|
IBM SAN Volume Controller
The IBM SAN Volume Controller (SVC) is a block storage virtualization appliance that belongs to the IBM System Storage product family. SVC implements an indirection, or "virtualization", layer in a Fibre Channel storage area network (SAN). Architecture The IBM 2145 SAN Volume Controller (SVC) is an inline virtualization or "gateway" device. It logically sits between hosts and storage arrays, presenting itself to hosts as the storage provider (target) and presenting itself to storage arrays as one big host. SVC is physically attached to one or several SAN fabrics. The virtualization approach allows for non-disruptive replacements of any part in the storage infrastructure, including the SVC devices themselves. It also aims at simplifying compatibility requirements in strongly heterogeneous server and storage landscapes. All advanced functions are therefore implemented in the virtualization layer, which allows switching storage array vendors without impact. Finally, spreading an S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IBM FlashSystem
IBM FlashSystem is an IBM Storage enterprise system that stores data on flash memory. Unlike storage systems that use standard solid-state drives, IBM FlashSystem products incorporate custom hardware based on technology from the 2012 IBM acquisition of Texas Memory Systems. According to Gartner, IBM was the number one all-flash storage array vendor in 2014 selling over 2,100 FlashSystems totaling 62 petabytes (PB) of capacity. The IBM FlashSystem commanded 33% of the total all-flash capacity sold by all vendors for the year. As of February 12, 2020, the FlashSystem brand has replaced both the IBM_Storwize_family, Storwize and IBM_XIV_Storage_System, XIV brands in IBM. History Origin The IBM FlashSystem architecture was originally developed by Texas Memory Systems (TMS) as their RamSan product line. TMS was a small private company founded in 1978 and based in Houston, Texas, that supplied solid-state drive products to the market longer than any other company. The TMS Ram ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Storage Virtualization
In computer science, storage virtualization is "the process of presenting a logical view of the physical storage resources to" a host computer system, "treating all storage media (hard disk, optical disk, tape, etc.) in the enterprise as a single pool of storage." A "storage system" is also known as a storage array, disk array, or ''filer''. Storage systems typically use special hardware and software along with disk drives in order to provide very fast and reliable storage for computing and data processing. Storage systems are complex, and may be thought of as a special purpose computer designed to provide storage capacity along with advanced data protection features. Disk drives are only one element within a storage system, along with hardware and special purpose embedded software within the system. Storage systems can provide either block accessed storage, or file accessed storage. Block access is typically delivered over Fibre Channel, iSCSI, SAS, FICON or other prot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
VDisk
A logical disk, logical volume or virtual disk (VD or vdisk for short) is a virtual device that provides an area of usable storage capacity on one or more physical disk drive(s) in a computer system. The disk is described as ''logical'' or ''virtual'' because it does not actually exist as a single physical entity in its own right. The goal of the logical disk is to provide computer software with what seems a contiguous storage area, sparing them the burden of dealing with the intricacies of storing files on multiple physical units. Most modern operating systems provide some form of logical volume management. Levels Logical disks can be defined at various levels in the storage infrastructure. Operating system An operating system may define ''volumes'' or ''logical disks'' and assign each to one physical disk, more than one physical disk or part of the storage area of a physical disk. For example, Windows NT can create several partitions on a hard disk drive, each of which a s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
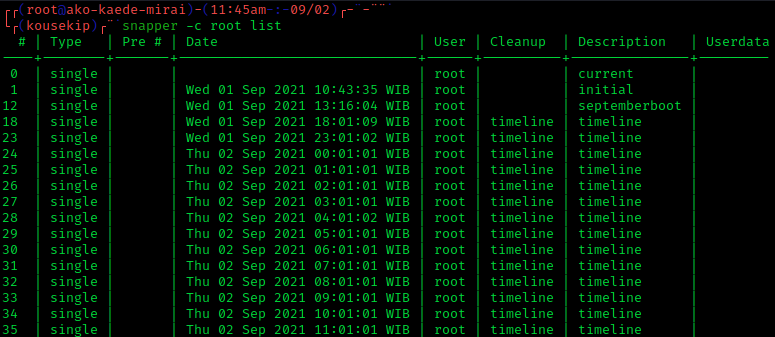
Disk Snapshot
In computer systems, a snapshot is the state of a system at a particular point in time. The term was coined as an analogy to that in photography. Rationale A full backup of a large data set may take a long time to complete. On multi-tasking or multi-user systems, there may be writes to that data while it is being backed up. This prevents the backup from being atomic and introduces a version skew that may result in data corruption. For example, if a user moves a file into a directory that has already been backed up, then that file would be completely missing on the backup media, since the backup operation had already taken place before the addition of the file. Version skew may also cause corruption with files which change their size or contents underfoot while being read. One approach to safely backing up live data is to temporarily disable write access to data during the backup, either by stopping the accessing applications or by using the locking API provided by the oper ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
FlashCopy
FlashCopy is an IBM feature supported on various IBM storage devices that made it possible to create, nearly instantaneously, point-in-time snapshot copies of entire logical volumes or data sets. The Hitachi Data Systems implementation providing similar function was branded as ShadowImage. Using either implementation, the copies are immediately available for both read and write access. Implementations Version 1 The first implementation of FlashCopy, Version 1 allowed entire volumes to be instantaneously “copied” to another volume by using the facilities of the newer Enterprise Storage Subsystems (ESS). Version 1 of FlashCopy had limitations however. Although the copy or “flash” of a volume occurred instantaneously, the FlashCopy commands were issued sequentially and the ESS required a brief moment to establish the new pointers. Because of this minute processing delay, the data residing on two volumes that were FlashCopied are not exactly time consistent. Version 2 FlashCo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lempel–Ziv–Welch
Lempel–Ziv–Welch (LZW) is a universal lossless data compression algorithm created by Abraham Lempel, Jacob Ziv, and Terry Welch. It was published by Welch in 1984 as an improved implementation of the LZ78 algorithm published by Lempel and Ziv in 1978. The algorithm is simple to implement and has the potential for very high throughput in hardware implementations. It is the algorithm of the Unix file compression utility compress and is used in the GIF image format. Algorithm The scenario described by Welch's 1984 paper encodes sequences of 8-bit data as fixed-length 12-bit codes. The codes from 0 to 255 represent 1-character sequences consisting of the corresponding 8-bit character, and the codes 256 through 4095 are created in a dictionary for sequences encountered in the data as it is encoded. At each stage in compression, input bytes are gathered into a sequence until the next character would make a sequence with no code yet in the dictionary. The code for th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Temporal Locality
In computer science, locality of reference, also known as the principle of locality, is the tendency of a processor to access the same set of memory locations repetitively over a short period of time. There are two basic types of reference locality temporal and spatial locality. Temporal locality refers to the reuse of specific data and/or resources within a relatively small time duration. Spatial locality (also termed ''data locality'')"NIST Big Data Interoperability Framework: Volume 1"urn:doi:10.6028/NIST.SP.1500-1r2 refers to the use of data elements within relatively close storage locations. Sequential locality, a special case of spatial locality, occurs when data elements are arranged and accessed linearly, such as traversing the elements in a one-dimensional Array data structure, array. Locality is a type of predictability, predictable behavior that occurs in computer systems. Systems which exhibit strong ''locality of reference'' are good candidates for performance optimiza ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Golden Copy
In informatics, a golden record is the valid version of a data element (record) in a single source of truth system. It may refer to a database, specific table or data field, or any unit of information used. A golden copy is a consolidated data set, and is supposed to provide a single source of truth and a "well-defined version of all the data entities in an organizational ecosystem". Other names sometimes used include master source or master version. The term has been used in conjunction with data quality, master data management, and similar topics. (Different technical solutions exist, see master data management). Master data In master data management (MDM), the golden copy refers to the master data (master version) of the reference data which works as an authoritative source for the "truth" for all applications in a given IT landscape.{{Cite web , last=IVPMarketing , date=2020-04-14 , title=Back to Basics: Golden Copy of Data Explained , url=https://www.ivp.in/ivp-security-mast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Live Partition Mobility
Live Partition Mobility is a chargeable Live migration feature of IBM POWER6, POWER7, POWER8 and POWER9 servers, available since 2007, that allows a running LPAR to be relocated from one system to another. In concept, it is similar to VMware VMotion. Live Partition Mobility, a component of the PowerVM Enterprise Edition hardware feature, provides the ability to move AIX, IBM i IBM i (the ''i'' standing for ''integrated'') is an operating system developed by IBM for IBM Power Systems. It was originally released in 1988 as OS/400, as the sole operating system of the IBM AS/400 line of systems. It was renamed to i5/OS in 2 ..., and Linux logical partitions from one system to another. The mobility process transfers the system environment that includes the processor state, memory, attached virtual devices, and connected users. The source and target systems must have access to the same network and SANs but need not be of the same type, the only requirement is they use POWER6 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IOPS
Input/output operations per second (IOPS, pronounced ''eye-ops'') is an input/output performance measurement used to characterize computer storage devices like hard disk drives (HDD), solid state drives (SSD), and storage area networks (SAN). Like benchmarks, IOPS numbers published by storage device manufacturers do not directly relate to real-world application performance. Background To meaningfully describe the performance characteristics of any storage device, it is necessary to specify a minimum of three metrics simultaneously: IOPS, response time, and (application) workload. Absent simultaneous specifications of response-time and workload, IOPS are essentially meaningless. In isolation, IOPS can be considered analogous to "revolutions per minute" of an automobile engine i.e. an engine capable of spinning at 10,000 RPMs with its transmission in neutral does not convey anything of value, however an engine capable of developing specified torque and horsepower at a given number ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Storage Performance Council
Storage may refer to: Goods Containers * Dry cask storage, for storing high-level radioactive waste * Food storage * Intermodal container, cargo shipping * Storage tank Facilities * Mail storage, storage by mail or delivery service * Self storage, a public storage facility * Storage room or storeroom, a room for storing objects ** Garage (residential), a storage space normally used to store cars ** Overhead storage, for example overhead storage bins, racks, shelves, cabinets or track systems in aircraft, trains or buildings * Warehouse, a commercial building for storage of goods Technology *Cloud storage *Computer data storage, a means to retain digital data *Data storage, general recording and retention of information *Energy storage *Specific storage, of groundwater in an aquifer Arts and entertainment * ''Storage'' (film), a 2009 Australian horror film * ''The Storage'', a 2011 Finnish film * ''Storage'' (album), a 1988 album by Merzbow * ''Storage Wars'', a reality televi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |