|
Ilokano Particles
Ilocano particles are an aspect of Ilocano grammar. Particles lack a meaning independent of a phrase or clause. For the most part, they impart meaning to the phrase or clause in which they occur. Ilocano has two morphological types: enclitic and independent. Enclitic Enclitic particles are very similar to the enclitic pronouns, in that they are tightly ''bound'' to the previous word with which they have a close relation. And, similar to the pronouns, their form depends on the last sound of the preceding word. These particles occur primarily with the ''Predicate'' of the sentence or clause. -(e)n The punctual particle lends the meaning of ''completion'' and ''punctuality'' or ''amazement''. The speaker asserts that the idea expressed in the predicate is completed, or to emphasize that it is currently underway. Or, it can express an intense emotion. * Forms: ** -en - After consonants and diphthongs ** -n - After simple vowels * With Verb Predicates The particle lends the meanin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
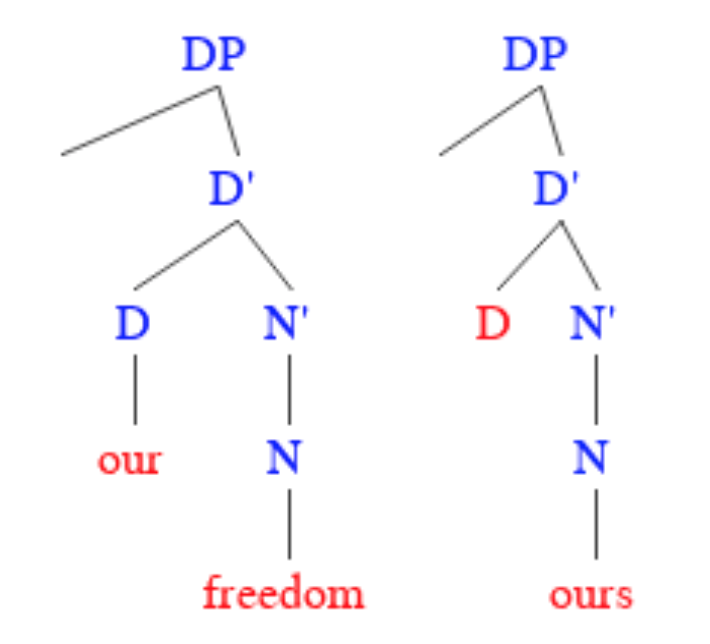
Ilocano Grammar
Ilocano grammar is the study of the morphological and syntactic structures of the Ilocano language, a language spoken in the northern Philippines by ethnic Ilocanos and Ilocano communities in other parts of the Philippines, especially in Mindanao and overseas such as the United States, Canada Australia, the Middle East and other parts of the world. Ilocano is an agglutinative language. This agglutinating characteristic is most apparent in its verbal morphology, which has a Philippine-type voice system. Determiners Ilocano has two subsets of determiners. Articles are similar to "the" and "a" or "an" in English. Demonstratives point out something ("this" or "that"), whether what is being referred to is in space, in time or is something previously mentioned. Ilocano determiners have only two forms (core and oblique) — unlike Ilocano pronouns, which have three distinct forms: absolutive, ergative and oblique. The core form may function for either the absolutive or ergative cases ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grammatical Particle
In grammar, the term ''particle'' ( abbreviated ) has a traditional meaning, as a part of speech that cannot be inflected, and a modern meaning, as a function word (functor) associated with another word or phrase in order to impart meaning. Although a particle may have an intrinsic meaning and may fit into other grammatical categories, the fundamental idea of the particle is to add context to the sentence, expressing a mood or indicating a specific action. In English, for example, the phrase "oh well" has no purpose in speech other than to convey a mood. The word "up" would be a particle in the phrase "look up" (as in "look up this topic"), implying that one researches something rather than that one literally gazes skywards. Many languages use particles in varying amounts and for varying reasons. In Hindi, they may be used as honorifics, or to indicate emphasis or negation. In some languages, they are clearly defined; for example, in Chinese, there are three types of (; ): ''str ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pronouns
In linguistics and grammar, a pronoun ( glossed ) is a word or a group of words that one may substitute for a noun or noun phrase. Pronouns have traditionally been regarded as one of the parts of speech, but some modern theorists would not consider them to form a single class, in view of the variety of functions they perform cross-linguistically. An example of a pronoun is "you", which can be either singular or plural. Sub-types include personal and possessive pronouns, reflexive and reciprocal pronouns, demonstrative pronouns, relative and interrogative pronouns, and indefinite pronouns. The use of pronouns often involves anaphora, where the meaning of the pronoun is dependent on an antecedent. For example, in the sentence ''That poor man looks as if he needs a new coat'', the meaning of the pronoun ''he'' is dependent on its antecedent, ''that poor man''. The adjective form of the word "pronoun" is "pronominal". A pronominal is also a word or phrase that acts as a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conditional Sentence
A conditional sentence is a sentence in a natural language that expresses that one thing is contingent on another, e.g., "If it rains, the picnic will be cancelled." They are so called because the impact of the sentence’s main clause is ''conditional'' on a subordinate clause. A full conditional thus contains two clauses: the subordinate clause, called the ''antecedent'' (or ''protasis'' or ''if-clause''), which expresses the condition, and the main clause, called the ''consequent'' (or ''apodosis'' or ''then-clause'') expressing the result. To form conditional sentences, languages use a variety of grammatical forms and constructions. The forms of verbs used in the antecedent and consequent are often subject to particular rules as regards their tense, aspect, and mood. Many languages have a specialized type of verb form called the conditional mood – broadly equivalent in meaning to the English "would (do something)" – for use in some types of conditional sentences. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Counterfactual Conditional
Counterfactual conditionals (also ''contrafactual'', ''subjunctive'' or ''X-marked'') are conditional sentences which discuss what would have been true under different circumstances, e.g. "If Peter believed in ghosts, he would be afraid to be here." Counterfactuals are contrasted with indicatives, which are generally restricted to discussing open possibilities. Counterfactuals are characterized grammatically by their use of fake tense morphology, which some languages use in combination with other kinds of morphology including aspect and mood. Counterfactuals are one of the most studied phenomena in philosophical logic, formal semantics, and philosophy of language. They were first discussed as a problem for the material conditional analysis of conditionals, which treats them all as trivially true. Starting in the 1960s, philosophers and linguists developed the now-classic possible world approach, in which a counterfactual's truth hinges on its consequent holding at certai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protasis
In drama, a protasis is the introductory part of a play, usually its first act. The term was coined by the fourth-century Roman grammarian Aelius Donatus. He defined a play as being made up of three separate parts, the other two being epitasis and catastrophe. In modern dramatic theory Dramatic theory attempts to form theories about theatre and drama. Drama is defined as a form of art in which a written play is used as basis for a performance. Dramatic theory is studied as part of theatre studies. Drama creates a sensory impre ... the term dramatic arc has substantially the same meaning, though with slightly different divisions. References Drama Ancient Greek theatre {{drama-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manang Biday
Manang Biday (Kurditan: ᜋᜈᜅ᜔ ᜊᜒᜇᜌ᜔) is a traditional Ilocano folksong in Northern Luzon, particularly in the province of Ilocos. This song implies the courtship of a young maiden named Manang Biday. Serenading a love interest is a custom of the Filipinos. Until today, it is still practiced by the Ilocano. It is also a courtship dance. "Manang Biday" was originally composed by Florante Aguilar. Lyrics Original Ilocano lyrics Manang Biday, ilukatmo man Ta bintana ikalumbabam Ta kitaem ‘toy kinayawan Ay, matayakon no dinak kaasian Siasino ka, nga aglabaslabas Ditoy hardinko pagay-ayamak Ammom ngarud a balasangak Sabong ni lirio, di pay nagukrad Denggem, ading, ta bilinenka Ta inkanto ‘diay sadi daya Agalakanto’t bunga’t mangga Ken lansones pay, adu a kita No nababa, dimo gaw-aten No nangato, dika sukdalen No naregreg, dika piduten Ngem labaslabasamto met laeng Daytoy paniok no maregregko Ti makapidut isublinanto Ta nagmarka iti naganko Nabordaan pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |