|
House Of Ligne
The House of Ligne is one of the oldest Belgian noble families, dating back to the eleventh century.''Genealogisches Handbuch des Adels, Fürstliche Häuser'' XIV. "Ligne". C.A. Starke Verlag, 1991, pp. 495-500. . The family's name comes from the village of where it originated, between Ath and Tournai in what is now the Hainaut province of Belgium. History Their progressive rise in the nobility began as barons in the twelfth century, counts of Fauquemberg and princes of Épinoy in the sixteenth century, then princes of Amblise in 1608. The family became Imperial counts on 18 December 1544, then Lamoral I received from Emperor Rudolf II the title of Prince of the Holy Roman Empire as ''Prince de Ligne'' on 20 March 1601, for all of his agnatic descendants, both male and female. Compensation for loss of the Imperial County of Ligne (Fagnolles, since that barony had become seat of the county in 1789) as a result of the Peace of Lunéville consisted of substitution of the secul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Princely Hat
A prince is a male ruler (ranked below a king, grand prince, and grand duke) or a male member of a monarch's or former monarch's family. ''Prince'' is also a title of nobility (often highest), often hereditary, in some European states. The female equivalent is a princess. The English word derives, via the French word ''prince'', from the Latin noun , from (first) and (head), meaning "the first, foremost, the chief, most distinguished, noble ruler, prince". Historical background The Latin word (older Latin *prīsmo-kaps, literally "the one who takes the first lace/position), became the usual title of the informal leader of the Roman senate some centuries before the transition to empire, the ''princeps senatus''. Emperor Augustus established the formal position of monarch on the basis of principate, not dominion. He also tasked his grandsons as summer rulers of the city when most of the government were on holiday in the country or attending religious rituals, and, fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prince Of The Holy Roman Empire
Prince of the Holy Roman Empire ( la, princeps imperii, german: Reichsfürst, cf. ''Fürst'') was a title attributed to a hereditary ruler, nobleman or prelate recognised as such by the Holy Roman Emperor. Definition Originally, possessors of the princely title bore it as immediate vassals of the Emperor who held a fief (secular or ecclesiastical) that had no suzerain except the Emperor. However, by the time the Holy Roman Empire was abolished in 1806, there were a number of holders of Imperial princely titles who did not meet these criteria. Thus, there were two main types of princes: those who exercised ''Landeshoheit'' (sovereignty within one's territory while respecting the laws and traditions of the empire) as well as an individual or shared vote in the College of Princes, and those whose title was honorary (the possessor lacking an immediate Imperial fief and/or a vote in the Imperial Diet). The first came to be reckoned as "royalty" in the sense of being treated as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
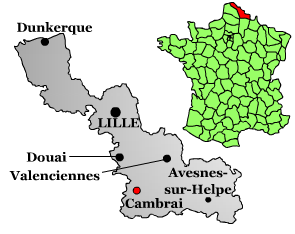
Cambrai
Cambrai (, ; pcd, Kimbré; nl, Kamerijk), formerly Cambray and historically in English Camerick or Camericke, is a city in the Nord department and in the Hauts-de-France region of France on the Scheldt river, which is known locally as the Escaut river. A sub-prefecture of the department, Cambrai is a town which had 32,501 inhabitants in 2018. It is in the heart of the urban unit of Cambrai with 46,772 inhabitants. Its functional area, a more extensive range, included 94,576 inhabitants in 2018.Comparateur de territoire: Aire d'attraction des villes 2020 de Cambrai (108), Unité urbaine 2020 de Cambrai (59403), Commune de Cambrai (59122) INSEE With |
House Of La Trémoille
A house is a single-unit residential building. It may range in complexity from a rudimentary hut to a complex structure of wood Wood is a porous and fibrous structural tissue found in the stems and roots of trees and other woody plants. It is an organic materiala natural composite of cellulose fibers that are strong in tension and embedded in a matrix of lignin ..., masonry, concrete or other material, outfitted with plumbing, electrical, and heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems.Schoenauer, Norbert (2000). ''6,000 Years of Housing'' (rev. ed.) (New York: W.W. Norton & Company). Houses use a range of different roofing systems to keep precipitation such as rain from getting into the dwelling space. Houses may have doors or lock (security device), locks to secure the dwelling space and protect its inhabitants and contents from burglars or other trespassers. Most conventional modern houses in Western cultures will contain one or more bedrooms and bathroo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
House Of Arenberg
The House of Arenberg is an aristocratic lineage that is constituted by three successive families that took their name from Arenberg, a small territory of the Holy Roman Empire in the Eifel region. The inheritance of the House of Croÿ-Aarschot made the Arenbergs the wealthiest and most influential noble family of the Habsburg Netherlands. The family's Duchy of Arenberg was mediatized in 1810. As such, the Arenbergs belong to the small group of families that constitute the ''Hochadel'' (). The current head of the house bears the title of Duke of Arenberg, while all other members are princes or princesses. They all enjoy the style of Serene Highness. In 1827 Prince Pierre d'Arenberg, third son of the 6th Duke of Arenberg, was made a Peer of France and his descendants are now a French branch of the family (French Dukes and Peers). Lords of Arenberg Counts of Arenberg Princely Counts and later Dukes of Arenberg The marriage contract in 1547 between Margaret de la Marck ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cadet Branch
In history and heraldry, a cadet branch consists of the male-line descendants of a monarch's or patriarch's younger sons ( cadets). In the ruling dynasties and noble families of much of Europe and Asia, the family's major assets— realm, titles, fiefs, property and income—have historically been passed from a father to his firstborn son in what is known as primogeniture; younger sons—cadets—inherited less wealth and authority to pass to future generations of descendants. In families and cultures in which this was not the custom or law, as in the feudal Holy Roman Empire, equal distribution of the family's holdings among male members was eventually apt to so fragment the inheritance as to render it too small to sustain the descendants at the socio-economic level of their forefather. Moreover, brothers and their descendants sometimes quarreled over their allocations, or even became estranged. While agnatic primogeniture became a common way of keeping the family's wea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Highness
Highness (abbreviation HH, oral address Your Highness) is a formal style used to address (in second person) or refer to (in third person) certain members of a reigning or formerly reigning dynasty. It is typically used with a possessive adjective: "His Highness", "Her Highness" (HH), "Their Highnesses", etc. Although often combined with other adjectives of honour indicating rank, such as "Imperial", "Royal" or "Serene", it may be used alone. ''Highness'' is, both literally and figuratively, the quality of being lofty or above. It is used as a term to evoke dignity or honour, and to acknowledge the exalted rank of the person so described. History in Europe Abstract styles arose in profusion in the Roman Empire, especially in the Byzantine. Styles were attached to various offices at court or in the state. In the early Middle Ages such styles, couched in the second or third person, were uncertain and much more arbitrary, and were more subject to the fancies of secretaries th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imperial State
An Imperial State or Imperial Estate ( la, Status Imperii; german: Reichsstand, plural: ') was a part of the Holy Roman Empire with representation and the right to vote in the Imperial Diet ('). Rulers of these Estates were able to exercise significant rights and privileges and were " immediate", meaning that the only authority above them was the Holy Roman Emperor. They were thus able to rule their territories with a considerable degree of autonomy. The system of imperial states replaced the more regular division of Germany into stem duchies in the early medieval period. The old Carolingian stem duchies were retained as the major divisions of Germany under the Salian dynasty, but they became increasingly obsolete during the early high medieval period under the Hohenstaufen, and they were finally abolished in 1180 by Frederick Barbarossa in favour of more numerous territorial divisions. From 1489, the imperial Estates represented in the Diet were divided into three chambers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a political entity in Western, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its dissolution in 1806 during the Napoleonic Wars. From the accession of Otto I in 962 until the twelfth century, the Empire was the most powerful monarchy in Europe. Andrew Holt characterizes it as "perhaps the most powerful European state of the Middle Ages". The functioning of government depended on the harmonic cooperation (dubbed ''consensual rulership'' by Bernd Schneidmüller) between monarch and vassals but this harmony was disturbed during the Salian period. The empire reached the apex of territorial expansion and power under the House of Hohenstaufen in the mid-thirteenth century, but overextending led to partial collapse. On 25 December 800, Pope Leo III crowned the Frankish king Charlemagne as emperor, reviving the title in Western Europe, more than three centuries after the fall of the earlier ancient Western Ro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nikolaus II, Prince Esterházy
Nicholas II, Prince Esterházy ( hu, Esterházy II. Miklós, german: Nikolaus II Esterházy; 12 December 176524 November 1833) was a wealthy Hungarian prince. He served the Austrian Empire and was a member of the famous Esterházy family. He is especially remembered for his art collection and for his role as the last patron of Joseph Haydn. After the Congress of Vienna, his family was considered one of the mediatised houses for their former Sovereign (Bavarian after 1806) Principality of Edelstetten ( Edelstetten Abbey), Life Nikolaus was born in Vienna on 12 December 1765, the son of Prince Anton Esterházy and his first wife, Maria Theresia, Countess Erdödy de Monyorokerek et Monoszlo (1745–1782). His father Anton was the son of Nikolaus I, whom he succeeded as reigning prince on the latter's death in 1790. In 1783, the younger Nikolaus, aged 17, married the 15-year-old Maria Josepha, Princess von und zu Liechtenstein (1768–1845). According to Mraz (2009b), the ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imperial Diet (Holy Roman Empire)
The Imperial Diet ( la, Dieta Imperii Comitium Imperiale; german: Reichstag) was the deliberative body of the Holy Roman Empire. It was not a legislative body in the contemporary sense; its members envisioned it more like a central forum where it was more important to negotiate than to decide. Its members were the Imperial Estates, divided into three colleges. The diet as a permanent, regularized institution evolved from the '' Hoftage'' (court assemblies) of the Middle Ages. From 1663 until the end of the empire in 1806, it was in permanent session at Regensburg. All Imperial Estates enjoyed immediacy and, therefore, they had no authority above them besides the Holy Roman Emperor himself. While all the estates were entitled to a seat and vote, only the higher temporal and spiritual princes of the College of Princes enjoyed an individual vote (''Virilstimme''), while lesser estates such as imperial counts and imperial abbots, were merely entitled to a collective vote (''Kuri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |