|
Interagency Advisory Panel On Responsible Conduct Of Research
The Interagency Advisory Panel on Responsible Conduct of Research (PRCR) is a creation of the three research funding agencies of the Government of Canada The Government of Canada (), formally His Majesty's Government (), is the body responsible for the federation, federal administration of Canada. The term ''Government of Canada'' refers specifically to the executive, which includes Minister of t ...: CIHR, NSERC and SSHRC. The PRCR publishes the ''Tri-Agency Framework: Responsible Conduct of Research'' ("The Framework"). The PRCR collaborative objective is "to ensure a coherent and uniform approach for promoting responsible conduct of research and for addressing allegations of breaches of Tri-Agency Policies". RCR Framework The Framework document "describes policies and requirements related to applying for and managing Agency funds, performing research, and disseminating results, and the processes that institutions and agencies follow in the event of an allegation of a breac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Government Of Canada
The Government of Canada (), formally His Majesty's Government (), is the body responsible for the federation, federal administration of Canada. The term ''Government of Canada'' refers specifically to the executive, which includes Minister of the Crown, ministers of the Crown (together in Cabinet of Canada, the Cabinet) and the Public Service of Canada, federal civil service (whom the Cabinet direct); it is Federal Identity Program, corporately branded as the ''Government of Canada''. There are over 100 departments and agencies, as well as over 300,000 persons employed in the Government of Canada. These institutions carry out the programs and enforce the laws established by the Parliament of Canada. The Structure of the Canadian federal government, federal government's organization and structure was established at Canadian Confederation, Confederation, through the ''Constitution Act, 1867'', wherein the Canadian Crown acts as the core, or "the most basic building block", of its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CIHR
The Canadian Institutes of Health Research (CIHR; ; IRSC) is a federal agency responsible for funding health and medical research in Canada. Comprising 13 institutes, it is the successor to the Medical Research Council of Canada. CIHR supports more than 15,000 researchers and trainees through grants, fellowships, scholarships, and other funding, as part of the federal government's investment in health research. The peer review process is a vital part of CIHR. Review by panels of peers from the research community ensures that proposals approved for funding by CIHR meet internationally accepted standards of scientific excellence. Along with the Social Sciences and Humanities Research Council, and the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council, the CIHR forms the major source of federal government funding to post-secondary research and are collectively referred to as the "Tri-Council" or "Tri-Agency". History The Canadian Institutes of Health Research (CIHR) is the major ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NSERC
The Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada (NSERC; , CRSNG) is the major federal agency responsible for funding natural sciences and engineering research in Canada. NSERC directly funds university professors and students as well as Canadian companies to perform research and training. With funding from the Government of Canada, NSERC supports the research of over 41,000 students, trainees and professors at universities and colleges in Canada with an annual budget of CA$1.1 billion in 2015. Its current director is Alejandro Adem. NSERC, combined with the Social Sciences and Humanities Research Council (SSHRC) and the Canadian Institutes of Health Research (CIHR), forms the major source of federal government funding to post-secondary research. These bodies are sometimes collectively referred to as the "Tri-Council" or "Tri-Agency". History NSERC came into existence on 1 May 1978 under the ''Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council Act'', which was pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SSHRC
The Social Sciences and Humanities Research Council of Canada (SSHRC; , CRSH), often colloquially pronounced 'shirk' (), is a Canadian federal research-funding agency that promotes and supports post-secondary research and training in the humanities and social sciences. It is one of three major federal granting agencies (the others being the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council and Canadian Institutes for Health Research) that together are referred to as the "Tri-Council" or "Tri-Agency. History Created by an act of the Parliament of Canada in 1977, SSHRC reports to Parliament through the Minister of Innovation, Science, and Economic Development. SSHRC came into existence on 1 May 1978 under the ''Social Sciences and Humanities Research Council Act'' which was passed in an omnibus manner by the government of Pierre Elliot Trudeau. Governance SSHRC creates policy, plans budgets, and directs priorities through a council established by the federal government. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethics Organizations
Ethics is the philosophical study of moral phenomena. Also called moral philosophy, it investigates normative questions about what people ought to do or which behavior is morally right. Its main branches include normative ethics, applied ethics, and metaethics. Normative ethics aims to find general principles that govern how people should act. Applied ethics examines concrete ethical problems in real-life situations, such as abortion, treatment of animals, and business practices. Metaethics explores the underlying assumptions and concepts of ethics. It asks whether there are objective moral facts, how moral knowledge is possible, and how moral judgments motivate people. Influential normative theories are consequentialism, deontology, and virtue ethics. According to consequentialists, an act is right if it leads to the best consequences. Deontologists focus on acts themselves, saying that they must adhere to duties, like telling the truth and keeping promises. Virtue ethics se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Health Canada
Health Canada (HC; )Health Canada is the applied title under the Federal Identity Program; the legal title is Department of Health (). is the Structure of the Canadian federal government#Departments, with subsidiary units, department of the Government of Canada responsible for national health policy. The department itself is also responsible for numerous federal health-related agencies, including the Canadian Food Inspection Agency (CFIA) and the Public Health Agency of Canada (PHAC), among others. These organizations help to ensure compliance with federal law in a variety of Healthcare in Canada, healthcare, Agriculture in Canada, agricultural, and Pharmaceutics, pharmaceutical activities. This responsibility also involves extensive collaboration with various other federal- and provincial-level organizations in order to ensure the safety of food, health, and Medication, pharmaceutical products—including the regulation of health research and pharmaceutical manufacturing/Clinical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Federal Departments And Agencies Of Canada
Federal or foederal (archaic) may refer to: Politics General *Federal monarchy, a federation of monarchies *Federation, or ''Federal state'' (federal system), a type of government characterized by both a central (federal) government and states or regional governments that are partially self-governing; a union of states *Federal republic, a federation which is a republic *Federalism, a political philosophy *Federalist, a political belief or member of a political grouping * Federalization, implementation of federalism Particular governments *Government of Argentina *Government of Australia *Federal government of Brazil *Government of Canada *Cabinet of Germany *Federal government of Iraq *Government of India *Federal government of Mexico *Federal government of Nigeria *Government of Pakistan *Government of the Philippines *Government of Russia *Government of South Africa *Federal government of the United States **United States federal law **United States federal courts *Federal gove ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Funding Bodies Of Canada
Funding is the act of providing resources to finance a need, program, or project. While this is usually in the form of money, it can also take the form of effort or time from an organization or company. Generally, this word is used when a firm uses its internal reserves to satisfy its necessity for cash, while the term financing is used when the firm acquires capital from external sources. Sources of funding include Credit (finance), credit, venture capital, donations, Grant (money), grants, savings, Subsidy, subsidies, and taxes. Funding methods such as donations, subsidies, and grants that have no direct requirement for return of investment are described as "soft funding" or "crowdfunding". Funding that facilitates the exchange of equity ownership in a company for capital investment via an online funding portal per the Jumpstart Our Business Startups Act (alternately, the "JOBS Act of 2012") (U.S.) is known as equity crowdfunding. Funds can be Asset allocation, allocated for eit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scientific Organizations Based In Canada
Science is a systematic discipline that builds and organises knowledge in the form of testable hypotheses and predictions about the universe. Modern science is typically divided into twoor threemajor branches: the natural sciences, which study the physical world, and the social sciences, which study individuals and societies. While referred to as the formal sciences, the study of logic, mathematics, and theoretical computer science are typically regarded as separate because they rely on deductive reasoning instead of the scientific method as their main methodology. Meanwhile, applied sciences are disciplines that use scientific knowledge for practical purposes, such as engineering and medicine. The history of science spans the majority of the historical record, with the earliest identifiable predecessors to modern science dating to the Bronze Age in Egypt and Mesopotamia (). Their contributions to mathematics, astronomy, and medicine entered and shaped the Greek natural philo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
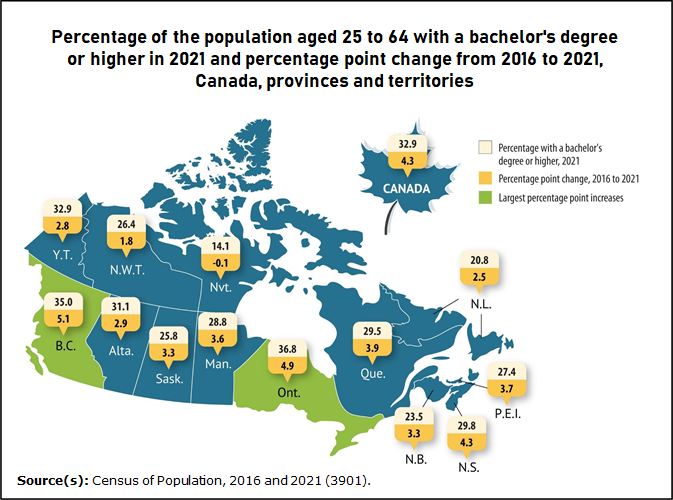
Higher Education In Canada
Higher education in Canada includes provincial, territorial, Indigenous and military higher education systems. The ideal objective of Canadian higher education is to offer every Canadian the opportunity to acquire the skills and knowledge necessary to realize their utmost potential. It aspires to cultivate a world-class workforce, enhance the employment rate of Canadians, and safeguard Canada's enduring prosperity. Higher education programs are intricately designed with the perspective of the learner in focus, striving to mitigate risks and assure definite outcomes. According to a 2022 report by the OECD, Canada is one of the most educated countries in the world; the country ranks first worldwide in the percentage of adults having tertiary education, with over 56 percent of Canadian adults having attained at least an undergraduate college or university degree. Higher education systems in Canada In Canada, the constitutional responsibility for higher education primarily rests wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Education Finance In Canada
Education is the transmission of knowledge and skills and the development of character traits. Formal education occurs within a structured institutional framework, such as public schools, following a curriculum. Non-formal education also follows a structured approach but occurs outside the formal schooling system, while informal education involves unstructured learning through daily experiences. Formal and non-formal education are categorized into levels, including early childhood education, primary education, secondary education, and tertiary education. Other classifications focus on teaching methods, such as teacher-centered and student-centered education, and on subjects, such as science education, language education, and physical education. Additionally, the term "education" can denote the mental states and qualities of educated individuals and the academic field studying educational phenomena. The precise definition of education is disputed, and there are disagreements ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Innovation, Science And Economic Development Canada
Innovation, Science and Economic Development Canada (ISED; ; )''Innovation, Science and Economic Development Canada'' is the applied title under the Federal Identity Program; the legal title is Department of Industry (). is a Ministry (government department), department of the Government of Canada. ISED is responsible for a number of the federal government's functions in regulating Industry (economics), industry and commerce, promoting science and innovation, and supporting economic development. The department was known as Industry Canada (IC) prior to 2015. The department is led by the Minister of Innovation, Science and Industry, Minister of Industry (currently Mélanie Joly), who also serves as the Minister responsible for Canada Economic Development for Quebec Regions. Several other ministerial portfolios are associated with the department. While the minister is head of the department, and provides policy/political direction, the day-to-day operations of the department are mana ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |