|
ICHD Classification And Diagnosis Of Migraine
The classification of all headaches, including migraines, is organized by the International Headache Society, and published in the International Classification of Headache Disorders (ICHD). The current version, the ICHD-3 beta, was published in 2013. /www.ichd-3.org/ ''Website The International Classification of Headache Disorders 3rd edition (Beta version)'' Retrieved 29. August 2016. The first category within the ICHD is ''Migraine''. Migraines in general are considered to be a neurological syndrome. It is estimated that 11% (303 million) of the global population, including 43 million Europeans and 28 million Americans, experience migraines. Organization of migraine subtypes The ICHD-3 beta classification includes 6 main subtypes of migraine (ICHD-1: 7 main subtypes, ICHD-2: 6 main subtypes), most of which are further subdivided. Overall ICHD-3 beta distinguishes 29 migraine subtypes. The following table outlines the main subtypes and their ICHD-1, -2, -3 beta and ICD-10 code ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Headache
A headache, also known as cephalalgia, is the symptom of pain in the face, head, or neck. It can occur as a migraine, tension-type headache, or cluster headache. There is an increased risk of Depression (mood), depression in those with severe headaches. Headaches can occur as a result of many conditions. There are a number of different classification systems for headaches. The most well-recognized is that of the International Headache Society, which classifies it into more than 150 types of Primary headache disorder, primary and secondary headaches. Causes of headaches may include dehydration; fatigue; sleep deprivation; Stress (biology), stress; the effects of medications (overuse) and recreational drugs, including withdrawal; viral infections; loud noises; head injury; rapid ingestion of a very cold food or beverage; and dental or sinus issues (such as sinusitis). Treatment of a headache depends on the underlying cause, but commonly involves analgesic, pain medication (esp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Contraindication
In medicine, a contraindication is a condition (a situation or factor) that serves as a reason not to take a certain medical treatment due to the harm that it would cause the patient. Contraindication is the opposite of indication, which is a reason to use a certain treatment. Absolute contraindications are contraindications for which there are no reasonable circumstances for undertaking a course of action (that is, overriding the prohibition). For example: * Children and teenagers with viral infections should not be given aspirin because of the risk of Reye syndrome. * A person with an anaphylactic food allergy should never eat the food to which they are allergic. * A person with hemochromatosis should not be administered iron preparations. * Some medications are so teratogenic that they are absolutely contraindicated in pregnancy; examples include thalidomide and isotretinoin. Relative contraindications are contraindications for circumstances in which the patient is at hig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pregnant
Pregnancy is the time during which one or more offspring gestation, gestates inside a woman's uterus. A multiple birth, multiple pregnancy involves more than one offspring, such as with twins. Conception (biology), Conception usually occurs following sexual intercourse, vaginal intercourse, but can also occur through assisted reproductive technology procedures. A pregnancy may end in a Live birth (human), live birth, a miscarriage, an Abortion#Induced, induced abortion, or a stillbirth. Childbirth typically occurs around 40 weeks from the start of the Menstruation#Onset and frequency, last menstrual period (LMP), a span known as the Gestational age (obstetrics), ''gestational age''; this is just over nine months. Counting by Human fertilization#Fertilization age, ''fertilization age'', the length is about 38 weeks. Implantation (embryology), Implantation occurs on average 8–9 days after Human fertilization, fertilization. An ''embryo'' is the term for the deve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
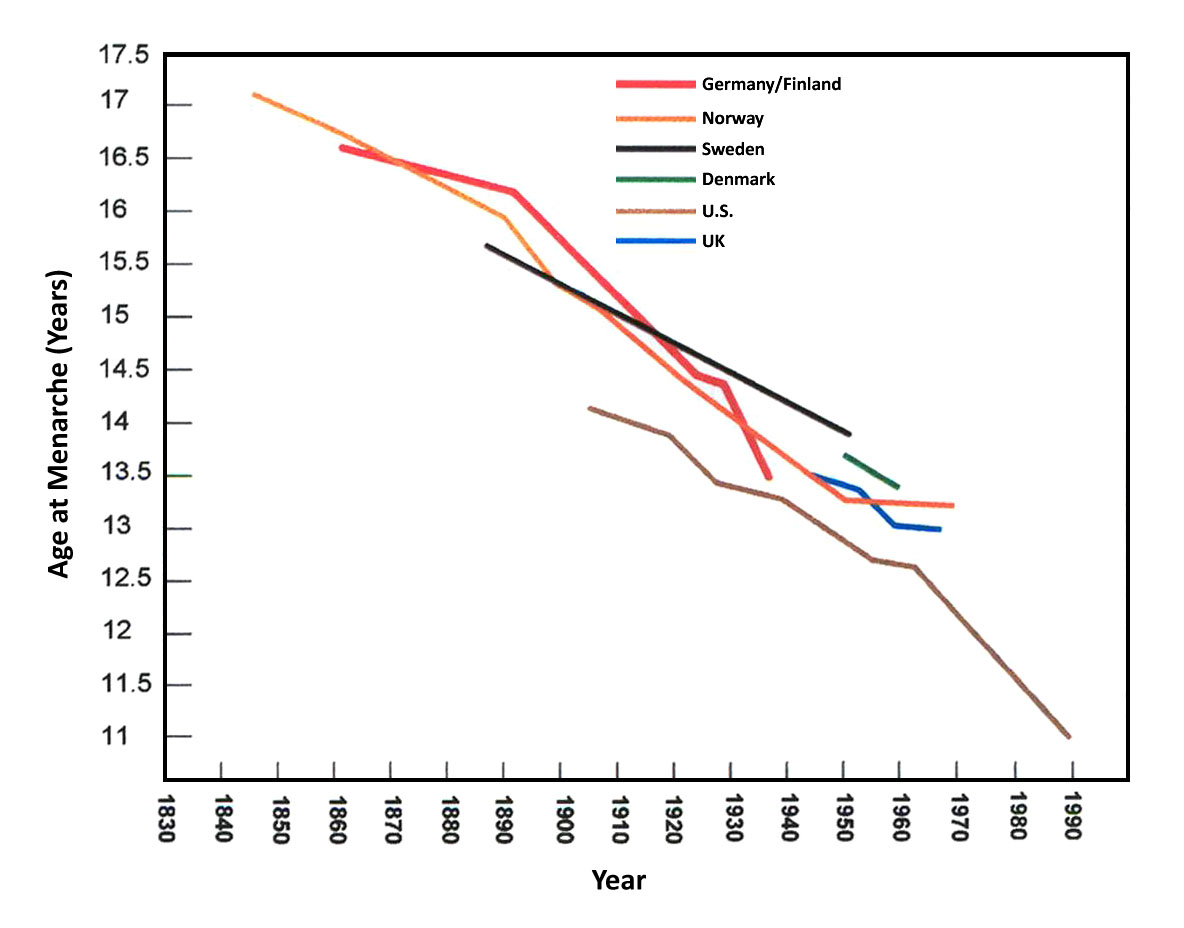
Menarche
Menarche ( ; ) is the first menstrual cycle, or first menstruation, menstrual bleeding, in female humans. From both social and medical perspectives, it is often considered the central event of female puberty, as it signals the possibility of fertility. Girls experience menarche at different ages, but the most common age is 12. Having menarche occur between the ages of 9–14 in the West is considered normal.US National Health Statistics Report September 2020 The timing of menarche is influenced by female biology, as well as Genetics, genetic, environmental factors, and nutritional factors. The mean age of menarche has declined over the last century, but the magnitude of the decline and the factors responsible remain subjects of contention. The worldwide average age of menarche is very difficult to estimate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Menstruating
The menstrual cycle is a series of natural changes in hormone production and the structures of the uterus and ovaries of the female reproductive system that makes pregnancy possible. The ovarian cycle controls the production and release of eggs and the cyclic release of estrogen and progesterone. The uterine cycle governs the preparation and maintenance of the lining of the uterus (womb) to receive an embryo. These cycles are concurrent and coordinated, normally last between 21 and 35 days, with a median length of 28 days. Menarche (the onset of the first period) usually occurs around the age of 12 years; menstrual cycles continue for about 30–45 years. Naturally occurring hormones drive the cycles; the cyclical rise and fall of the follicle stimulating hormone prompts the production and growth of oocytes (immature egg cells). The hormone estrogen stimulates the uterus lining (endometrium) to thicken to accommodate an embryo should fertilization occur. The blood supply of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epidemiological
Epidemiology is the study and analysis of the distribution (who, when, and where), patterns and Risk factor (epidemiology), determinants of health and disease conditions in a defined population, and application of this knowledge to prevent diseases. It is a cornerstone of public health, and shapes policy decisions and evidence-based practice by identifying Risk factor (epidemiology), risk factors for disease and targets for preventive healthcare. Epidemiologists help with study design, collection, and statistical analysis of data, amend interpretation and dissemination of results (including peer review and occasional systematic review). Epidemiology has helped develop methodology used in clinical research, public health studies, and, to a lesser extent, basic research in the biological sciences. Major areas of epidemiological study include disease causation, transmission (medicine), transmission, outbreak investigation, disease surveillance, environmental epidemiology, forensic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clinical Study
Clinical trials are prospective biomedical or behavioral research studies on human subject research, human participants designed to answer specific questions about biomedical or behavioral interventions, including new treatments (such as novel vaccines, pharmaceutical drug, drugs, medical nutrition therapy, dietary choices, dietary supplements, and medical devices) and known interventions that warrant further study and comparison. Clinical trials generate data on dosage, safety and efficacy. They are conducted only after they have received institutional review board, health authority/ethics committee approval in the country where approval of the therapy is sought. These authorities are responsible for vetting the risk/benefit ratio of the trial—their approval does not mean the therapy is 'safe' or effective, only that the trial may be conducted. Depending on product type and development stage, investigators initially enroll volunteers or patients into small Pilot experiment, pi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclic Vomiting Syndrome
Cyclic vomiting syndrome (CVS) is a chronic functional condition of unknown pathogenesis. CVS is characterized as recurring episodes lasting a single day to multiple weeks. Each episode is divided into four phases: inter-episodic, prodrome, vomiting, and recovery. During the inter-episodic phase, which typically lasts one week to one month, there are no discernible symptoms and normal activities can occur. The prodrome phase is known as the pre-emetic phase, characterized by the initial feeling of an approaching episode but still being able to keep down oral medication. The emetic or vomiting phase is characterized by intense persistent nausea and repeated vomiting, typically lasting hours to days. During the recovery phase, vomiting ceases, nausea diminishes or is absent, and appetite returns. "Cyclic vomiting syndrome (CVS) is a rare abnormality of the neuroendocrine system that affects 2% of children." This disorder is thought to be closely related to migraines and fami ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Appendicitis
Appendicitis is inflammation of the Appendix (anatomy), appendix. Symptoms commonly include right lower abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, fever and anorexia (symptom), decreased appetite. However, approximately 40% of people do not have these typical symptoms. Severe complications of a ruptured appendix include widespread, agonising and awful peritonitis, inflammation of the inner lining of the abdominal wall and sepsis. Appendicitis is primarily caused by a blockage of the Lumen (anatomy), hollow portion in the appendix. This blockage typically results from a Fecalith, faecolith, a calcified "stone" made of feces. Some studies show a correlation between appendicoliths and disease severity. Other factors such as inflamed Mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue, lymphoid tissue from a viral infection, Human parasite, intestinal parasites, gallstone, or Neoplasm, tumors may also lead to this blockage. When the appendix becomes blocked, it experiences increased pressure, reduced blood f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emergency Department
An emergency department (ED), also known as an accident and emergency department (A&E), emergency room (ER), emergency ward (EW) or casualty department, is a medical treatment facility specializing in emergency medicine, the Acute (medicine), acute care of patients who present without prior appointment; either by their own means or by that of an ambulance. The emergency department is usually found in a hospital or other primary care center. Due to the unplanned nature of patient attendance, the department must provide initial treatment for a broad spectrum of illnesses and injuries, some of which may be Medical emergency, life-threatening and require immediate attention. In some countries, emergency departments have become important entry points for those without other means of access to medical care. The emergency departments of most hospitals operate 24 hours a day, although staffing levels may be varied in an attempt to reflect patient volume. History Accident services wer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abdominal Migraine
Abdominal migraine (AM) is a functional disorder that usually manifests in childhood and adolescence, without a clear pathologic mechanism or biochemical irregularity. Children frequently experience sporadic episodes of excruciating central abdominal pain accompanied by migrainous symptoms like nausea, vomiting, severe headaches, and general pallor. Abdominal migraine can be diagnosed based on clinical criteria and the exclusion of other disorders. The US Food and Drug Administration has not approved any drugs for the treatment of abdominal migraine. The goal of treatment is usually to prevent attacks, and this is often achieved through nonpharmacologic intervention. Research has indicated that the incidence of abdominal migraine in children falls within the range of 0.4% to 4%. The condition primarily affects children aged 3 to 10 years, with a higher prevalence in females. Signs and Symptoms Midline abdominal pain with paroxysmal, recurrent, acute onset attacks that last an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scotoma
A scotoma is an area of partial alteration in the field of vision consisting of a partially diminished or entirely degenerated visual acuity that is surrounded by a field of normal – or relatively well-preserved – vision. Every normal mammalian eye has a scotoma in its field of vision, usually termed its blind spot. This is a location with no photoreceptor cells, where the retinal ganglion cell axons that compose the optic nerve exit the retina. This location is called the optic disc. There is no direct conscious awareness of visual scotomas. They are simply regions of reduced information within the visual field. Rather than recognizing an incomplete image, patients with scotomas report that things "disappear" on them. The presence of the blind spot scotoma can be demonstrated subjectively by covering one eye, carefully holding fixation with the open eye, and placing an object (such as one's thumb) in the lateral and horizontal visual field, about 15 degrees from fixati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |