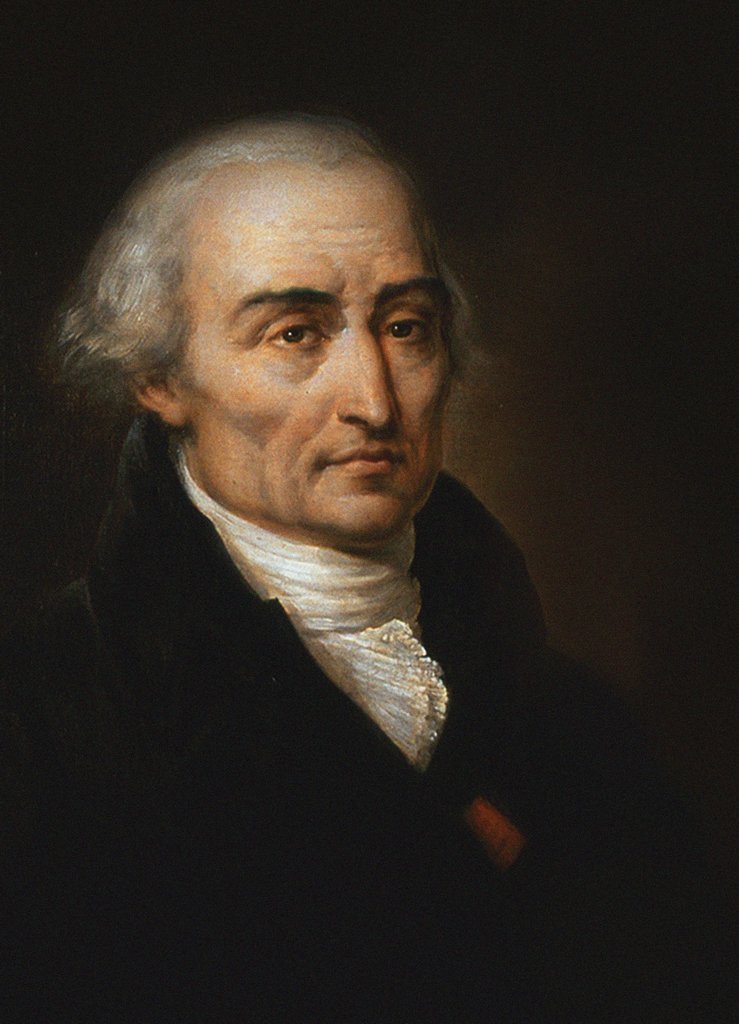|
International Council For Industrial And Applied Mathematics
The International Council for Industrial and Applied Mathematics (ICIAM) is an organisation for professional applied mathematics societies and related organisations. The current president is Wil Schilders. The cash award for each of the prizes is 5000 USD.ICIAM Prizes from the ICIAM web site. History Until 1999 the Council was known as the Committee for International Conferences on Industrial and Applied Mathematics (CICIAM). Formed in 1987 with the start of the ICIAM conference series, this committee represented the leaders of four applied mathematics societies: the (GAMM), in ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Nongovernmental Organization
An international non-governmental organization (INGO) is an organization which is independent of government involvement and extends the concept of a non-governmental organization (NGO) to an international scope. INGOs can admit members affiliated to government authorities as long as it does not interfere with their freedom to express themselves. INGOs operate under the principles of neutrality, humanity, impartiality, and independence. Around the world, there are about 75,000 International organization, international organizations and about 42,000 of them are active. NGOs are independent of governments and can be seen as two types: ''advocacy NGOs'', which aim to influence governments with a specific goal, and ''operational NGOs'', which provide services. Examples of NGO mandates are environmental preservation, human rights defender, human rights promotions or the women's empowerment, advancement of women. NGOs are typically not-for-profit, but receive funding from companies or me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Felix Otto (mathematician)
Felix Otto (born 19 May 1966) is a German mathematician. Biography He studied mathematics at the University of Bonn, finishing his PhD thesis in 1993 under the supervision of Stephan Luckhaus. After postdoctoral studies at the Courant Institute of Mathematical Sciences of New York University and at Carnegie Mellon University, in 1997 he became a professor at the University of California, Santa Barbara. From 1999 to 2010 he was professor for applied mathematics at the University of Bonn, and currently serves as one of the directors of the Max Planck Institute for Mathematics in the Sciences, Leipzig. Work Otto specialises in materials science, including work on the theory of partial differential equations. He is known for his work on the Otto–Villani theorem and the invention of the Otto calculus. Honours In 2006, he received the Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz Prize of the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft, which is the highest honour awarded in German research. In 2009, he was a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alfio Quarteroni
Alfio Quarteroni (born 30 May 1952) is an Italian mathematician. He is Professor Emeritus at the Politecnico of Milan (Italy), and Professor Emeritus at the EPFL (Swiss Federal Institute of Technology). He has been the director of the Chair of Modelling and Scientific Computing at the EPFL (Swiss Federal Institute of Technology), Lausanne (Switzerland), from 1998 until 2017. He is the founder (and first director) of MOX at Politecnico of Milan (2002) anMATHICSEat EPFL, Lausanne (2010). He is co-founder (and President) oMOXOFF a spin-off company at Politecnico of Milan (2010). He is member of the Italian Academy of Science (Accademia Nazionale dei Lincei), the European Academy of Science, the Academia Europaea(Academy of Europe), the Lisbon Academy of Sciences, the Istituto Lombardo Accademia di Scienze e Lettere and the Italian Academy of Engineering and Technology. He is author of 26 books (some of them translated into up to 7 languages), editor of 8 books, author of about ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George C
George may refer to: Names * George (given name) * George (surname) People * George (singer), American-Canadian singer George Nozuka, known by the mononym George * George Papagheorghe, also known as Jorge / GEØRGE * George, stage name of Giorgio Moroder * George, son of Andrew I of Hungary Places South Africa * George, South Africa, a city ** George Airport United States * George, Iowa, a city * George, Missouri, a ghost town * George, Washington, a city * George County, Mississippi * George Air Force Base, a former U.S. Air Force base located in California Computing * George (algebraic compiler) also known as 'Laning and Zierler system', an algebraic compiler by Laning and Zierler in 1952 * GEORGE (computer), early computer built by Argonne National Laboratory in 1957 * GEORGE (operating system), a range of operating systems (George 1–4) for the ICT 1900 range of computers in the 1960s * GEORGE (programming language), an autocode system invented by Charles Leo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andrew Majda
Andrew Joseph Majda (30 January 1949 – 12 March 2021) was an American mathematician and the Morse Professor of Arts and Sciences at the Courant Institute of Mathematical Sciences of New York University. He was known for his theoretical contributions to partial differential equations as well as his applied contributions to diverse areas including shock waves, combustion, incompressible flow, vortex dynamics, and atmospheric sciences. Career Born in East Chicago, Indiana, Majda received a B.S. degree in mathematics from Purdue University in 1970. He then received M.S. and Ph.D. degrees in mathematics from Stanford University in 1971 and 1973, respectively. His Ph.D. thesis advisor was Ralph S. Phillips. He began his scientific career as an instructor at the Courant Institute of Mathematical Sciences from 1973 to 1975. Prior to returning to the Courant Institute in 1994, he held professorships at Princeton University during 1984–1994, the University of California, Berkeley duri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexandre Chorin
Alexandre Joel Chorin (born 25 June 1938) is an American mathematician known for his contributions to computational fluid mechanics, turbulence, and computational statistical mechanics. Chorin's work involves developing methods for solving physics and fluid mechanics problems computationally. His early work introduced several widely used numerical methods for solving the Navier-Stokes equations, including the method of artificial compressibility, the projection method, and vortex methods. He has made numerous contributions to turbulence theory. In recent years he has been developing methods for prediction in the face of uncertainty and for filtering and data assimilation. Early life Chorin was born on 25 June 1938 in Warsaw, Poland. Born just one year before Hitler's invasion, his family fled Poland through Lithuania and Russia before spending 10 years living in Israel and 11 years living in Switzerland Switzerland, officially the Swiss Confederation, is a land ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joseph Keller
Joseph Bishop Keller (July 31, 1923 – September 7, 2016) was an American mathematician who specialized in applied mathematics. He was best known for his work on the "geometrical theory of diffraction" (GTD). Early life and education Born in Paterson, New Jersey on July 31, 1923, Keller attended Eastside High School, where he was a member of the math team. After earning his undergraduate degree in 1943 at New York University, Keller obtained his PhD in 1948 from NYU under the supervision of Richard Courant. He was a professor of mathematics in the Courant Institute at New York University until 1979. Then he was Professor of Mathematics and Mechanical Engineering at Stanford University until 1993, when he became professor emeritus. Research Keller worked on the application of mathematics to problems in science and engineering, such as wave propagation. He contributed to the Einstein–Brillouin–Keller method for computing eigenvalues in quantum mechanical systems. Awar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jacques-Louis Lions
Jacques-Louis Lions (; 2 May 1928 – 17 May 2001) was a French mathematician who made contributions to the theory of partial differential equations and to stochastic control, among other areas. He received the SIAM's John von Neumann Lecture prize in 1986 and numerous other distinctions.Jacques-Louis Lions Casinapioiv.va. Retrieved on 9 May 2016. isces.org Lions is listed as an ISI highly cited researcher. Biography Lions was born in |
Joseph-Louis Lagrange
Joseph-Louis Lagrange (born Giuseppe Luigi LagrangiaJoseph-Louis Lagrange, comte de l’Empire ''Encyclopædia Britannica'' or Giuseppe Ludovico De la Grange Tournier; 25 January 1736 – 10 April 1813), also reported as Giuseppe Luigi Lagrange or Lagrangia, was an Italian and naturalized French mathematician, physicist and astronomer. He made significant contributions to the fields of mathematical analysis, analysis, number theory, and both classical mechanics, classical and celestial mechanics. In 1766, on the recommendation of Leonhard Euler and Jean le Rond d'Alembert, d'Alembert, Lagrange succeeded Euler as the director of mathematics at the Prussian Academy of Sciences in Berlin, Prussia, where he stayed for over twenty y ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maria Colombo (mathematician)
Maria Colombo (born 25 May 1989) is an Italian mathematician specializing in mathematical analysis. She is a professor at the EPFL (École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne) in Switzerland, where she holds the chair for mathematical analysis, calculus of variations and partial differential equations. Education and career Colombo was born in Luino, near the Swiss border of Italy. She competed for Italy in the 2005, 2006, and 2007 International Mathematical Olympiads, earning bronze, gold, and silver medals respectively. She earned bachelor's and master's degrees in mathematics at the University of Pisa in 2010 and 2011, and completed a Ph.D. in 2015 at the Scuola Normale Superiore di Pisa, under the joint supervision of Luigi Ambrosio and Alessio Figalli. Her dissertation, ''Flows of non-smooth vector fields and degenerate elliptic equations: With applications to the Vlasov-Poisson and semigeostrophic systems'', was published as a book in 2017 by Edizioni della Normale. Af ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |