|
Infraclavicular Fossa
The Infraclavicular fossa is an indentation, or fossa, immediately below the clavicle, above the third rib and between the deltoid muscle laterally and medioclavicular line medially. See also * Supraclavicular fossa The supraclavicular fossa is an indentation (fossa) immediately above the clavicle. In terminologia anatomica, it is divided into ''fossa supraclavicularis major'' and ''fossa supraclavicularis minor'' Fullness in the supraclavicular fossa can b ... References Thorax (human anatomy) {{anatomy-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
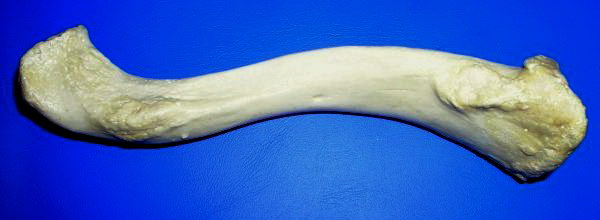
Clavicle
The clavicle, collarbone, or keybone is a slender, S-shaped long bone approximately long that serves as a strut between the scapula, shoulder blade and the sternum (breastbone). There are two clavicles, one on each side of the body. The clavicle is the only long bone in the body that lies horizontally. Together with the shoulder blade, it makes up the shoulder girdle. It is a palpable bone and, in people who have less fat in this region, the location of the bone is clearly visible. It receives its name from Latin ''clavicula'' 'little key' because the bone rotates along its axis like a key when the shoulder is Abduction (kinesiology), abducted. The clavicle is the most commonly fractured bone. It can easily be fractured by impacts to the shoulder from the force of falling on outstretched arms or by a direct hit. Structure The collarbone is a thin doubly curved long bone that connects the human arm, arm to the torso, trunk of the body. Located directly above the first rib, it ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deltoid Muscle
The deltoid muscle is the muscle forming the rounded contour of the shoulder, human shoulder. It is also known as the 'common shoulder muscle', particularly in other animals such as the domestic cat. Anatomically, the deltoid muscle is made up of three distinct sets of muscle fibers, namely the # anterior or clavicular part (pars clavicularis) ( More commonly known as the front delt.) # posterior or scapular part (pars scapularis) ( More commonly known as the rear delt.) # intermediate or acromial part (pars acromialis) ( More commonly known as the side delt) The deltoid's fibres are pennate muscle. However, electromyography suggests that it consists of at least seven groups that can be independently coordinated by the nervous system. It was previously called the deltoideus (plural ''deltoidei'') and the name is still used by some anatomists. It is called so because it is in the shape of the Greek alphabet, Greek capital letter Delta (letter), delta (Δ). Deltoid is also further ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supraclavicular Fossa
The supraclavicular fossa is an indentation (fossa) immediately above the clavicle. In terminologia anatomica, it is divided into ''fossa supraclavicularis major'' and ''fossa supraclavicularis minor'' Fullness in the supraclavicular fossa can be a sign of upper extremity deep venous thrombosis. Additional images File:Slide1EEEE.JPG, Dissection of the supraclavicular fossa File:Supraclavicular fossa on chest X-ray.jpg, The margins of the supraclavicular fossa are often visible on chest X-ray A chest radiograph, chest X-ray (CXR), or chest film is a Projectional radiography, projection radiograph of the chest used to diagnose conditions affecting the chest, its contents, and nearby structures. Chest radiographs are the most common fi ... References External links Diagram at droid.cuhk.edu.hk Human head and neck Triangles of the neck {{Anatomy-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |