|
Influence Diagrams
An influence diagram (ID) (also called a relevance diagram, decision diagram or a decision network) is a compact graphical and mathematical representation of a decision situation. It is a generalization of a Bayesian network, in which not only probabilistic inference problems but also decision making problems (following the maximum expected utility criterion) can be modeled and solved. ID was first developed in the mid-1970s by decision analysts with an intuitive semantic that is easy to understand. It is now adopted widely and becoming an alternative to the decision tree which typically suffers from exponential growth in number of branches with each variable modeled. ID is directly applicable in team decision analysis, since it allows incomplete sharing of information among team members to be modeled and solved explicitly. Extensions of ID also find their use in game theory as an alternative representation of the game tree. Semantics An ID is a directed acyclic graph with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bayesian Network
A Bayesian network (also known as a Bayes network, Bayes net, belief network, or decision network) is a probabilistic graphical model that represents a set of variables and their conditional dependencies via a directed acyclic graph (DAG). While it is one of several forms of causal notation, causal networks are special cases of Bayesian networks. Bayesian networks are ideal for taking an event that occurred and predicting the likelihood that any one of several possible known causes was the contributing factor. For example, a Bayesian network could represent the probabilistic relationships between diseases and symptoms. Given symptoms, the network can be used to compute the probabilities of the presence of various diseases. Efficient algorithms can perform inference and learning in Bayesian networks. Bayesian networks that model sequences of variables (''e.g.'' speech signals or protein sequences) are called dynamic Bayesian networks. Generalizations of Bayesian networks tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Simple Influence Diagram
Simple or SIMPLE may refer to: *Simplicity, the state or quality of being simple Arts and entertainment * ''Simple'' (album), by Andy Yorke, 2008, and its title track * "Simple" (Florida Georgia Line song), 2018 * "Simple", a song by Johnny Mathis from the 1984 album ''A Special Part of Me'' * "Simple", a song by Collective Soul from the 1995 album ''Collective Soul'' * "Simple", a song by Katy Perry from the 2005 soundtrack to ''The Sisterhood of the Traveling Pants'' * "Simple", a song by Khalil from the 2017 album ''Prove It All'' * "Simple", a song by Kreesha Turner from the 2008 album '' Passion'' * "Simple", a song by Ty Dolla Sign from the 2017 album ''Beach House 3'' deluxe version * ''Simple'' (video game series), budget-priced console games Businesses and organisations * Simple (bank), an American direct bank * SIMPLE Group, a consulting conglomeration based in Gibraltar * Simple Shoes, an American footwear brand * Simple Skincare, a British brand of soap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
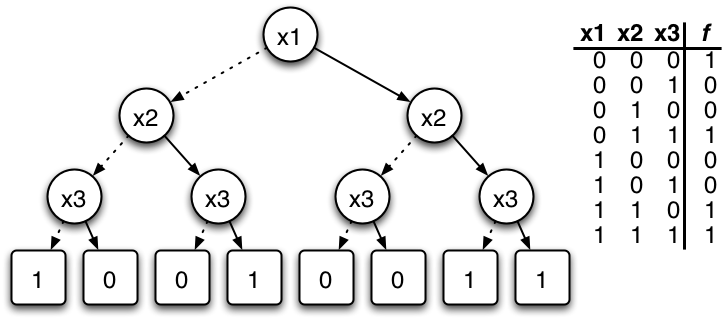
Decision Tree
A decision tree is a decision support system, decision support recursive partitioning structure that uses a Tree (graph theory), tree-like Causal model, model of decisions and their possible consequences, including probability, chance event outcomes, resource costs, and utility. It is one way to display an algorithm that only contains conditional control statements. Decision trees are commonly used in operations research, specifically in decision analysis, to help identify a strategy most likely to reach a goal, but are also a popular tool in Decision tree learning, machine learning. Overview A decision tree is a flowchart-like structure in which each internal node represents a test on an attribute (e.g. whether a coin flip comes up heads or tails), each branch represents the outcome of the test, and each leaf node represents a class label (decision taken after computing all attributes). The paths from root to leaf represent classification rules. In decision analysis, a de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Decision Making Software
Decision-making software (DM software) is software for computer applications that help individuals and organisations make choices and take decisions, typically by ranking, prioritizing or choosing from a number of options. An early example of DM software was described in 1973.Dyer, JS (1973), "A time-sharing computer program for the solution of the multiple criteria problem", ''Management Science'', 19: 1379-83.Wallenius, J, Dyer, JS, Fishburn, PC, Steuer, RE, Zionts, S and Deb, K (1992), "Multiple criteria decision making, multiattribute utility theory: The next ten years", ''Management Science'', 38: 645-54. Before the advent of the World Wide Web, most DM software was spreadsheet-based, with the first web-based DM software appearing in the mid-1990s.Koksalan, M, Wallenius, J, and Zionts, S, ''Multiple Criteria Decision Making: From Early History to the 21st Century'', World Scientific Publishing: Singapore, 2011. Nowadays, many DM software products (mostly web-based) are availabl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Binary Decision Diagram
In computer science, a binary decision diagram (BDD) or branching program is a data structure that is used to represent a Boolean function. On a more abstract level, BDDs can be considered as a compressed representation of sets or relations. Unlike other compressed representations, operations are performed directly on the compressed representation, i.e. without decompression. Similar data structures include negation normal form (NNF), Zhegalkin polynomials, and propositional directed acyclic graphs (PDAG). Definition A Boolean function can be represented as a rooted, directed, acyclic graph, which consists of several (decision) nodes and two terminal nodes. The two terminal nodes are labeled 0 (FALSE) and 1 (TRUE). Each (decision) node u is labeled by a Boolean variable x_i and has two child nodes called low child and high child. The edge from node u to a low (or high) child represents an assignment of the value FALSE (or TRUE, respectively) to variable x_i. Such a BDD i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Symmetric
Symmetry () in everyday life refers to a sense of harmonious and beautiful proportion and balance. In mathematics, the term has a more precise definition and is usually used to refer to an object that is invariant under some transformations, such as translation, reflection, rotation, or scaling. Although these two meanings of the word can sometimes be told apart, they are intricately related, and hence are discussed together in this article. Mathematical symmetry may be observed with respect to the passage of time; as a spatial relationship; through geometric transformations; through other kinds of functional transformations; and as an aspect of abstract objects, including theoretic models, language, and music. This article describes symmetry from three perspectives: in mathematics, including geometry, the most familiar type of symmetry for many people; in science and nature; and in the arts, covering architecture, art, and music. The opposite of symmetry is asymmetr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Relevance
Relevance is the connection between topics that makes one useful for dealing with the other. Relevance is studied in many different fields, including cognitive science, logic, and library and information science. Epistemology studies it in general, and different theories of knowledge have different implications for what is considered relevant. Definition "Something (''A'') is relevant to a task (''T'') if it increases the likelihood of accomplishing the goal (''G''), which is implied by ''T''." A thing might be relevant, a document or a piece of information may be relevant. Relevance does not depend on whether we speak of "things" or "information". Epistemology If you believe that schizophrenia is caused by bad communication between mother and child, then family interaction studies become relevant. If, on the other hand, you subscribe to a genetic theory of relevance then the study of genes becomes relevant. If you subscribe to the epistemology of empiricism, then only inte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Belief Propagation
Belief propagation, also known as sum–product message passing, is a message-passing algorithm for performing inference on graphical models, such as Bayesian networks and Markov random fields. It calculates the marginal distribution for each unobserved node (or variable), conditional on any observed nodes (or variables). Belief propagation is commonly used in artificial intelligence and information theory, and has demonstrated empirical success in numerous applications, including low-density parity-check codes, turbo codes, free energy approximation, and satisfiability. The algorithm was first proposed by Judea Pearl in 1982, who formulated it as an exact inference algorithm on trees, later extended to polytrees. While the algorithm is not exact on general graphs, it has been shown to be a useful approximate algorithm. Motivation Given a finite set of discrete random variables X_1, \ldots, X_n with joint probability mass function p, a common task is to compute ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bayesian Inference
Bayesian inference ( or ) is a method of statistical inference in which Bayes' theorem is used to calculate a probability of a hypothesis, given prior evidence, and update it as more information becomes available. Fundamentally, Bayesian inference uses a prior distribution to estimate posterior probabilities. Bayesian inference is an important technique in statistics, and especially in mathematical statistics. Bayesian updating is particularly important in the dynamic analysis of a sequence of data. Bayesian inference has found application in a wide range of activities, including science, engineering, philosophy, medicine, sport, and law. In the philosophy of decision theory, Bayesian inference is closely related to subjective probability, often called "Bayesian probability". Introduction to Bayes' rule Formal explanation Bayesian inference derives the posterior probability as a consequence of two antecedents: a prior probability and a "likelihood function" derive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artificial Intelligence
Artificial intelligence (AI) is the capability of computer, computational systems to perform tasks typically associated with human intelligence, such as learning, reasoning, problem-solving, perception, and decision-making. It is a field of research in computer science that develops and studies methods and software that enable machines to machine perception, perceive their environment and use machine learning, learning and intelligence to take actions that maximize their chances of achieving defined goals. High-profile applications of AI include advanced web search engines (e.g., Google Search); recommendation systems (used by YouTube, Amazon (company), Amazon, and Netflix); virtual assistants (e.g., Google Assistant, Siri, and Amazon Alexa, Alexa); autonomous vehicles (e.g., Waymo); Generative artificial intelligence, generative and Computational creativity, creative tools (e.g., ChatGPT and AI art); and Superintelligence, superhuman play and analysis in strategy games (e.g., ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Node Removal
In general, a node is a localized swelling (a "knot") or a point of intersection (a vertex). Node may refer to: In mathematics *Vertex (graph theory), a vertex in a mathematical graph *Vertex (geometry), a point where two or more curves, lines, or edges meet. * Node (autonomous system), behaviour for an ordinary differential equation near a critical point *Singular point of an algebraic variety, a type of singular point of a curve In science and engineering Spherical geometry * node, the points where a great circle crosses a plane of reference, or the equator of a sphere Astronomy *Orbital node, the points where an orbit crosses a plane of reference ** Lunar node, where the orbits of the Sun and Moon intersect ** Longitude of the ascending node, how orbital nodes are parameterized Biology *Lymph node, an immune system organ used to store white blood cells *Node of Ranvier, periodic gaps in the insulating myelin sheaths of myelinated axons *Sinoatrial node and atrioventricula ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |