|
Hipparchus Of Nicaea
Hipparchus (; el, Ἵππαρχος, ''Hipparkhos''; BC) was a Greek astronomer, geographer, and mathematician. He is considered the founder of trigonometry, but is most famous for his incidental discovery of the precession of the equinoxes. Hipparchus was born in Nicaea, Bithynia, and probably died on the island of Rhodes, Greece. He is known to have been a working astronomer between 162 and 127 BC. Hipparchus is considered the greatest ancient astronomical observer and, by some, the greatest overall astronomer of antiquity. He was the first whose quantitative and accurate models for the motion of the Sun and Moon survive. For this he certainly made use of the observations and perhaps the mathematical techniques accumulated over centuries by the Babylonians and by Meton of Athens (fifth century BC), Timocharis, Aristyllus, Aristarchus of Samos, and Eratosthenes, among others. He developed trigonometry and constructed trigonometric tables, and he solved several pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nicaea
Nicaea, also known as Nicea or Nikaia (; ; grc-gre, Νίκαια, ) was an ancient Greek city in Bithynia, where located in northwestern Anatolia and is primarily known as the site of the First and Second Councils of Nicaea (the first and seventh Ecumenical councils in the early history of the Christian Church), the Nicene Creed (which comes from the First Council), and as the capital city of the Empire of Nicaea following the Fourth Crusade in 1204, until the recapture of Constantinople by the Byzantines in 1261. The ancient city is located within the modern Turkish city of İznik (whose modern name derives from Nicaea's), and is situated in a fertile basin at the eastern end of Lake Ascanius, bounded by ranges of hills to the north and south. It is situated with its west wall rising from the lake itself, providing both protection from siege from that direction, as well as a source of supplies which would be difficult to cut off. The lake is large enough that it coul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Babylonia
Babylonia (; Akkadian: , ''māt Akkadī'') was an ancient Akkadian-speaking state and cultural area based in the city of Babylon in central-southern Mesopotamia (present-day Iraq and parts of Syria). It emerged as an Amorite-ruled state c. 1894 BCE. During the reign of Hammurabi and afterwards, Babylonia was called "the country of Akkad" (''Māt Akkadī'' in Akkadian), a deliberate archaism in reference to the previous glory of the Akkadian Empire. It was often involved in rivalry with the older state of Assyria to the north and Elam to the east in Ancient Iran. Babylonia briefly became the major power in the region after Hammurabi (fl. c. 1792–1752 BCE middle chronology, or c. 1696–1654 BCE, short chronology) created a short-lived empire, succeeding the earlier Akkadian Empire, Third Dynasty of Ur, and Old Assyrian Empire. The Babylonian Empire rapidly fell apart after the death of Hammurabi and reverted to a small kingdom. Like Assyria, the Babylonian state ret ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jean Baptiste Joseph Delambre
Jean Baptiste Joseph, chevalier Delambre (19 September 1749 – 19 August 1822) was a French mathematician, astronomer, historian of astronomy, and geodesist. He was also director of the Paris Observatory, and author of well-known books on the history of astronomy from ancient times to the 18th century. Biography After a childhood fever, he suffered from very sensitive eyes, and believed that he would soon go blind. For fear of losing his ability to read, he devoured any book available and trained his memory. He thus immersed himself in Greek and Latin literature, acquired the ability to recall entire pages verbatim weeks after reading them, became fluent in Italian, English and German and even wrote an unpublished ''Règle ou méthode facile pour apprendre la langue anglaise'' (Easy rule or method for learning English). Delambre's quickly achieved success in his career in astronomy, such that in 1788, he was elected a foreign member of the Royal Swedish Academy of Scien ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Armillary Sphere
An armillary sphere (variations are known as spherical astrolabe, armilla, or armil) is a model of objects in the sky (on the celestial sphere), consisting of a spherical framework of rings, centered on Earth or the Sun, that represent lines of celestial longitude and latitude and other astronomically important features, such as the ecliptic. As such, it differs from a celestial globe, which is a smooth sphere whose principal purpose is to map the constellations. It was invented separately first in ancient China during the 4th century BC and ancient Greece during the 3rd century BC, with later uses in the Islamic world and Medieval Europe. With the Earth as center, an armillary sphere is known as '' Ptolemaic''. With the Sun as center, it is known as '' Copernican''. The flag of Portugal features an armillary sphere. The armillary sphere is also featured in Portuguese heraldry, associated with the Portuguese discoveries during the Age of Exploration. Manuel I of Portugal, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astrolabe
An astrolabe ( grc, ἀστρολάβος ; ar, ٱلأَسْطُرلاب ; persian, ستارهیاب ) is an ancient astronomical instrument that was a handheld model of the universe. Its various functions also make it an elaborate inclinometer and an analog calculation device capable of working out several kinds of problems in astronomy. In its simplest form it is a metal disc with a pattern of wires, cutouts, and perforations that allows a user to calculate astronomical positions precisely. Historically used by astronomers, it is able to measure the altitude above the horizon of a celestial body, day or night; it can be used to identify stars or planets, to determine local latitude given local time (and vice versa), to survey, or to triangulate. It was used in classical antiquity, the Islamic Golden Age, the European Middle Ages and the Age of Discovery for all these purposes. The astrolabe's importance comes not only from the early developments into the study of astron ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Star Catalog
A star catalogue is an astronomical catalogue that lists stars. In astronomy, many stars are referred to simply by catalogue numbers. There are a great many different star catalogues which have been produced for different purposes over the years, and this article covers only some of the more frequently quoted ones. Star catalogues were compiled by many different ancient people, including the Babylonians, Greeks, Chinese, Persians, and Arabs. They were sometimes accompanied by a star chart for illustration. Most modern catalogues are available in electronic format and can be freely downloaded from space agencies' data centres. The largest is being compiled from the spacecraft Gaia and thus far has over a billion stars. Completeness and accuracy are described by the faintest limiting magnitude V (largest number) and the accuracy of the positions. Historical catalogues Ancient Near East From their existing records, it is known that the ancient Egyptians recorded the names of on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solar Eclipse
A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby obscuring the view of the Sun from a small part of the Earth, totally or partially. Such an alignment occurs during an eclipse season, approximately every six months, during the new moon phase, when the Moon's orbital plane is closest to the plane of the Earth's orbit. In a total eclipse, the disk of the Sun is fully obscured by the Moon. In partial and annular eclipses, only part of the Sun is obscured. Unlike a lunar eclipse, which may be viewed from anywhere on the night side of Earth, a solar eclipse can only be viewed from a relatively small area of the world. As such, although total solar eclipses occur somewhere on Earth every 18 months on average, they recur at any given place only once every 360 to 410 years. If the Moon were in a perfectly circular orbit and in the same orbital plane as Earth, there would be total solar eclipses once a month, at every new moon. Instead, because the Mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lunar Theory
Lunar theory attempts to account for the motions of the Moon. There are many small variations (or perturbations) in the Moon's motion, and many attempts have been made to account for them. After centuries of being problematic, lunar motion can now be modeled to a very high degree of accuracy (see section Modern developments). Lunar theory includes: * the background of general theory; including mathematical techniques used to analyze the Moon's motion and to generate formulae and algorithms for predicting its movements; and also * quantitative formulae, algorithms, and geometrical diagrams that may be used to compute the Moon's position for a given time; often by the help of tables based on the algorithms. Lunar theory has a history of over 2000 years of investigation. Its more modern developments have been used over the last three centuries for fundamental scientific and technological purposes, and are still being used in that way. Applications Applications of lunar theory have i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
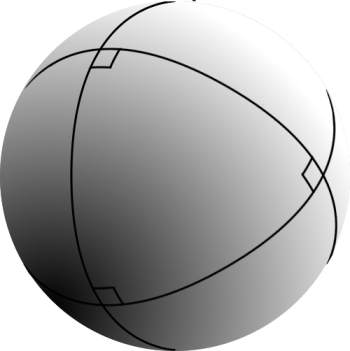
Spherical Trigonometry
Spherical trigonometry is the branch of spherical geometry that deals with the metrical relationships between the sides and angles of spherical triangles, traditionally expressed using trigonometric functions. On the sphere, geodesics are great circles. Spherical trigonometry is of great importance for calculations in astronomy, geodesy, and navigation. The origins of spherical trigonometry in Greek mathematics and the major developments in Islamic mathematics are discussed fully in History of trigonometry and Mathematics in medieval Islam. The subject came to fruition in Early Modern times with important developments by John Napier, Delambre and others, and attained an essentially complete form by the end of the nineteenth century with the publication of Todhunter's textbook ''Spherical trigonometry for the use of colleges and Schools''. Since then, significant developments have been the application of vector methods, quaternion methods, and the use of numerical methods. P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
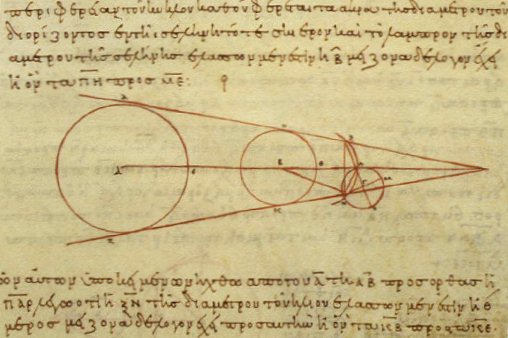
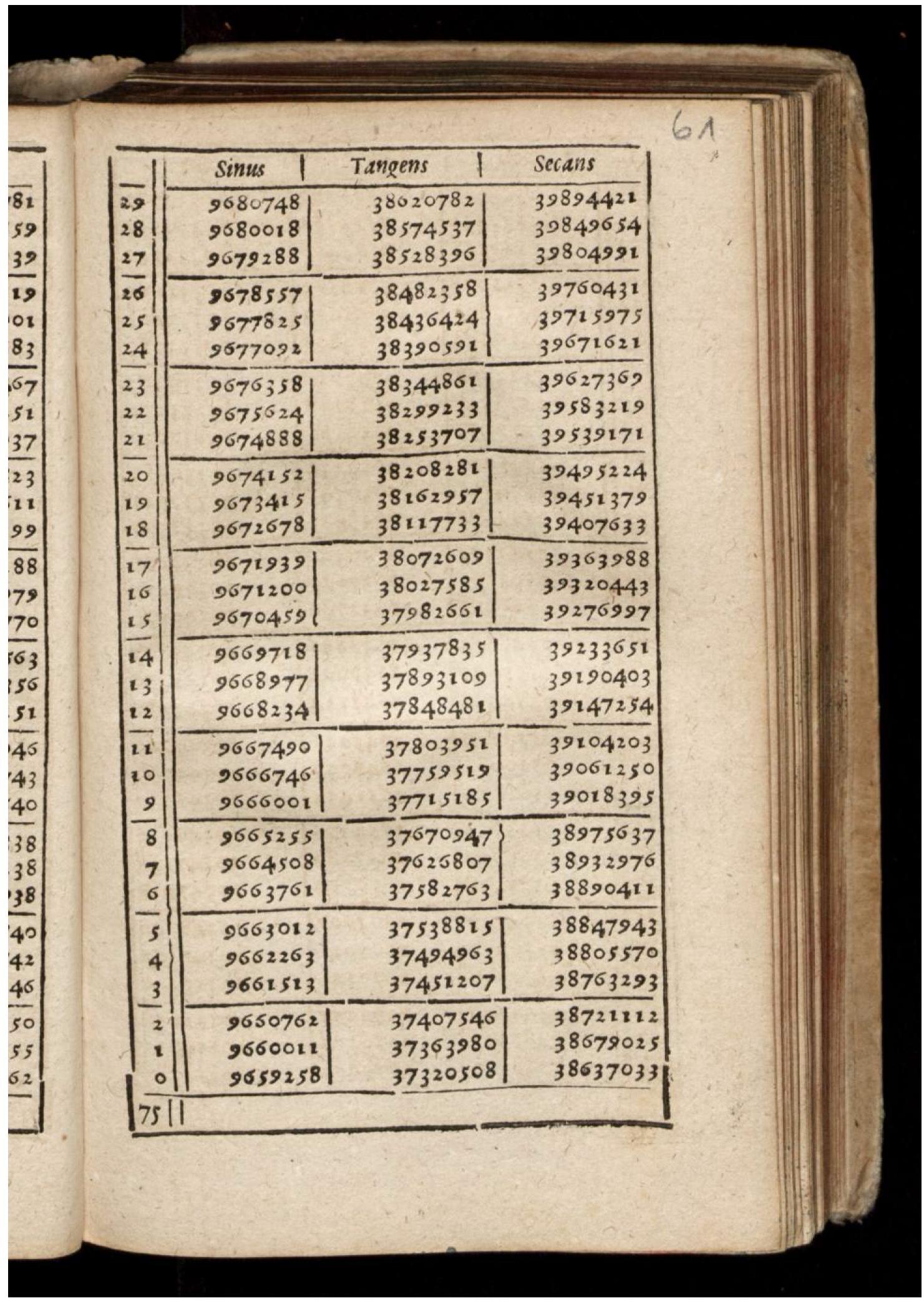
Trigonometric Tables
In mathematics, tables of trigonometric functions are useful in a number of areas. Before the existence of pocket calculators, trigonometric tables were essential for navigation, science and engineering. The calculation of mathematical tables was an important area of study, which led to the development of the first mechanical computing devices. Modern computers and pocket calculators now generate trigonometric function values on demand, using special libraries of mathematical code. Often, these libraries use pre-calculated tables internally, and compute the required value by using an appropriate interpolation method. Interpolation of simple look-up tables of trigonometric functions is still used in computer graphics, where only modest accuracy may be required and speed is often paramount. Another important application of trigonometric tables and generation schemes is for fast Fourier transform (FFT) algorithms, where the same trigonometric function values (called ''twiddle fa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eratosthenes
Eratosthenes of Cyrene (; grc-gre, Ἐρατοσθένης ; – ) was a Greek polymath: a mathematician, geographer, poet, astronomer, and music theorist. He was a man of learning, becoming the chief librarian at the Library of Alexandria. His work is comparable to what is now known as the study of geography, and he introduced some of the terminology still used today. He is best known for being the first person known to calculate the circumference of the Earth, which he did by using the extensive survey results he could access in his role at the Library; his calculation was remarkably accurate. He was also the first to calculate Earth's axial tilt, which has also proved to have remarkable accuracy. He created the first global projection of the world, incorporating parallels and meridians based on the available geographic knowledge of his era. Eratosthenes was the founder of scientific chronology; he used Egyptian and Persian records to estimate the dates of the ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aristarchus Of Samos
Aristarchus of Samos (; grc-gre, Ἀρίσταρχος ὁ Σάμιος, ''Aristarkhos ho Samios''; ) was an ancient Greek astronomer and mathematician who presented the first known heliocentric model that placed the Sun at the center of the known universe, with the Earth revolving around the Sun once a year and rotating about its axis once a day. He was a student of Strato of Lampsacus, who was the third head of the Peripatetic School in Greece. According to Ptolemy, during Aristarchus' time there, he observed the summer solstice of 280 BCE. Along with his contributions to the heliocentric model, as reported by Vitruvius, he created two separate sundials: one that is a flat disc; and one hemispherical. Aristarchus was influenced by the concept presented by Philolaus of Croton (c. 470 – 385 BCE) of a fire at the center of the universe, but Aristarchus identified the "central fire" with the Sun and he put the other planets in their correct order of distance around t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)






.jpg)