|
Hippolyte Morestin
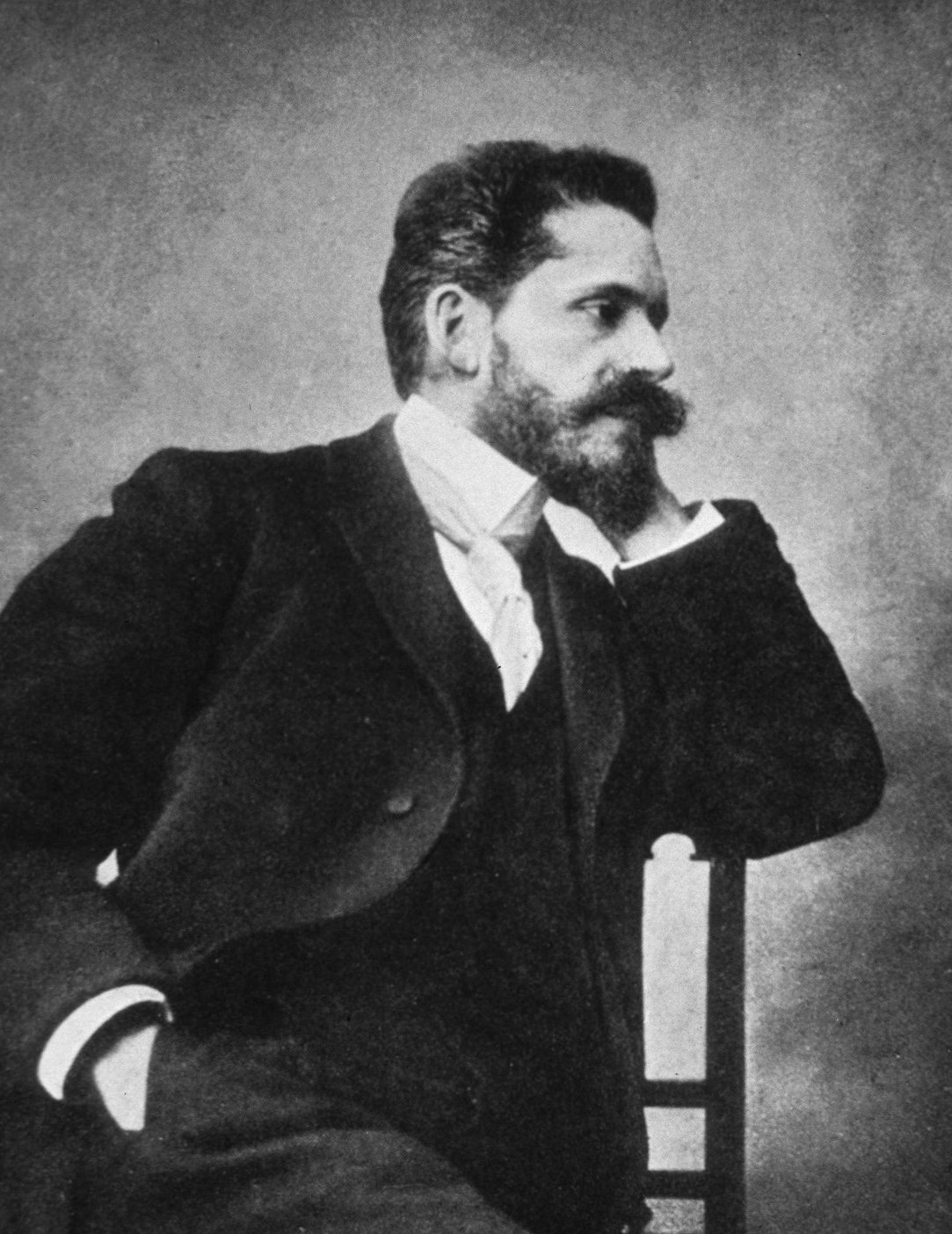
Hippolyte Morestin (1 September 1869 – 12 February 1919) was a French surgeon, and associate professor of anatomy at the University of Paris. He was one of the founders of cosmetic surgery. He was dubbed "The Father of the Mouths" after his breakthroughs in oral and maxillofacial surgery. Morestin was born at Basse-Pointe, a Communes of France, commune in the France, French overseas department of Martinique. His father Charles Amédée Morestin (d. 1902) was a prominent doctor who influenced both Hippolyte and his younger brother Amédée to study medicine. Both Hippolyte and Amédée dedicated their doctoral theses, defended in Paris in 1894 and 1912, respectively, to their father, and the work of Amédée used observations by Hippolyte. Morestin greatly influenced the British-New Zealand surgeon Harold Gillies, who met him on leave in Paris during the First World War. Gillies was attached to the British General Hospital in Rouen. Morestin, when Gillies was observing him, remo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hippolyte Morestin
Hippolyte Morestin (1 September 1869 – 12 February 1919) was a French surgeon, and associate professor of anatomy at the University of Paris. He was one of the founders of cosmetic surgery. He was dubbed "The Father of the Mouths" after his breakthroughs in oral and maxillofacial surgery. Morestin was born at Basse-Pointe, a Communes of France, commune in the France, French overseas department of Martinique. His father Charles Amédée Morestin (d. 1902) was a prominent doctor who influenced both Hippolyte and his younger brother Amédée to study medicine. Both Hippolyte and Amédée dedicated their doctoral theses, defended in Paris in 1894 and 1912, respectively, to their father, and the work of Amédée used observations by Hippolyte. Morestin greatly influenced the British-New Zealand surgeon Harold Gillies, who met him on leave in Paris during the First World War. Gillies was attached to the British General Hospital in Rouen. Morestin, when Gillies was observing him, remo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Paris
, image_name = Coat of arms of the University of Paris.svg , image_size = 150px , caption = Coat of Arms , latin_name = Universitas magistrorum et scholarium Parisiensis , motto = ''Hic et ubique terrarum'' (Latin) , mottoeng = Here and anywhere on Earth , established = Founded: c. 1150Suppressed: 1793Faculties reestablished: 1806University reestablished: 1896Divided: 1970 , type = Corporative then public university , city = Paris , country = France , campus = Urban The University of Paris (french: link=no, Université de Paris), metonymically known as the Sorbonne (), was the leading university in Paris, France, active from 1150 to 1970, with the exception between 1793 and 1806 under the French Revolution. Emerging around 1150 as a corporation associated with the cathedral school of Notre Dame de Paris, it was considered the second-oldest university in Europe. Haskins, C. H.: ''The Rise of Universities'', Henry Holt and Company, 1923, p. 292. Officially chartered i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basse-Pointe
Basse-Pointe (; gcf, label=Martinican Creole, Baspwent) is a town and commune in the French overseas department and region, and island of Martinique. Geography Climate Basse-Pointe has a tropical rainforest climate (Köppen climate classification ''Af''). The average annual temperature in Basse-Pointe is . The average annual rainfall is with November as the wettest month. The temperatures are highest on average in August, at around , and lowest in February, at around . The highest temperature ever recorded in Basse-Pointe was on 1 October 2019; the coldest temperature ever recorded was on 21 September 1978. Population See also *Communes of Martinique The following is a list of the 34 communes of the Martinique overseas department of France. The communes cooperate in the following intercommunalities (as of 2020): [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Communes Of France
The () is a level of administrative division in the French Republic. French are analogous to civil townships and incorporated municipalities in the United States and Canada, ' in Germany, ' in Italy, or ' in Spain. The United Kingdom's equivalent are civil parishes, although some areas, particularly urban areas, are unparished. are based on historical geographic communities or villages and are vested with significant powers to manage the populations and land of the geographic area covered. The are the fourth-level administrative divisions of France. vary widely in size and area, from large sprawling cities with millions of inhabitants like Paris, to small hamlets with only a handful of inhabitants. typically are based on pre-existing villages and facilitate local governance. All have names, but not all named geographic areas or groups of people residing together are ( or ), the difference residing in the lack of administrative powers. Except for the municipal arrondi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
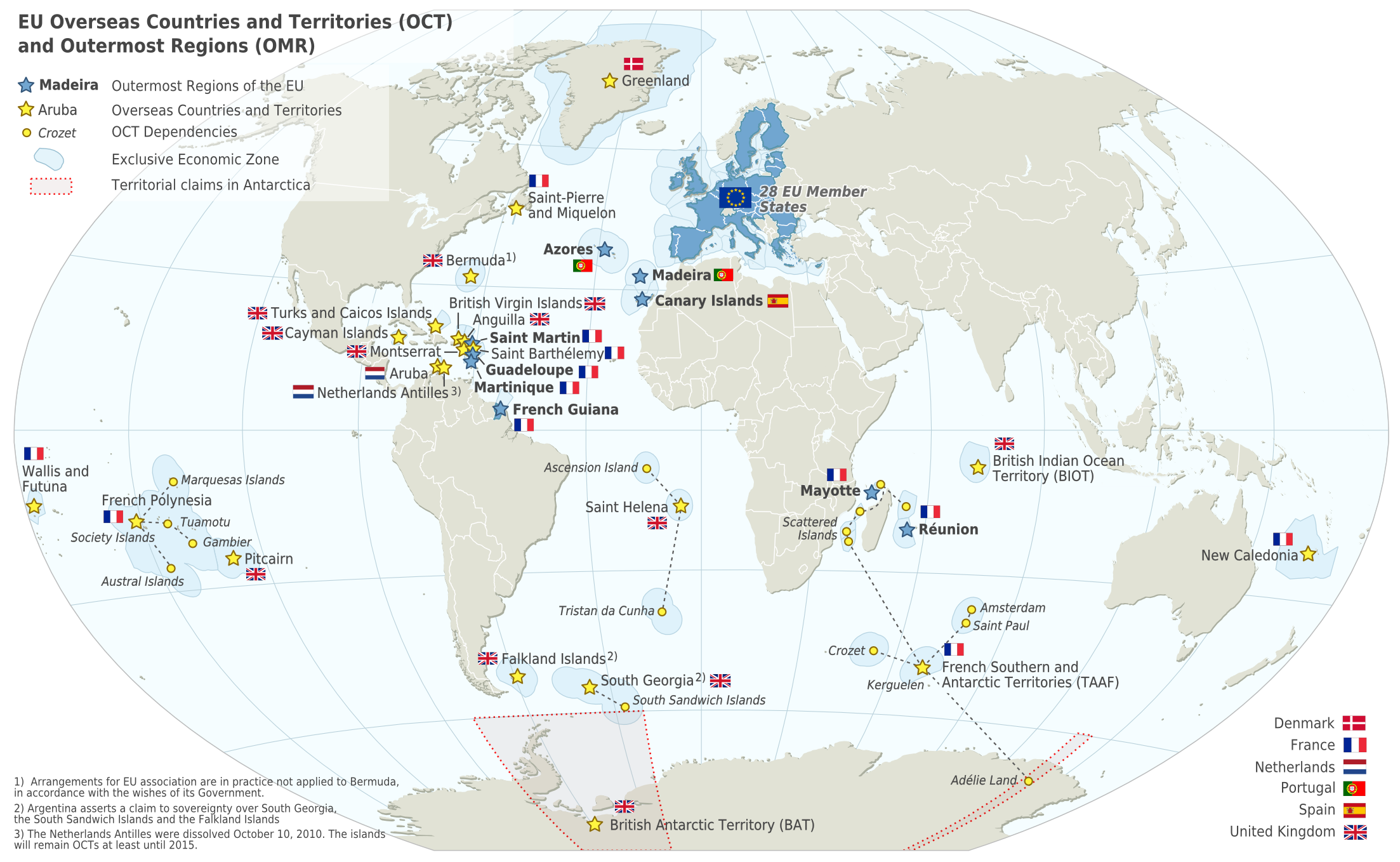
France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its Metropolitan France, metropolitan area extends from the Rhine to the Atlantic Ocean and from the Mediterranean Sea to the English Channel and the North Sea; overseas territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the North Atlantic, the French West Indies, and many islands in Oceania and the Indian Ocean. Due to its several coastal territories, France has the largest exclusive economic zone in the world. France borders Belgium, Luxembourg, Germany, Switzerland, Monaco, Italy, Andorra, and Spain in continental Europe, as well as the Kingdom of the Netherlands, Netherlands, Suriname, and Brazil in the Americas via its overseas territories in French Guiana and Saint Martin (island), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Overseas Department
The overseas departments and regions of France (french: départements et régions d'outre-mer, ; ''DROM'') are departments of France that are outside metropolitan France, the European part of France. They have exactly the same status as mainland France's regions and departments. The French Constitution provides that, in general, French laws and regulations (France's civil code, penal code, administrative law, social laws, tax laws, etc.) apply to French overseas regions the same as in metropolitan France, but can be adapted as needed to suit the region's particular needs. Hence, the local administrations of French overseas regions cannot themselves pass new laws. As integral parts of France and the European Union, overseas departments are represented in the National Assembly, Senate, and Economic and Social Council, vote to elect members of the European Parliament (MEP), and also use the euro as their currency. The overseas departments and regions are not the same as the overs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Martinique
Martinique ( , ; gcf, label=Martinican Creole, Matinik or ; Kalinago: or ) is an island and an overseas department/region and single territorial collectivity of France. An integral part of the French Republic, Martinique is located in the Lesser Antilles of the West Indies in the eastern Caribbean Sea. It has a land area of and a population of 364,508 inhabitants as of January 2019.Populations légales 2019: 972 Martinique INSEE One of the , it is directly north of Saint Lucia, northwest of |
Harold Gillies
Sir Harold Delf Gillies (17 June 1882 – 10 September 1960) was a New Zealand otolaryngologist and father of modern plastic surgery. Early life Gillies was born in Dunedin, New Zealand, the son of Member of Parliament in Otago, Robert Gillies. He attended Wanganui Collegiate School and studied medicine at Gonville and Caius College, Cambridge, where despite a stiff elbow sustained sliding down the banisters at home as a child, he was an excellent sportsman. He was a golf blue in 1903, 1904 and 1905 and also a rowing blue, competing in the 1904 Boat Race. Career World War I Following the outbreak of World War I he joined the Royal Army Medical Corps. Initially posted to Wimereux, near Boulogne, he acted as medical minder to a French-American dentist, Valadier, who was not allowed to operate unsupervised but was attempting to develop jaw repair work. Gillies, eager after seeing Valadier experimenting with nascent skin graft techniques, then decided to leave for Paris, to meet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
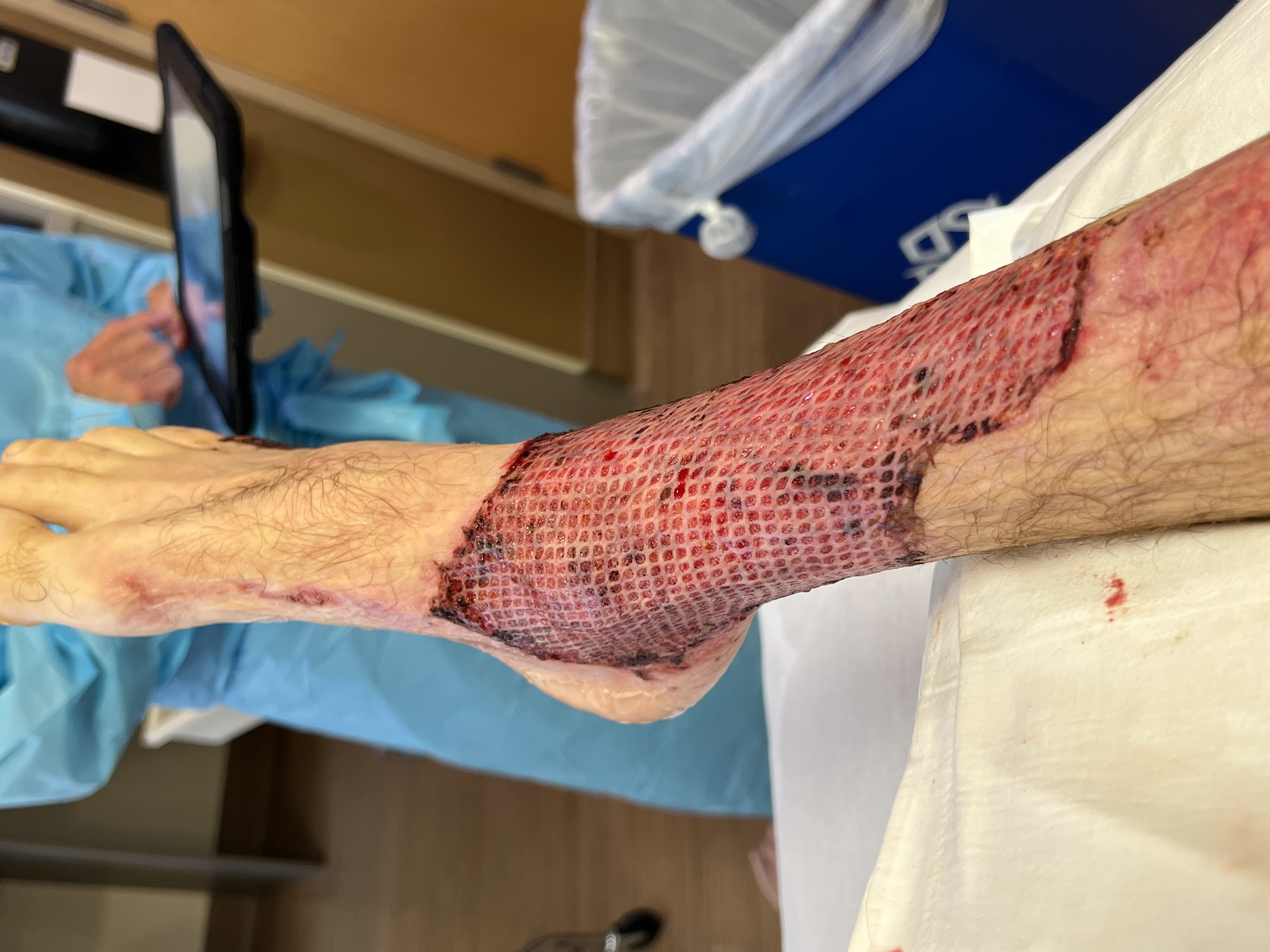
Skin Grafting
Skin grafting, a type of graft surgery, involves the transplantation of skin. The transplanted tissue is called a skin graft. Surgeons may use skin grafting to treat: * extensive wounding or trauma * burns * areas of extensive skin loss due to infection such as necrotizing fasciitis or purpura fulminans * specific surgeries that may require skin grafts for healing to occur - most commonly removal of skin cancers Skin grafting often takes place after serious injuries when some of the body's skin is damaged. Surgical removal (excision or debridement) of the damaged skin is followed by skin grafting. The grafting serves two purposes: reducing the course of treatment needed (and time in the hospital), and improving the function and appearance of the area of the body which receives the skin graft. There are two types of skin grafts: * The more common type involves removing a thin layer of skin from a healthy part of the body (the donor section) - like peeling a potato. * A full ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1918 Flu Pandemic
The 1918–1920 influenza pandemic, commonly known by the misnomer Spanish flu or as the Great Influenza epidemic, was an exceptionally deadly global influenza pandemic caused by the H1N1 influenza A virus. The earliest documented case was March 1918 in Kansas, United States, with further cases recorded in France, Germany and the United Kingdom in April. Two years later, nearly a third of the global population, or an estimated 500 million people, had been infected in four successive waves. Estimates of deaths range from 17 million to 50 million, and possibly as high as 100 million, making it one of the deadliest pandemics in history. The pandemic broke out near the end of World War I, when wartime censors suppressed bad news in the belligerent countries to maintain morale, but newspapers freely reported the outbreak in neutral Spain, creating a false impression of Spain as the epicenter and leading to the "Spanish flu" misnomer. Limited historical epidemiological ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1869 Births
Events January–March * January 3 – Abdur Rahman Khan is defeated at Tinah Khan, and exiled from Afghanistan. * January 5 – Scotland's oldest professional football team, Kilmarnock F.C., is founded. * January 20 – Elizabeth Cady Stanton is the first woman to testify before the United States Congress. * January 21 – The P.E.O. Sisterhood, a philanthropic educational organization for women, is founded at Iowa Wesleyan College in Mount Pleasant, Iowa. * January 27 – The Republic of Ezo is proclaimed on the northern Japanese island of Ezo (which will be renamed Hokkaidō on September 20) by remaining adherents to the Tokugawa shogunate. * February 5 – Prospectors in Moliagul, Victoria, Australia, discover the largest alluvial gold nugget ever found, known as the "Welcome Stranger". * February 20 – Ranavalona II, the Merina Queen of Madagascar, is baptized. * February 25 – The Iron and Steel Institute is formed in Lon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |