|
Homing Endonuclease
The homing endonucleases are a collection of endonucleases encoded either as freestanding genes within introns, as fusions with host proteins, or as self-splicing inteins. They catalyze the hydrolysis of genomic DNA within the cells that synthesize them, but do so at very few, or even singular, locations. Repair of the hydrolyzed DNA by the host cell frequently results in the gene encoding the homing endonuclease having been copied into the cleavage site, hence the term 'homing' to describe the movement of these genes. Homing endonucleases can thereby transmit their genes horizontally within a host population, increasing their allele frequency at greater than Mendelian rates. Origin and mechanism Although the origin and function of homing endonucleases is still being researched, the most established hypothesis considers them as selfish genetic elements, similar to transposons, because they facilitate the perpetuation of the genetic elements that encode them independent of provi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
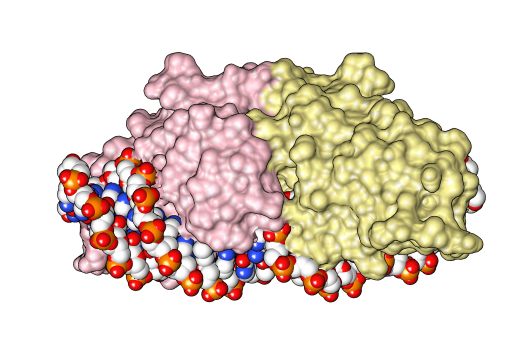
I-CreI Dimer DNA 4
I-''Cre''I is a homing endonuclease whose gene was first discovered in the chloroplast genome of ''Chlamydomonas reinhardtii'', a species of unicellular green algae. It is named for the facts that: it resides in an Intron; it was isolated from ''Clamydomonas reinhardtii''; it was the first (I) such gene isolated from ''C. reinhardtii''. Its gene resides in a group I intron in the 23S ribosomal RNA gene of the ''C. reinhardtii'' chloroplast, and I-''Cre''I is only expressed when its mRNA is spliced from the primary transcript of the 23S gene. I-''Cre''I enzyme, which functions as a homodimer, recognizes a 22-nucleotide sequence of duplex DNA and cleaves one phosphodiester bond on each strand at specific positions. I-''Cre''I is a member of the LAGLIDADG family of homing endonucleases, all of which have a conserved LAGLIDADG amino acid motif that contributes to their associative domains and active sites. When the I-''Cre''I-containing intron encounters a 23S allele lacking the intron, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermococcus Litoralis
''Thermococcus litoralis'' (''T. litoralis'') is a species of Archaea that is found around deep-sea hydrothermal vents as well as shallow submarine thermal springs and oil wells. It is an anaerobic organotroph hyperthermophile that is between in diameter. Like the other species in the order thermococcales, ''T. litoralis'' is an irregular hyperthermophile coccus that grows between . Unlike many other thermococci, ''T. litoralis'' is non-motile. Its cell wall consists only of a single S-layer that does not form hexagonal lattices. Additionally, while many thermococcales obligately use sulfur as an electron acceptor in metabolism, ''T. litoralis'' only needs sulfur to help stimulate growth, and can live without it. ''T. litoralis'' has recently been popularized by the scientific community for its ability to produce an alternative DNA polymerase to the commonly used Taq polymerase. The ''T. litoralis'' polymerase, dubbed the vent polymerase, has been shown to have a lower error ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phylogenetics
In biology, phylogenetics (; from Greek φυλή/ φῦλον [] "tribe, clan, race", and wikt:γενετικός, γενετικός [] "origin, source, birth") is the study of the evolutionary history and relationships among or within groups of organisms. These relationships are determined by Computational phylogenetics, phylogenetic inference methods that focus on observed heritable traits, such as DNA sequences, protein amino acid sequences, or morphology. The result of such an analysis is a phylogenetic tree—a diagram containing a hypothesis of relationships that reflects the evolutionary history of a group of organisms. The tips of a phylogenetic tree can be living taxa or fossils, and represent the "end" or the present time in an evolutionary lineage. A phylogenetic diagram can be rooted or unrooted. A rooted tree diagram indicates the hypothetical common ancestor of the tree. An unrooted tree diagram (a network) makes no assumption about the ancestral line, and do ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein Subunit
In structural biology, a protein subunit is a polypeptide chain or single protein molecule that assembles (or "''coassembles''") with others to form a protein complex. Large assemblies of proteins such as viruses often use a small number of types of protein subunits as building blocks. A subunit is often named with a Greek or Roman letter, and the numbers of this type of subunit in a protein is indicated by a subscript. For example, ATP synthase has a type of subunit called α. Three of these are present in the ATP synthase molecule, leading to the designation α3. Larger groups of subunits can also be specified, like α3β3-hexamer and c-ring. Naturally-occurring proteins that have a relatively small number of subunits are referred to as oligomeric.Quote: ''Oligomer molecule: A molecule of intermediate relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises a small plurality of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of lower relative molecular ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cold Spring Harbor Press
Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press was founded in 1933 to aid in Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory's purpose of furthering the advance and spread of scientific knowledge. CSHL Press publishes monographs, technical manuals, handbooks, review volumes, conference proceedings, scholarly journals and videotapes. These examine important topics in molecular biology, genetics, development, virology, neurobiology, immunology and cancer biology. Manuscripts for books and for journal publication are invited from scientists worldwide. Revenue from sales of CSHL Press publications is used solely in support of research at Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory. Journals Scientific journals published by CSHL Press: * ''Cold Spring Harbor Molecular Case Studies'' * ''Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Biology'' * ''Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Medicine'' * ''Cold Spring Harbor Protocols'' * '' Cold Spring Harbor Symposia on Quantitative Biology'' * '' Genes & Development'' * ''Genome Research'' * ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ribonucleoprotein
Nucleoproteins are proteins conjugated with nucleic acids (either DNA or RNA). Typical nucleoproteins include ribosomes, nucleosomes and viral nucleocapsid proteins. Structures Nucleoproteins tend to be positively charged, facilitating interaction with the negatively charged nucleic acid chains. The tertiary structures and biological functions of many nucleoproteins are understood.Graeme K. Hunter G. K. (2000): Vital Forces. The discovery of the molecular basis of life. Academic Press, London 2000, . Important techniques for determining the structures of nucleoproteins include X-ray diffraction, nuclear magnetic resonance and cryo-electron microscopy. Viruses Virus genomes (either DNA or RNA) are extremely tightly packed into the viral capsid. Many viruses are therefore little more than an organised collection of nucleoproteins with their binding sites pointing inwards. Structurally characterised viral nucleoproteins include influenza, rabies, Ebola, Bunyamwera, Schmal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homodimer
In biochemistry, a protein dimer is a macromolecular complex formed by two protein monomers, or single proteins, which are usually non-covalently bound. Many macromolecules, such as proteins or nucleic acids, form dimers. The word ''dimer'' has roots meaning "two parts", '' di-'' + '' -mer''. A protein dimer is a type of protein quaternary structure. A protein homodimer is formed by two identical proteins. A protein heterodimer is formed by two different proteins. Most protein dimers in biochemistry are not connected by covalent bonds. An example of a non-covalent heterodimer is the enzyme reverse transcriptase, which is composed of two different amino acid chains. An exception is dimers that are linked by disulfide bridges such as the homodimeric protein NEMO. Some proteins contain specialized domains to ensure dimerization (dimerization domains) and specificity. The G protein-coupled cannabinoid receptors have the ability to form both homo- and heterodimers with several ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monomer
In chemistry, a monomer ( ; '' mono-'', "one" + ''-mer'', "part") is a molecule that can react together with other monomer molecules to form a larger polymer chain or three-dimensional network in a process called polymerization. Classification Monomers can be classified in many ways. They can be subdivided into two broad classes, depending on the kind of the polymer that they form. Monomers that participate in condensation polymerization have a different stoichiometry than monomers that participate in addition polymerization: : Other classifications include: *natural vs synthetic monomers, e.g. glycine vs caprolactam, respectively *polar vs nonpolar monomers, e.g. vinyl acetate vs ethylene, respectively *cyclic vs linear, e.g. ethylene oxide vs ethylene glycol, respectively The polymerization of one kind of monomer gives a homopolymer. Many polymers are copolymers, meaning that they are derived from two different monomers. In the case of condensation polymerizations ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Structural Motif
In a chain-like biological molecule, such as a protein or nucleic acid, a structural motif is a common three-dimensional structure that appears in a variety of different, evolutionarily unrelated molecules. A structural motif does not have to be associated with a sequence motif; it can be represented by different and completely unrelated sequences in different proteins or RNA. In nucleic acids Depending upon the sequence and other conditions, nucleic acids can form a variety of structural motifs which is thought to have biological significance. ;Stem-loop: Stem-loop intramolecular base pairing is a pattern that can occur in single-stranded DNA or, more commonly, in RNA. The structure is also known as a hairpin or hairpin loop. It occurs when two regions of the same strand, usually complementary in nucleotide sequence when read in opposite directions, base-pair to form a double helix that ends in an unpaired loop. The resulting structure is a key building block of many ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Recognition Sequence
A recognition sequence is a DNA sequence to which a structural motif of a DNA-binding domain exhibits binding specificity. Recognition sequences are palindromes. The transcription factor Sp1 for example, binds the sequences 5'-(G/T)GGGCGG(G/A)(G/A)(C/T)-3', where (G/T) indicates that the domain will bind a guanine or thymine at this position. The restriction endonuclease PstI recognizes, binds, and cleaves the sequence 5'-CTGCAG-3'. A recognition sequence is different from a recognition site. A given recognition sequence can occur one or more times, or not at all, on a specific DNA fragment. A recognition site is specified by the position of the site. For example, there are two PstI recognition sites in the following DNA sequence fragment, starting at base 9 and 31 respectively. A recognition sequence is a specific sequence, usually very short (less than 10 bases). Depending on the degree of specificity of the protein, a DNA-binding protein can bind to more than one specific se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Restriction Enzyme
A restriction enzyme, restriction endonuclease, REase, ENase or'' restrictase '' is an enzyme that cleaves DNA into fragments at or near specific recognition sites within molecules known as restriction sites. Restriction enzymes are one class of the broader endonuclease group of enzymes. Restriction enzymes are commonly classified into five types, which differ in their structure and whether they cut their DNA substrate at their recognition site, or if the recognition and cleavage sites are separate from one another. To cut DNA, all restriction enzymes make two incisions, once through each sugar-phosphate backbone (i.e. each strand) of the DNA double helix. These enzymes are found in bacteria and archaea and provide a defense mechanism against invading viruses. Inside a prokaryote, the restriction enzymes selectively cut up ''foreign'' DNA in a process called ''restriction digestion''; meanwhile, host DNA is protected by a modification enzyme (a methyltransferase) that mod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
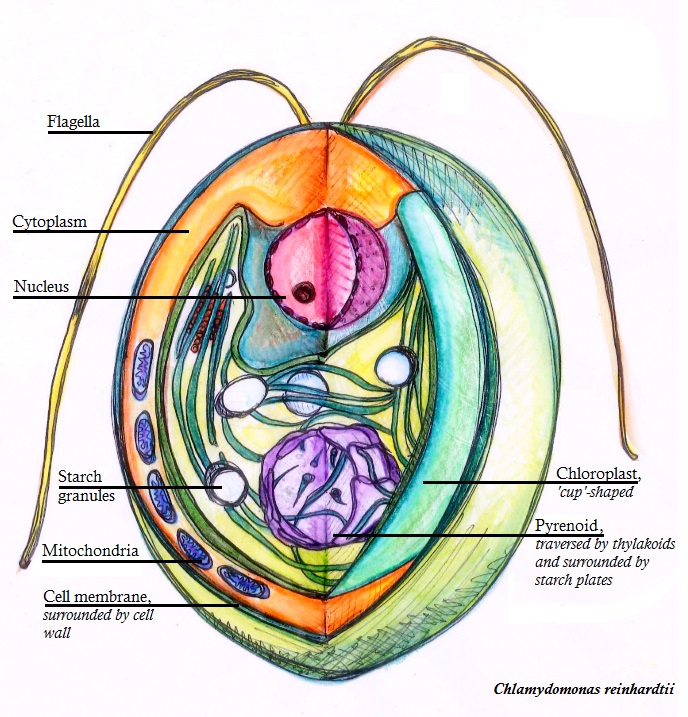
Chlamydomonas Reinhardtii
''Chlamydomonas reinhardtii'' is a single-cell green alga about 10 micrometres in diameter that swims with two flagella. It has a cell wall made of hydroxyproline-rich glycoproteins, a large cup-shaped chloroplast, a large pyrenoid, and an eyespot that senses light. ''Chlamydomonas'' species are widely distributed worldwide in soil and fresh water. ''Chlamydomonas reinhardtii'' is an especially well studied biological model organism, partly due to its ease of culturing and the ability to manipulate its genetics. When illuminated, ''C. reinhardtii'' can grow photoautotrophically, but it can also grow in the dark if supplied with organic carbon. Commercially, ''C. reinhardtii'' is of interest for producing biopharmaceuticals and biofuel, as well being a valuable research tool in making hydrogen. History The ''C. reinhardtii'' wild-type laboratory strain c137 (mt+) originates from an isolate collected near Amherst, Massachusetts, in 1945 by Gilbert M. Smith. The species' name ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |