 |
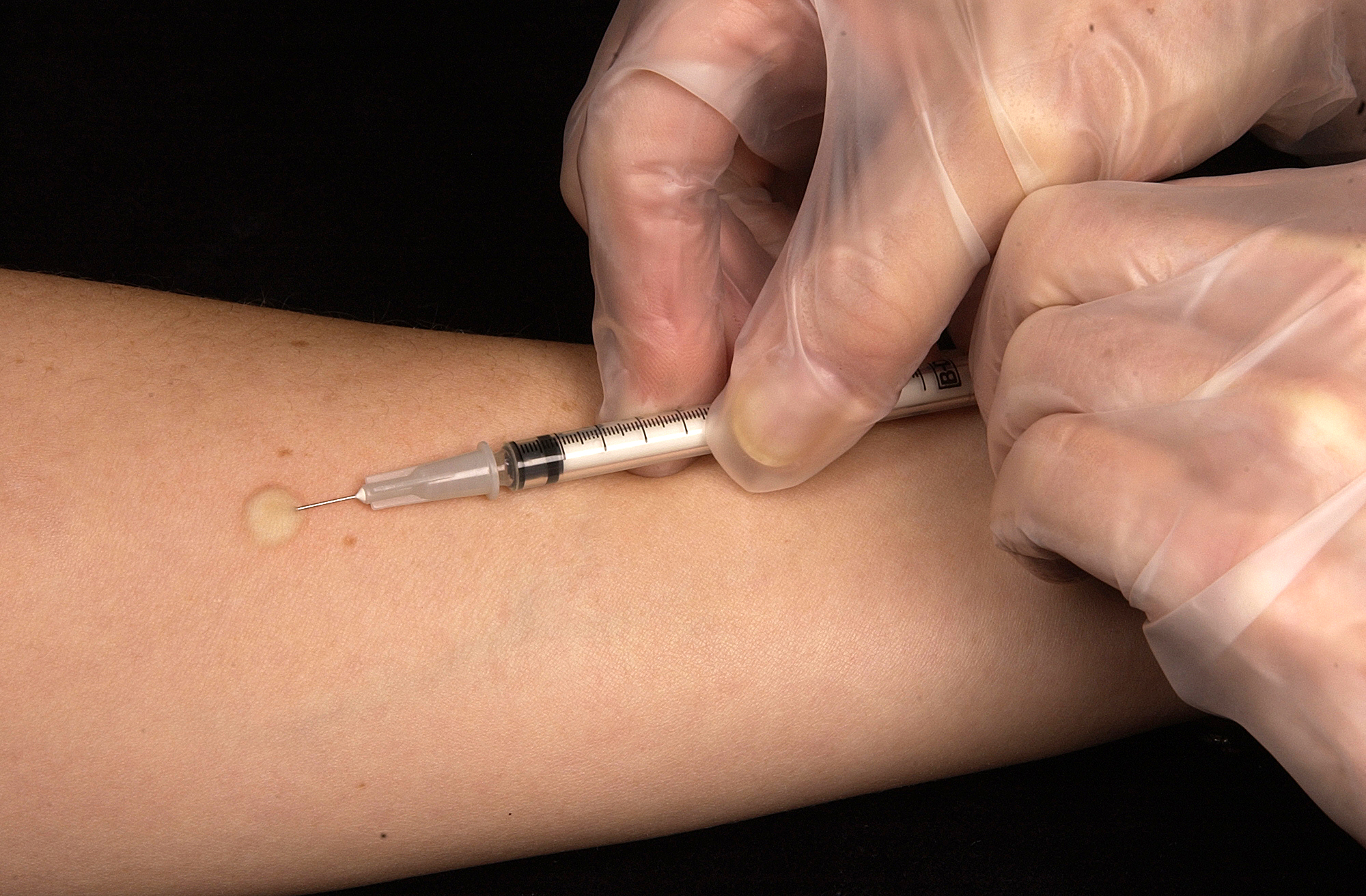
Intradermal Injection
Intradermal injection (also intracutaneous or intradermic, abbreviated as ID) is a shallow or superficial injection of a substance into the dermis, which is located between the epidermis and the hypodermis. For certain substances, administration via an ID route can result in a faster systemic uptake compared with subcutaneous injections, leading to a stronger immune response to vaccinations, immunology and novel cancer treatments, and faster drug uptake. Additionally, since administration is closer to the surface of the skin, the body's reaction to substances is more easily visible. However, due to complexity of the procedure compared to subcutaneous injection and intramuscular injection, administration via ID is relatively rare, and is only used for tuberculosis and allergy tests, monkeypox vaccination, and certain therapies. Vaccine dose sparing For vaccination many clinical studies have proven efficacy of ID administration over subcutaneous (SC), intramuscular (IM) or other ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
 |
Medical Injection
An injection (often and usually referred to as a "shot" in US English, a "jab" in UK English, or a "jag" in Scottish English and Scots Language, Scots) is the act of administering a liquid, especially a drug, into a person's body using a needle (usually a hypodermic needle) and a syringe. An injection is considered a form of parenteral administration, parenteral drug administration; it does not involve absorption in the digestive tract. This allows the medication to be absorbed more rapidly and avoid the first pass effect. There are many types of injection, which are generally named after the body tissue the injection is administered into. This includes common injections such as subcutaneous injection, subcutaneous, intramuscular injection, intramuscular, and intravenous injections, as well as less common injections such as Epidural administration , epidural, intraperitoneal injection, intraperitoneal, intraosseous injection, intraosseous, intracardiac injection, intracardiac, int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
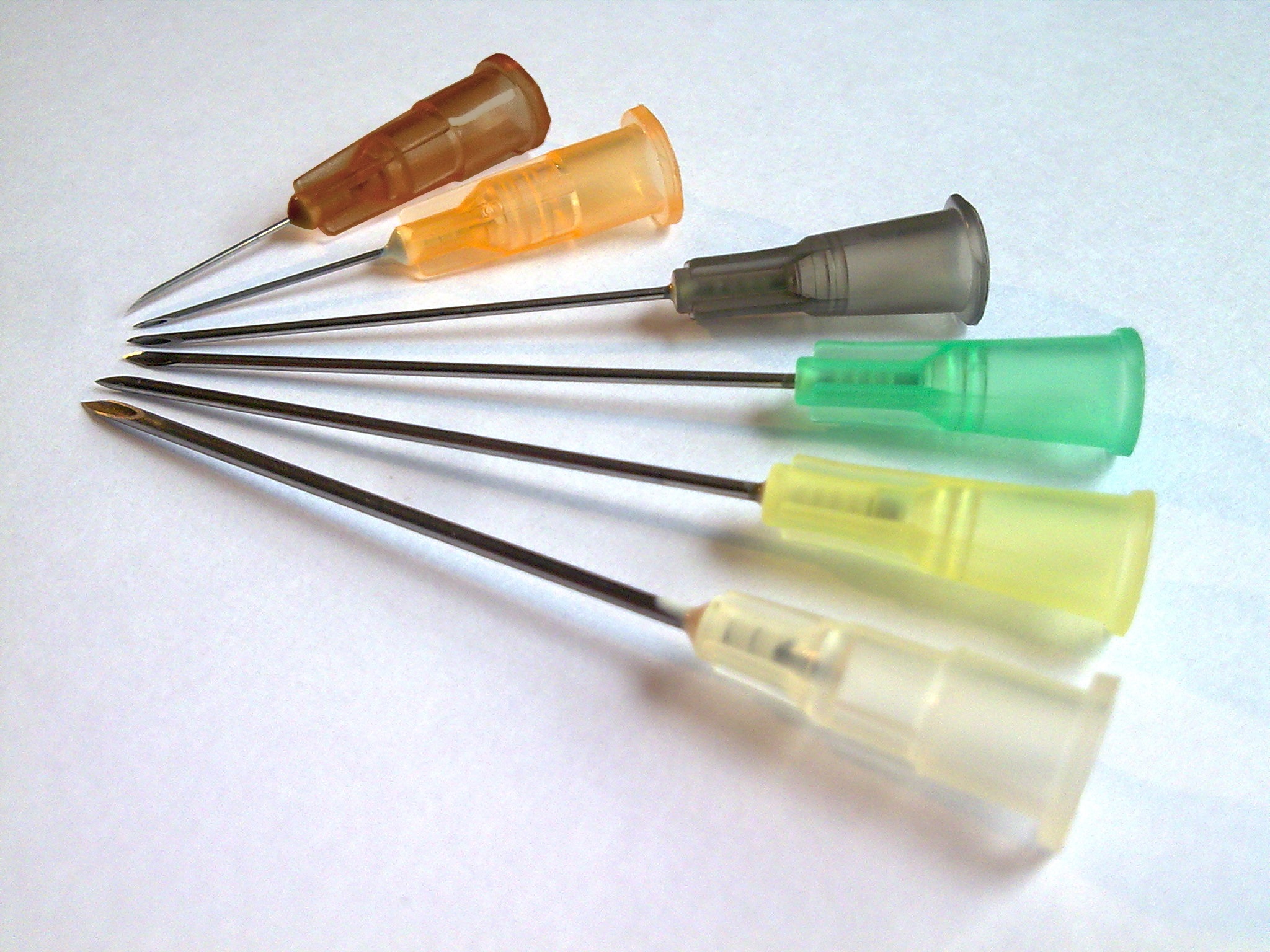 |
Birmingham Gauge
The Birmingham gauge, officially the Birmingham Wire Gauge and often abbreviated as ''G'' or ''ga'', is unit or wire gauge used to measure the thickness or diameter of wires and tubing, including hypodermic needles and other medical tube products. Terminology The Birmingham gauge is also known as the Stubs Iron Wire Gauge or Birmingham Wire Gauge and is distinct from the Stubs Steel Wire Gauge and the British Standard Wire Gauge. It is commonly referred to simply as ''gauge'' (abbreviated as ''G''), but this should not be confused with the French gauge, a separate system used for measuring the outer diameter of catheters. System The Birmingham gauge ranges from 5/0 or 00000, the lowest gauge number corresponding to the largest size of , to 36, the highest gauge number corresponding to the smallest size of . The increments between gauge sizes are not linear and vary. At higher gauge numbers, the increment between the two highest gauges is , while at lower gauge numbers, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
 |
Intravenous Injection
Intravenous therapy (abbreviated as IV therapy) is a medical technique that administers fluids, medications and nutrients directly into a person's vein. The intravenous route of administration is commonly used for rehydration or to provide nutrients for those who cannot, or will not—due to reduced mental states or otherwise—consume food or water by mouth. It may also be used to administer medications or other medical therapy such as blood products or electrolytes to correct electrolyte imbalances. Attempts at providing intravenous therapy have been recorded as early as the 1400s, but the practice did not become widespread until the 1900s after the development of techniques for safe, effective use. The intravenous route is the fastest way to deliver medications and fluid replacement throughout the body as they are introduced directly into the circulatory system and thus quickly distributed. For this reason, the intravenous route of administration is also used for the consump ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
 |
Intramuscular Injection
Intramuscular injection, often abbreviated IM, is the medical injection, injection of a substance into a muscle. In medicine, it is one of several methods for parenteral, parenteral administration of medications. Intramuscular injection may be preferred because muscles have larger and more numerous blood vessels than subcutaneous tissue, leading to faster absorption than subcutaneous injection, subcutaneous or intradermal injections. Medication administered via intramuscular injection is not subject to the first-pass metabolism effect which affects oral medications. Common sites for intramuscular injections include the deltoid muscle of the upper arm and the gluteal muscle of the buttock. In infants, the vastus lateralis muscle of the thigh is commonly used. The injection site must be cleaned before administering the injection, and the injection is then administered in a fast, darting motion to decrease the discomfort to the individual. The volume to be injected in the muscle is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
 |
Subcutaneous Injection
Subcutaneous administration is the insertion of medications beneath the skin either by injection or infusion. A subcutaneous injection is administered as a bolus (medicine), bolus into the subcutis, the layer of skin directly below the dermis and Epidermis (skin), epidermis, collectively referred to as the Cutis (anatomy), cutis. The instruments are usually a hypodermic needle and a syringe. Subcutaneous injections are highly effective in administering medications such as insulin, morphine, heroin, diacetylmorphine and goserelin. Subcutaneous administration may be List of medical abbreviations, abbreviated as SC, SQ, subcu, sub-Q, SubQ, or subcut. Subcut is the preferred abbreviation to reduce the risk of misunderstanding and potential errors. Subcutaneous tissue has few blood vessels and so drugs injected into it are intended for slow, sustained rates of absorption, often with some amount of depot injection, depot effect. Compared with other route of administration, routes of ad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
 |
Blister
A blister is a small pocket of body fluid (lymph, serum, plasma, blood, or pus) within the upper layers of the skin, usually caused by forceful rubbing (friction), burning, freezing, chemical exposure or infection. Most blisters are filled with a clear fluid, either serum or plasma. However, blisters can be filled with blood (known as "blood blisters") or with pus (for instance, if they become infected). Smaller blisters are called ''blebs''. The word "blister" entered English in the 14th century. It came from the Middle Dutch and was a modification of the Old French , which meant a leprous nodule—a rise in the skin due to leprosy. In dermatology, the words cutaneous condition#Vesicle, ''vesicle'' and ''bulla'' refer to blisters of smaller or greater size, respectively. Some sources recommend not to pop a blister. If popped, bacteria can enter. Excess skin should not necessarily be removed as the top layer protects the soft tissue underneath. However, some sources a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
Wheal Response
A skin condition, also known as cutaneous condition, is any medical condition that affects the integumentary system—the organ system that encloses the body and includes skin, Nail (anatomy), nails, and related muscle and glands. The major function of this system is as a barrier against the external environment. Conditions of the human integumentary system constitute a broad spectrum of diseases, also known as dermatoses, as well as many nonpathologic states (like, in certain circumstances, melanonychia and racquet nails). While only a small number of skin diseases account for most visits to the physician, thousands of skin conditions have been described. Classification of these conditions often presents many nosological challenges, since underlying causes and pathogenetics are often not known. Therefore, most current textbooks present a classification based on location (for example, List of cutaneous conditions#Conditions of the mucous membranes, conditions of the mucous membran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
 |
Bevel
A bevelled edge (UK) or beveled edge (US) is an edge of a structure that is not perpendicular to the faces of the piece. The words bevel and chamfer overlap in usage; in general usage, they are often interchanged, while in technical usage, they may be differentiated as shown in the image on the right. A bevel is typically used to soften the edge of a piece for the sake of safety, wear resistance, aesthetics; or to facilitate engineering fit, mating with another piece. Applications Cutting tools Most cutting tools have a bevelled edge which is apparent when one examines the grind. Bevel angles can be duplicated using a sliding T bevel. Graphic design Typographic bevels are shading and artificial shadows that emulate the appearance of a three-dimensional space, 3-dimensional letter. The bevel is a relatively common effect in graphic editors such as Adobe Photoshop, Photoshop. As such, it is in widespread use in mainstream logos and other design elements. Glass and mirrors Beve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
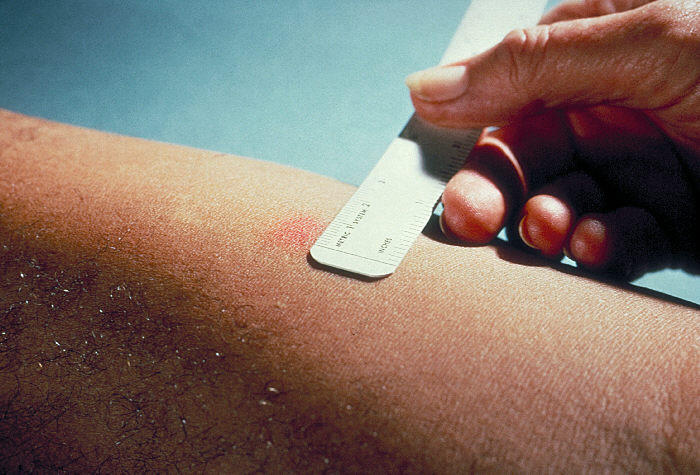 |
Mantoux Test
The Mantoux test or Mendel–Mantoux test (also known as the Mantoux screening test, tuberculin sensitivity test, Pirquet test, or PPD test for purified protein derivative) is a tool for screening (medicine), screening for tuberculosis, tuberculosis (TB) and for tuberculosis diagnosis. It is one of the major tuberculin skin tests used around the world, largely replacing multiple-puncture tests such as the tine test. The Heaf test, a form of tine test, was used until 2005 in the UK, when it was replaced by the Mantoux test. The Mantoux test is endorsed by the American Thoracic Society and Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. It was also used in the Soviet Union, USSR and is now prevalent in most of the post-Soviet states, although Soviet mantoux produced many false positives due to children's allergic reaction. History Tuberculin is a glycerol extract of the tubercle bacillus. Purified protein derivative (PPD) tuberculin is a precipitate of species-nonspecific molecules ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
Mantoux Tuberculin Skin Test
Mantoux may refer to: * Charles Mantoux (1877–1947), French physician * Étienne Mantoux (1913–1945), French economist * Paul Mantoux (1877–1956), French historian * Mantoux test, a method of testing for tuberculosis {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
|
Hypodermic Needle
A hypodermic needle (from Greek Language, Greek ὑπο- (''hypo-'' = under), and δέρμα (''derma'' = skin)) is a very thin, hollow tube with one sharp tip. As one of the most important intravenous inventions in the field of drug administration, it is one of a category of medical tools which enter the skin, called sharps. It is commonly used with a syringe, a hand-operated device with a plunger, to Injection (medicine), inject substances into the body (e.g., saline solution, solutions containing various drugs or liquid medicines) or extract fluids from the body (e.g., blood). Large-bore hypodermic intervention is especially useful in catastrophic blood loss or treating Shock (circulatory), shock. A hypodermic needle is used for rapid delivery of liquids, or when the injected substance cannot be ingested, either because it would not be Absorption (pharmacokinetics), absorbed (as with insulin), or because it would harm the liver. It is also useful to deliver certain medica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |