|
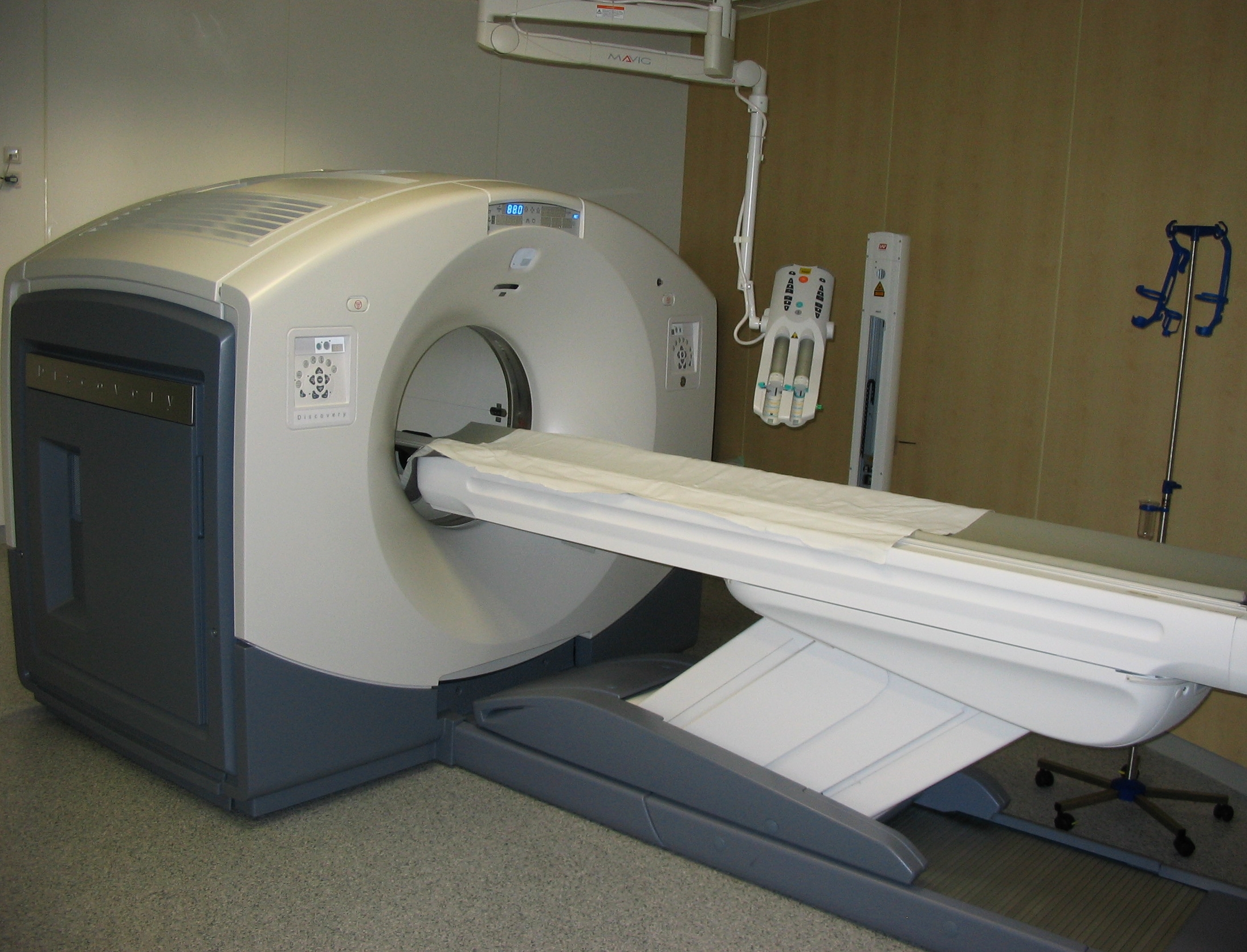
Imaging Phantom
Imaging phantom, or simply phantom, is a specially designed object that is scanned or imaged in the field of medical imaging to evaluate, analyze, and tune the performance of various imaging devices. A phantom is more readily available and provides more consistent results than the use of a living subject or cadaver, and likewise avoids subjecting a living subject to direct risk. Phantoms were originally employed for use in 2D x-ray based imaging techniques such as radiography or fluoroscopy, though more recently phantoms with desired imaging characteristics have been developed for 3D techniques such as SPECT, MRI, CT, Ultrasound, PET, and other imaging methods or modalities. Design A phantom used to evaluate an imaging device should respond in a similar manner to how human tissues and organs would act in that specific imaging modality. For instance, phantoms made for 2D radiography may hold various quantities of x-ray contrast agents with similar x-ray absorbing properties to n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Positron Emission Tomography
Positron emission tomography (PET) is a functional imaging technique that uses radioactive substances known as radiotracers to visualize and measure changes in metabolic processes, and in other physiological activities including blood flow, regional chemical composition, and absorption. Different tracers are used for various imaging purposes, depending on the target process within the body. For example, -FDG is commonly used to detect cancer, NaF is widely used for detecting bone formation, and oxygen-15 is sometimes used to measure blood flow. PET is a common imaging technique, a medical scintillography technique used in nuclear medicine. A radiopharmaceutical — a radioisotope attached to a drug — is injected into the body as a tracer. When the radiopharmaceutical undergoes beta plus decay, a positron is emitted, and when the positron collides with an ordinary electron, the two particles annihilate and gamma rays are emitted. These gamma rays are detecte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phantom Structure
Phantom structures are artificial structures designed to emulate properties of the human body in matters such as, including, but not limited to, light scattering and optics, electrical conductivity, and sound wave reception. Phantoms have been used experimentally in lieu of, or as a supplement to, human subjects to maintain consistency, verify reliability of technologies, or reduce experimental expense. They also have been employed as material for training technicians to perform imaging. Optical phantoms Optical tissue phantoms, or imaging phantoms, are reported to be used largely for three main purposes: to calibrate optical devices, record baseline reference measurements, and for imaging the human body. Optical tissue phantoms may have irregular shape of body parts. Composite Materials Optical phantoms can be made from a number of materials. These are including but not limited to: * homogenized milk * non-dairy creamer * wax * blood and yeast suspension * water-soluble dy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jaszczak Phantom
A Jaszczak phantom (pronounced "JAY-zak") aka Data Spectrum ECT phantom is an imaging phantom used for validating scanner geometry, 3D contrast, uniformity, resolution, attenuation and scatter correction or alignment tasks in nuclear medicine. It is commonly used in academic centers and hospitals to characterize a SPECT or some gamma camera systems for quality control purposes. It is used for accreditation by clinical and academic facilities for the American College of Radiology. The phantom was developed by Ronald J. Jaszczak of Duke University, and was filed for a patent in 1982. It is a cylinder containing fillable inserts that is often used with a radionuclide such as Technetium-99m or Fluorine-18. Although the phantom can be used for acceptance testing, the National Electrical Manufacturers Association recommends a 30 million count acquisition and section reconstruction of the phantom be performed quarterly. In 1981 Ronald J. Jaszczak founded Data Spectrum Corporation which m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computational Human Phantom
Computational human phantoms are models of the human body used in computerized analysis. Since the 1960s, the radiological science community has developed and applied these models for ionizing radiation dosimetry studies. These models have become increasingly accurate with respect to the internal structure of the human body. As computing evolved, so did the phantoms. Graduating from phantoms based on simple quadratic equations to voxelized phantoms, which were based on actual medical images of the human body, was a major step. The newest models are based on more advanced mathematics, such as non-uniform rational B-spline (NURBS) and polygon meshes, which allow for 4-D phantoms where simulations can take place not only 3-dimensional space but in time as well. Phantoms have been developed for a wide variety of humans, from children to adolescents to adults, male and female, as well as pregnant women. With such a variety of phantoms, many kinds of simulations can be run, from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ultrasound
Ultrasound is sound waves with frequencies higher than the upper audible limit of human hearing. Ultrasound is not different from "normal" (audible) sound in its physical properties, except that humans cannot hear it. This limit varies from person to person and is approximately 20 kilohertz (20,000 hertz) in healthy young adults. Ultrasound devices operate with frequencies from 20 kHz up to several gigahertz. Ultrasound is used in many different fields. Ultrasonic devices are used to detect objects and measure distances. Ultrasound imaging or sonography is often used in medicine. In the nondestructive testing of products and structures, ultrasound is used to detect invisible flaws. Industrially, ultrasound is used for cleaning, mixing, and accelerating chemical processes. Animals such as bats and porpoises use ultrasound for locating prey and obstacles. History Acoustics, the science of sound, starts as far back as Pythagoras in the 6th century BC, who ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rheological
Rheology (; ) is the study of the flow of matter, primarily in a fluid (liquid or gas) state, but also as "soft solids" or solids under conditions in which they respond with plastic flow rather than deforming elastically in response to an applied force. Rheology is a branch of physics, and it is the science that deals with the deformation and flow of materials, both solids and liquids.W. R. Schowalter (1978) Mechanics of Non-Newtonian Fluids Pergamon The term ''rheology'' was coined by Eugene C. Bingham, a professor at Lafayette College, in 1920, from a suggestion by a colleague, Markus Reiner.The Deborah Number The term was inspired by the of |
Radiocontrast
Radiocontrast agents are substances used to enhance the visibility of internal structures in X-ray-based imaging techniques such as computed tomography ( contrast CT), projectional radiography, and fluoroscopy. Radiocontrast agents are typically iodine, or more rarely barium sulfate. The contrast agents absorb external X-rays, resulting in decreased exposure on the X-ray detector. This is different from radiopharmaceuticals used in nuclear medicine which emit radiation. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) functions through different principles and thus MRI contrast agents have a different mode of action. These compounds work by altering the magnetic properties of nearby hydrogen nuclei. Types and uses Radiocontrast agents used in X-ray examinations can be grouped in positive (iodinated agents, barium sulfate), and negative agents (air, carbon dioxide, methylcellulose). Iodine (circulatory system) Iodinated contrast contains iodine. It is the main type of radiocontrast used for i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medical Ultrasonography
Medical ultrasound includes diagnostic techniques (mainly imaging techniques) using ultrasound, as well as therapeutic applications of ultrasound. In diagnosis, it is used to create an image of internal body structures such as tendons, muscles, joints, blood vessels, and internal organs, to measure some characteristics (e.g. distances and velocities) or to generate an informative audible sound. Its aim is usually to find a source of disease or to exclude pathology. The usage of ultrasound to produce visual images for medicine is called medical ultrasonography or simply sonography. The practice of examining pregnant women using ultrasound is called obstetric ultrasonography, and was an early development of clinical ultrasonography. Ultrasound is composed of sound waves with frequencies which are significantly higher than the range of human hearing (>20,000 Hz). Ultrasonic images, also known as sonograms, are created by sending pulses of ultrasound into tissue usin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imaging Phantom As Seen On Medical Ultrasound
Imaging is the representation or reproduction of an object's form; especially a visual representation (i.e., the formation of an image). Imaging technology is the application of materials and methods to create, preserve, or duplicate images. Imaging science is a multidisciplinary field concerned with the generation, collection, duplication, analysis, modification, and visualization of images,Joseph P. Hornak, ''Encyclopedia of Imaging Science and Technology'' (John Wiley & Sons, 2002) including imaging things that the human eye cannot detect. As an evolving field it includes research and researchers from physics, mathematics, electrical engineering, computer vision, computer science, and perceptual psychology. ''Imager'' are imaging sensors. Imaging chain The foundation of imaging science as a discipline is the "imaging chain" – a conceptual model describing all of the factors which must be considered when developing a system for creating visual renderings (images). In g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |