|
Indus Script
The Indus script, also known as the Harappan script and the Indus Valley script, is a corpus of symbols produced by the Indus Valley Civilisation. Most inscriptions containing these symbols are extremely short, making it difficult to judge whether or not they constituted a writing system used to record a Harappan language, any of which are yet to be identified. Despite many attempts, the "script" has not yet been deciphered. There is no known bilingual inscription to help decipher the script, which shows no significant changes over time. However, some of the syntax (if that is what it may be termed) varies depending upon location. The first publication of a seal with Harappan symbols dates to 1875, in a drawing by Alexander Cunningham. By 1992, an estimated 4,000 inscribed objects had been discovered, some as far afield as Mesopotamia due to existing Indus–Mesopotamia relations, with over 400 distinct signs represented across known inscriptions. Some scholars, such as G.&nbs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bronze Age Writing
The history of writing traces the development of writing systems and how their use transformed and was transformed by different societies. The use of writing prefigures various social and psychological consequences associated with literacy and literary culture. Each historical invention of writing emerged from systems of proto-writing that used ideographic and mnemonic symbols but were not capable of fully recording spoken language. True writing, where the content of linguistic utterances can be accurately reconstructed by later readers, is a later development. As proto-writing is not capable of fully reflecting the grammar and lexicon used in languages, it is often only capable of encoding broad or imprecise information. Early uses of writing included documenting agricultural transactions and contracts, but it was soon used in the areas of finance, religion, government, and law. Writing allowed the spread of these social modalities and their associated knowledge, and ultima ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Papyrus
Papyrus ( ) is a material similar to thick paper that was used in ancient times as a writing surface. It was made from the pith of the papyrus plant, ''Cyperus papyrus'', a wetland sedge. ''Papyrus'' (plural: ''papyri'' or ''papyruses'') can also refer to a document written on sheets of such material, joined side by side and rolled up into a scroll, an early form of a book. Papyrus was first known to have been used in Egypt (at least as far back as the First Dynasty of Egypt, First Dynasty), as the papyrus plant was once abundant across the Nile Delta. It was also used History of the Mediterranean, throughout the Mediterranean region. Apart from writing material, ancient Egyptians employed papyrus in the construction of other Artifact (archaeology), artifacts, such as reed boats, mats, rope, sandals, and baskets. History Papyrus was first manufactured in Egypt as far back as the third millennium BCE.H. Idris Bell and T.C. Skeat, 1935"Papyrus and its uses"(British Museum pam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Textual Corpus
In linguistics and natural language processing, a corpus (: corpora) or text corpus is a dataset, consisting of natively digital and older, digitalized, language resources, either annotated or unannotated. Annotated, they have been used in corpus linguistics for statistical hypothesis testing, checking occurrences or validating linguistic rules within a specific language territory. Overview A corpus may contain texts in a single language (''monolingual corpus'') or text data in multiple languages (''multilingual corpus''). In order to make the corpora more useful for doing linguistic research, they are often subjected to a process known as annotation. An example of annotating a corpus is part-of-speech tagging, or ''POS-tagging'', in which information about each word's part of speech (verb, noun, adjective, etc.) is added to the corpus in the form of ''tags''. Another example is indicating the lemma (base) form of each word. When the language of the corpus is not a working ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian Copper Plate Inscriptions
Indian copper plate inscriptions are legal records engraved on copper plates. The practice was widespread and long-running in the Indian subcontinent; it may date back to as early as the 3rd millennium BCE, however the vast majority of recovered plates were produced in the 1st millennium CE. The plates were legal documents which registered and recorded an act of endowment, i.e. a grant or donation, typically of land or concessions. The plate contained bureaucratic information on land tenure and taxation essential to the operation of the state. The copper plates can survive intact indefinitely: copper, being a non-ferrous metal, does not rust or otherwise deteriorate when exposed to oxygen the way iron does, but rather develops a protective patina. Historical significance As primary historical documents and archaeological artifacts, the copper plates are invaluable tools for scholarly research in the general history and society of the Indian subcontinent in the 1st mil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stamp Seal
__NOTOC__ The stamp seal (also impression seal) is a common seal die, frequently carved from stone, known at least since the 6th millennium BC (Halaf culture) and probably earlier. The dies were used to impress their picture or inscription into soft, prepared clay and sometimes in sealing wax. The oldest stamp seals were button-shaped objects with primitive ornamental forms chiseled onto them. The stamp seals were replaced in the 4th millennium BC by cylinder seals that had to be rolled over the soft clay to leave an imprint. From the 12th century BC the previous designs were largely abandoned in favor of amphora stamps. Romans introduced their '' signaculum'' around the first century BC; Byzantine maintained the tradition in their commercial stamps. In antiquity the stamp seals were common, largely because they served to authenticate legal documents, such as tax receipts, contracts, wills and decrees. Indus stamp-seal The Indus stamp-seals probably had a different func ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stamp Seal And Modern Impression- Unicorn And Incense Burner (?) MET DP23101 (cropped)
Stamp or Stamps or Stamping may refer to: Official documents and related impressions * Postage stamp, used to indicate prepayment of fees for public mail * Ration stamp, indicating the right to rationed goods * Revenue stamp, used on documents to indicate payment of tax * Rubber stamp, device used to apply inked markings to objects ** Passport stamp, a rubber stamp inked impression received in one's passport upon entering or exiting a country ** National Park Passport Stamps * Food stamps, tickets used in the United States that indicate the right to benefits in the Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program Collectibles * Trading stamp, a small paper stamp given to customers by merchants in loyalty programs that predate the modern loyalty card * Eki stamp, a free collectible rubber ink stamp found at many train stations in Japan Places * Stamp Creek, a stream in Georgia * Stamps, Arkansas People * Stamp Brooksbank, English MP * Stamp Fairtex, mixed martial artist * Sta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indus Script
The Indus script, also known as the Harappan script and the Indus Valley script, is a corpus of symbols produced by the Indus Valley Civilisation. Most inscriptions containing these symbols are extremely short, making it difficult to judge whether or not they constituted a writing system used to record a Harappan language, any of which are yet to be identified. Despite many attempts, the "script" has not yet been deciphered. There is no known bilingual inscription to help decipher the script, which shows no significant changes over time. However, some of the syntax (if that is what it may be termed) varies depending upon location. The first publication of a seal with Harappan symbols dates to 1875, in a drawing by Alexander Cunningham. By 1992, an estimated 4,000 inscribed objects had been discovered, some as far afield as Mesopotamia due to existing Indus–Mesopotamia relations, with over 400 distinct signs represented across known inscriptions. Some scholars, such as G.& ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Copper Plates With Indus Script
Copper is a chemical element; it has Chemical symbol, symbol Cu (from Latin ) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductility, ductile metal with very high thermal conductivity, thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a Copper (color), pinkish-orange color. Copper is used as a conductor of heat and electricity, as a building material#Metal, building material, and as a constituent of various metal alloys, such as sterling silver used in jewelry, cupronickel used to make marine hardware and coins, and constantan used in strain gauges and thermocouples for temperature measurement. Copper is one of the few metals that can occur in nature in a directly usable, unalloyed metallic form. This means that copper is a native metal. This led to very early human use in several regions, from . Thousands of years later, it was the first metal to be Smelting, smelted from sulfide ores, ; the first metal to be cast into a shape in a mold, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
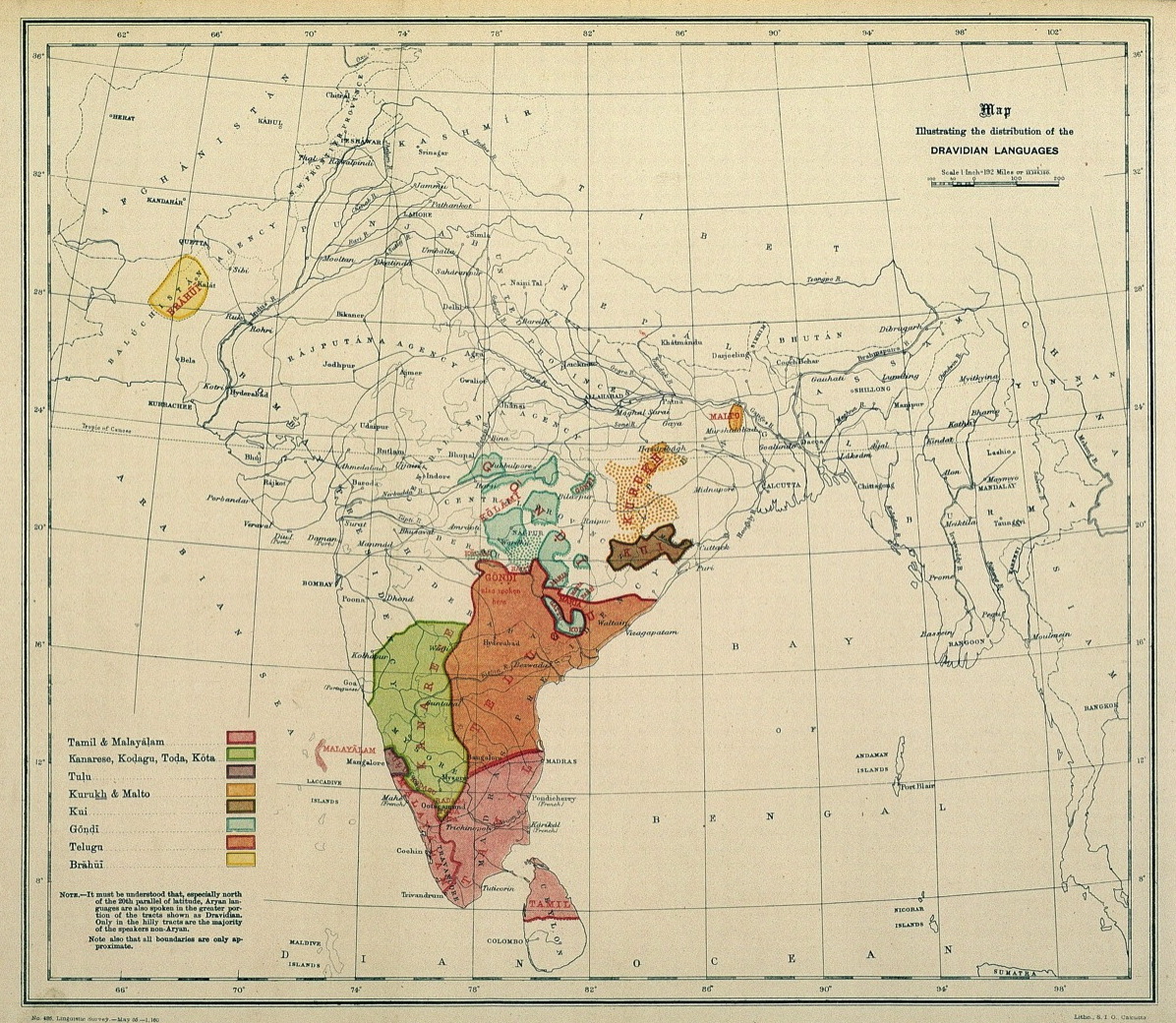
Dravidian Languages
The Dravidian languages are a language family, family of languages spoken by 250 million people, primarily in South India, north-east Sri Lanka, and south-west Pakistan, with pockets elsewhere in South Asia. The most commonly spoken Dravidian languages are (in descending order) Telugu language, Telugu, Tamil language, Tamil, Kannada, and Malayalam, all of which Classical languages of India, have long literary traditions. Smaller literary languages are Tulu language, Tulu and Kodava language, Kodava. Together with several smaller languages such as Gondi language, Gondi, these languages cover the southern part of India and the northeast of Sri Lanka, and account for the overwhelming majority of speakers of Dravidian languages. Malto language, Malto and Kurukh language, Kurukh are spoken in isolated pockets in eastern India. Kurukh is also spoken in parts of Nepal, Bhutan and Bangladesh. Brahui language, Brahui is mostly spoken in the Balochistan region of Pakistan, Sistan and Baluc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asko Parpola
Asko Heikki Siegfried Parpola (born 12 July 1941, in Forssa) is a Finnish Indologist, current professor emeritus of Indology at the University of Helsinki. He specializes in the Indus Valley Civilization, specifically the study of the Indus script. Biography Parpola is a brother of the Akkadian language epigrapher Simo Parpola. He is married to Marjatta Parpola, who has authored a study on the traditions of Kerala's Nambudiri Brahmins. Scholarship Parpola's research and teaching interests fall within the following topics: * Indus Civilization / Indus script and religion / Corpus of Indus Seals and Inscriptions * Veda / Vedic ritual / Samaveda / Jaiminiya Samaveda texts and rituals / Purva-Mimamsa * South Asian religions / Hinduism / Saiva and Sakta tradition / Goddess Durga * South India / Kerala / Tamil Nadu / Karnataka * Sanskrit / Malayalam / Kannada / Tamil / Prehistory of Indian languages * Prehistoric archaeology of South Asia and (in broad sense) Central Asia / Co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |