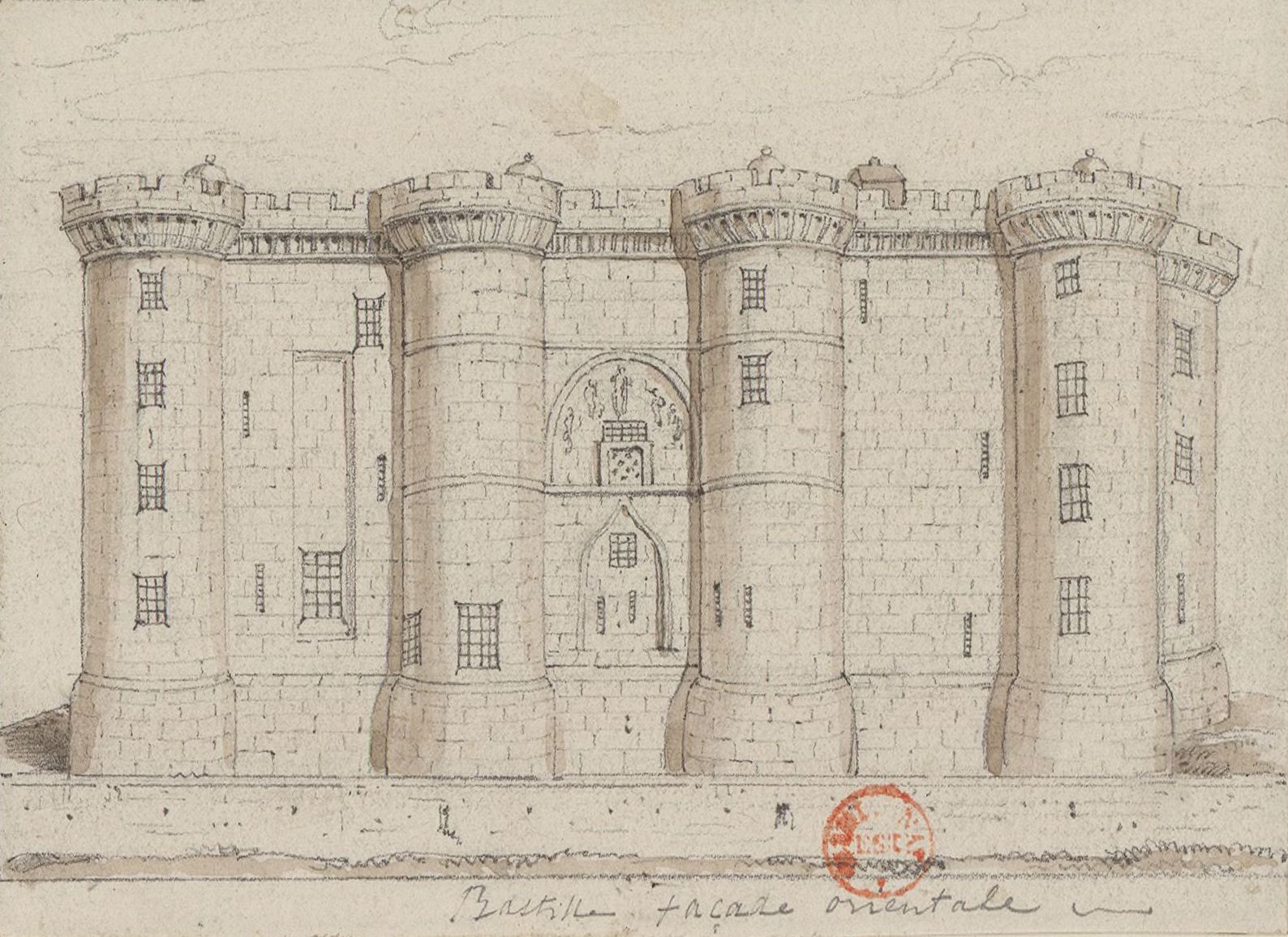
Bastille
The Bastille (, ) was a fortress in Paris, known as the Bastille Saint-Antoine. It played an important role in the internal conflicts of France and for most of its history was used as a state prison by the kings of France. It was stormed by a crowd on 14 July 1789, in the French Revolution, becoming an important symbol for the French Republican movement. It was later demolished and replaced by the Place de la Bastille. The castle was built to defend the eastern approach to the city from potential English attacks during the Hundred Years' War. Construction was underway by 1357, but the main construction occurred from 1370 onwards, creating a strong fortress with eight towers that protected the strategic gateway of the Porte Saint-Antoine heading out to the east. The innovative design proved influential in both France and England and was widely copied. The Bastille figured prominently in France's domestic conflicts, including the fighting between the rival factions of the Bur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Edict Of Compiègne
The Edict of Compiègne (), issued from his Château de Compiègne by Henry II of France, 24 July 1557, applied the death penalty for all convictions of relapsed and obstinate "sacramentarians", for those who went to Geneva or published books there, for iconoclast blasphemers against images, and even for illegal preaching or participation in religious gatherings, whether public or private. It was the third in a series of increasingly severe punishments for expressions of Protestantism in France, which had for an aim the extirpation of the Reformation. By raising the stakes, which now literally became matters of life and death, the Edict had the result of precipitating the long religious crisis in France and hastening the onset of armed civil war between armies mustered on the basis of religion, the series of French Wars of Religion, which were not settled until Henri IV's edict of toleration, the Edict of Nantes (1598). The source of the "contagion", as court pamphleteers put it, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Edict Of Châteaubriant
The Edict of Châteaubriant, issued from the seat of Anne, duc de Montmorency in Brittany, was promulgated by Henri II of France, 27 June 1551. The Edict was one of an increasingly severe series of measures taken by Henry II against Protestants, whom he regarded as heretics. In the preamble, the Edict frankly reported that previous measures against heresy in the kingdom had proved ineffectual. "Heretics", the Edict reported, met in conventicles, infected schools, invaded the judicial bench and forced toleration upon judges. To ensure more rigorous judgements, in 1547 Henri had already created a special judicial chamber drawn from members of the ''parlements'', solely to judge cases of heresy (called by Protestants the ''Chambre Ardente'' (the "Burning Chamber"). The Edict contained quite detailed provisions: it called upon the civil and ecclesiastical courts to detect and punish all heretics, and placed severe restrictions on Protestants, including loss of one-third of property gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Étienne Dolet
Étienne Dolet (; 3 August 15093 August 1546) was a French scholar, translation, translator and printer (publisher), printer. He was a controversial figure throughout his lifetime, which was buffeted by the opposing forces of the Renaissance and the French Inquisition. His early attacks upon the Inquisition and the municipal authorities of Toulouse, together with his later publications in Lyon, caused the French Inquisition to monitor his activities closely. After several stays in prison, the combined efforts of the ''parlement'' of Paris, the Inquisition, and the theological faculty of the University of Paris, Sorbonne resulted in his conviction for heresy and a death sentence. He was hanged and burned with his books on the Place Maubert in Paris. In modern times, Dolet is remembered as a martyr for what is now known as freedom of speech and freedom of the press. Early life and education Born in 1509 to parents who are not known to modern historians, Dolet lived in Orléans unti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Printing Presses
A printing press is a mechanical device for applying pressure to an inked surface resting upon a print medium (such as paper or cloth), thereby transferring the ink. It marked a dramatic improvement on earlier printing methods in which the cloth, paper, or other medium was brushed or rubbed repeatedly to achieve the transfer of ink and accelerated the process. Typically used for texts, the invention and global spread of the printing press was one of the most influential events in the second millennium. In Germany, around 1440, the goldsmith Johannes Gutenberg invented the movable-type printing press, which started the Printing Revolution. Modelled on the design of existing screw presses, a single Renaissance movable-type printing press could produce up to 3,600 pages per workday, compared to forty by hand-printing and a few by hand-copying. Gutenberg's newly devised hand mould made possible the precise and rapid creation of metal movable type in large quantities. His ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
City Of London
The City of London, also known as ''the City'', is a Ceremonial counties of England, ceremonial county and Districts of England, local government district with City status in the United Kingdom, city status in England. It is the Old town, historic centre of London, though it forms only a small part of the larger Greater London metropolis. The City of London had a population of 8,583 at the 2021 United Kingdom census, 2021 census, however over 500,000 people were employed in the area as of 2019. It has an area of , the source of the nickname ''the Square Mile''. The City is a unique local authority area governed by the City of London Corporation, which is led by the Lord Mayor of London, Lord Mayor of the City of London. Together with Canary Wharf and the West End of London, West End, the City of London forms the primary central business district of London, which is one of the leading financial centres of the world. The Bank of England and the London Stock Exchange are both ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Stationers' Company
The Worshipful Company of Stationers and Newspaper Makers (until 1937 the Worshipful Company of Stationers), usually known as the Stationers' Company, is one of the livery companies of the City of London. The Stationers' Company was formed in 1403; it received a royal charter in 1557. It held a monopoly over the publishing industry and was officially responsible for setting and enforcing regulations until the enactment of the Statute of Anne, also known as the Copyright Act 1710. Once the company received its charter, "the company's role was to regulate and discipline the industry, define proper conduct and maintain its own corporate privileges." The company members, including master, wardens, assistants, liverymen, freemen and apprentices are mostly involved with the modern visual and graphic communications industries that have evolved from the company's original trades. These include printing, paper-making, packaging, office products, engineering, advertising, design, photogra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
English Crown
This list of kings and reigning queens of the Kingdom of England begins with Alfred the Great, who initially ruled Wessex, one of the seven Anglo-Saxon kingdoms which later made up modern England. Alfred styled himself king of the Anglo-Saxons from about 886, and while he was not the first king to claim to rule all of the English, his rule represents the start of the first unbroken line of kings to rule the whole of England, the House of Wessex. Arguments are made for a few different kings thought to have controlled enough Anglo-Saxon kingdoms to be deemed the first king of England. For example, Offa of Mercia and Egbert of Wessex are sometimes described as kings of England by popular writers, but it is no longer the majority view of historians that their wide dominions were part of a process leading to a unified England. The historian Simon Keynes states, for example, "Offa was driven by a lust for power, not a vision of English unity; and what he left was a reputation, no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |