|
Index (database)
A database index is a data structure that improves the speed of data retrieval operations on a database table at the cost of additional writes and storage space to maintain the index data structure. Indexes are used to quickly locate data without having to search every row in a database table every time said table is accessed. Indexes can be created using one or more columns of a database table, providing the basis for both rapid random lookups and efficient access of ordered records. An index is a copy of selected columns of data, from a table, that is designed to enable very efficient search. An index normally includes a "key" or direct link to the original row of data from which it was copied, to allow the complete row to be retrieved efficiently. Some databases extend the power of indexing by letting developers create indexes on column values that have been transformed by functions or expressions. For example, an index could be created on upper(last_name), which would o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Data Structure
In computer science, a data structure is a data organization and storage format that is usually chosen for Efficiency, efficient Data access, access to data. More precisely, a data structure is a collection of data values, the relationships among them, and the Function (computer programming), functions or Operator (computer programming), operations that can be applied to the data, i.e., it is an algebraic structure about data. Usage Data structures serve as the basis for abstract data types (ADT). The ADT defines the logical form of the data type. The data structure implements the physical form of the data type. Different types of data structures are suited to different kinds of applications, and some are highly specialized to specific tasks. For example, Relational database, relational databases commonly use B-tree indexes for data retrieval, while compiler Implementation, implementations usually use hash tables to look up Identifier (computer languages), identifiers. Data s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Hash Table
In computer science, a hash table is a data structure that implements an associative array, also called a dictionary or simply map; an associative array is an abstract data type that maps Unique key, keys to Value (computer science), values. A hash table uses a hash function to compute an ''index'', also called a ''hash code'', into an array of ''buckets'' or ''slots'', from which the desired value can be found. During lookup, the key is hashed and the resulting hash indicates where the corresponding value is stored. A map implemented by a hash table is called a hash map. Most hash table designs employ an Perfect hash function, imperfect hash function. Hash collision, Hash collisions, where the hash function generates the same index for more than one key, therefore typically must be accommodated in some way. In a well-dimensioned hash table, the average time complexity for each lookup is independent of the number of elements stored in the table. Many hash table designs also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Jennifer Widom
Jennifer Widom (born ) is an American computer scientist known for her work in database systems and data management. She is notable for foundational contributions to semi-structured data management and data stream management systems. Since 2017, Widom is the dean of the School of Engineering and professor of computer science at Stanford University. Her honors include the Fletcher Jones Professor of Computer Science and multiple lifetime achievement awards from the Association for Computing Machinery. Education Widom earned a bachelor's degree in trumpet performance from the Indiana University Jacobs School of Music in 1982 and a PhD in computer science under David Gries from Cornell University in 1987. Academic career Widom began her career as a researcher at the IBM Almaden Research Center and joined Stanford University as a professor in 1993. She was the chair of the Stanford computer science department from 2009 to 2014, and served as senior associate dean for faculty a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Jeffrey Ullman
Jeffrey David Ullman (born November 22, 1942) is an American computer scientist and the Stanford W. Ascherman Professor of Engineering, Emeritus, at Stanford University. His textbooks on compilers (various editions are popularly known as the dragon book), theory of computation (also known as the Cinderella book), data structures, and databases are regarded as standards in their fields. He and his long-time collaborator Alfred Aho are the recipients of the 2020 Turing Award, generally recognized as the highest distinction in computer science.ACM Turing Award Honors Innovators Who Shaped the Foundations of Programming Language Compilers and Algorithms Retrieved March 31, 2021. Career Ullman received a Bachelor of S ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Hector Garcia-Molina
In Greek mythology, Hector (; , ) was a Trojan prince, a hero and the greatest warrior for Troy during the Trojan War. He is a major character in Homer's ''Iliad'', where he leads the Trojans and their allies in the defense of Troy, killing countless Greek warriors. He is ultimately killed in single combat by the Greek hero Achilles, who later drags his dead body around the city of Troy behind his chariot. Etymology In Greek, is a derivative of the verb ἔχειν ''ékhein'', archaic form * ('to have' or 'to hold'), from Proto-Indo-European *'' seɡ́ʰ-'' ('to hold'). , or as found in Aeolic poetry, is also an epithet of Zeus in his capacity as 'he who holds verything together. Hector's name could thus be taken to mean 'holding fast'. The name was in use during Mycenaean times, as evidenced by a servant with the name referred to in a Linear B tablet. In the tablet, the name is spelled , ''E-ko-to''. Moses I. Finley proposed that the Homeric hero was partly based ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Record (computer Science)
In computer science, a record (also called a structure, struct (C programming language), struct, or compound data type) is a composite data structure a collection of Field (computer science), fields, possibly of different data types, typically fixed in number and sequence. For example, a date could be stored as a record containing a Number, numeric year field, a month field represented as a string, and a numeric day-of-month field. A circle record might contain a numeric radius and a center that is a point record containing x and y coordinates. Notable applications include the programming language ''record type'' and for row-based storage, data organized as a sequence of records, such as a database table, spreadsheet or comma-separated values (CSV) file. In general, a record type value is stored in main memory, memory and row-based storage is in mass storage. A ''record type'' is a data type that describes such values and variables. Most modern programming languages allow the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Pointer (computer Programming)
In computer science, a pointer is an object in many programming languages that stores a memory address. This can be that of another value located in computer memory, or in some cases, that of memory-mapped computer hardware. A pointer ''references'' a location in memory, and obtaining the value stored at that location is known as ''dereferencing'' the pointer. As an analogy, a page number in a book's index could be considered a pointer to the corresponding page; dereferencing such a pointer would be done by flipping to the page with the given page number and reading the text found on that page. The actual format and content of a pointer variable is dependent on the underlying computer architecture. Using pointers significantly improves performance for repetitive operations, like traversing iterable data structures (e.g. strings, lookup tables, control tables, linked lists, and tree structures). In particular, it is often much cheaper in time and space to copy and deref ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Computer File
A computer file is a System resource, resource for recording Data (computing), data on a Computer data storage, computer storage device, primarily identified by its filename. Just as words can be written on paper, so too can data be written to a computer file. Files can be shared with and transferred between computers and Mobile device, mobile devices via removable media, Computer networks, networks, or the Internet. Different File format, types of computer files are designed for different purposes. A file may be designed to store a written message, a document, a spreadsheet, an Digital image, image, a Digital video, video, a computer program, program, or any wide variety of other kinds of data. Certain files can store multiple data types at once. By using computer programs, a person can open, read, change, save, and close a computer file. Computer files may be reopened, modified, and file copying, copied an arbitrary number of times. Files are typically organized in a file syst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
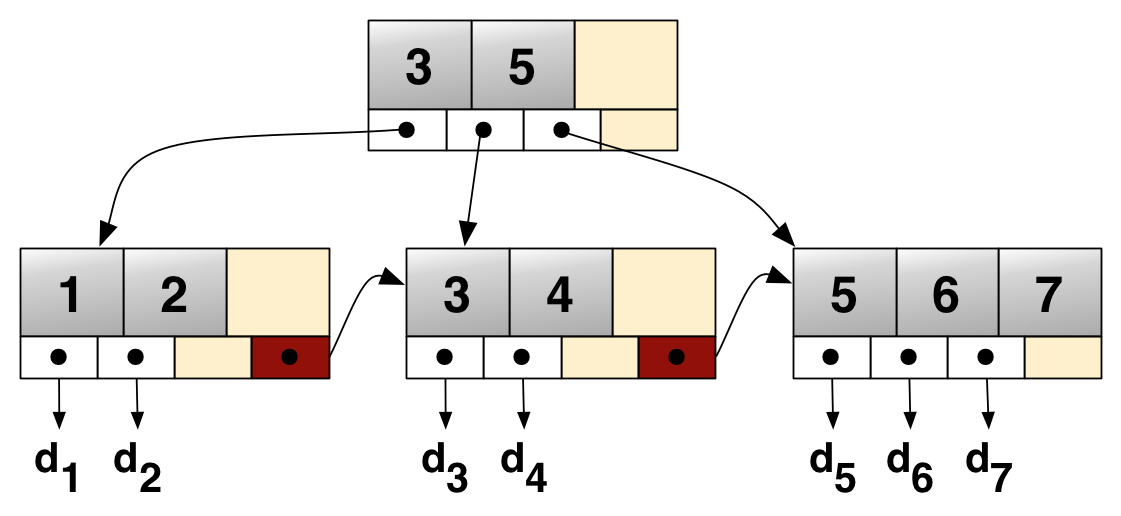 |
B+ Tree
A B+ tree is an m-ary tree with a variable but often large number of children per node. A B+ tree consists of a root, internal nodes and leaves. The root may be either a leaf or a node with two or more children. A B+ tree can be viewed as a B-tree in which each node contains only keys (not key–value pairs), and to which an additional level is added at the bottom with linked leaves. The primary value of a B+ tree is in storing data for efficient retrieval in a Block (data storage), block-oriented storage context—in particular, filesystems. This is primarily because unlike binary search trees, B+ trees have very high fanout (number of pointers to child nodes in a node, typically on the order of 100 or more), which reduces the number of I/O operations required to find an element in the tree. History There is no single paper introducing the B+ tree concept. Instead, the notion of maintaining all data in leaf nodes is repeatedly brought up as an interesting variant of the B- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Bitwise Operation
In computer programming, a bitwise operation operates on a bit string, a bit array or a binary numeral (considered as a bit string) at the level of its individual bits. It is a fast and simple action, basic to the higher-level arithmetic operations and directly supported by the central processing unit, processor. Most bitwise operations are presented as two-operand instructions where the result replaces one of the input operands. On simple low-cost processors, typically, bitwise operations are substantially faster than division, several times faster than multiplication, and sometimes significantly faster than addition. While modern processors usually perform addition and multiplication just as fast as bitwise operations due to their longer instruction pipelines and other computer architecture, architectural design choices, bitwise operations do commonly use less power because of the reduced use of resources. Bitwise operators In the explanations below, any indication of a bit's p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Bit Array
A bit array (also known as bitmask, bit map, bit set, bit string, or bit vector) is an array data structure that compactly stores bits. It can be used to implement a simple set data structure. A bit array is effective at exploiting bit-level parallelism in hardware to perform operations quickly. A typical bit array stores ''kw'' bits, where ''w'' is the number of bits in the unit of storage, such as a byte or Word (computer architecture), word, and ''k'' is some nonnegative integer. If ''w'' does not divide the number of bits to be stored, some space is wasted due to Fragmentation (computing), internal fragmentation. Definition A bit array is a mapping from some domain (almost always a range of integers) to values in the set . The values can be interpreted as dark/light, absent/present, locked/unlocked, valid/invalid, et cetera. The point is that there are only two possible values, so they can be stored in one bit. As with other arrays, the access to a single bit can be managed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Sargable
In relational databases, a condition (or predicate) in a query is said to be sargable if the DBMS engine can take advantage of an index to speed up the execution of the query. The term is derived from a contraction of ''Search ARGument ABLE''. It was first used by IBM researchers as a contraction of Search ARGument, and has come to mean simply "can be looked up by an index." For database query optimizers, sargable is an important property in OLTP workloads because it suggests a good query plan can be obtained by a simple heuristic matching query to indexes instead of a complex, time-consuming cost-based search, thus it is often desired to write sargable queries. A query failing to be sargable is known as a non-sargable query and typically has a negative effect on query time, so one of the steps in query optimization is to convert them to be sargable. The effect is similar to searching for a specific term in a book that has no index, beginning at page one each time, instead of jum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |