|
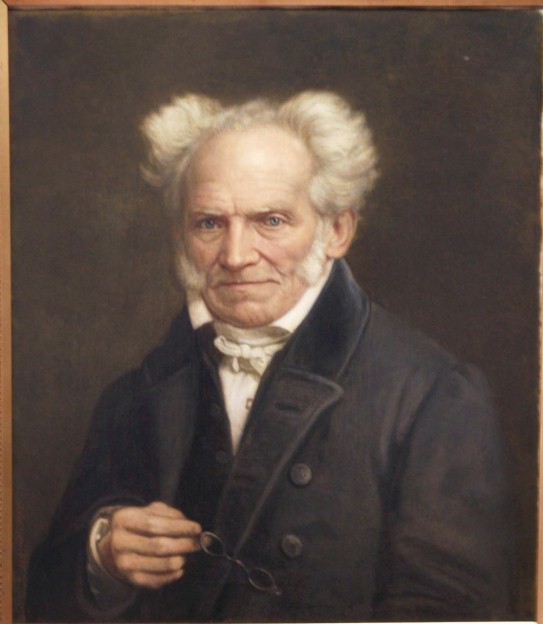
Hedgehog's Dilemma
The hedgehog's dilemma, or sometimes the porcupine dilemma, is a metaphor about the challenges of human intimacy. It describes a situation in which a group of hedgehogs seek to move close to one another to share heat during cold weather. They must remain apart, however, as they cannot avoid hurting one another with their sharp spines. Though they all share the intention of a close reciprocal relationship, this cannot occur, for unavoidable reasons. Arthur Schopenhauer conceived this metaphor for the state of the individual in society. Despite goodwill, humans cannot be intimate without the risk of mutual harm, leading to cautious and tentative relationships. It could be seen as wise to be guarded with others for fear of getting hurt and also fear of causing hurt, however this may lead to unsatisfying relationships. The dilemma may encourage self-imposed isolation. Schopenhauer The concept originates in the following parable from the German philosopher Schopenhauer: One ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psychological Sciences
Psychology is the scientific study of mind and behavior. Its subject matter includes the behavior of humans and nonhumans, both conscious and unconscious phenomena, and mental processes such as thoughts, feelings, and motives. Psychology is an academic discipline of immense scope, crossing the boundaries between the natural and social sciences. Biological psychologists seek an understanding of the emergent properties of brains, linking the discipline to neuroscience. As social scientists, psychologists aim to understand the behavior of individuals and groups.Hockenbury & Hockenbury. Psychology. Worth Publishers, 2010. A professional practitioner or researcher involved in the discipline is called a psychologist. Some psychologists can also be classified as behavioral or cognitive scientists. Some psychologists attempt to understand the role of mental functions in individual and social behavior. Others explore the physiological and neurobiological processes that underlie cogn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philosophy Of Life
(; meaning "philosophy of life") was a dominant philosophical movement of German-speaking countries in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, which had developed out of German Romanticism. emphasised the meaning of life, meaning, value and purpose of life as the foremost focus of philosophy. Its central theme was that an understanding of life can only be apprehended by life itself, and from within itself. Drawing on the critiques of epistemology offered by Schopenhauer and Nietzsche, notable ideas of the movement have been seen as precursors to both Husserlian Phenomenology (philosophy), phenomenology and Heideggerian existential phenomenology. criticised both mechanism (philosophy), mechanistic and materialist approaches to science and philosophy and as such has also been referred to as the German vitalist movement, though its relationship to vitalism, biological vitalism is questionable. Vitality in this sense is instead understood as part of a biocentrism (ethics), biocen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metaphors Referring To Animals
A metaphor is a figure of speech that, for rhetorical effect, directly refers to one thing by mentioning another. It may provide, or obscure, clarity or identify hidden similarities between two different ideas. Metaphors are usually meant to create a likeness or an Analogy, analogy. Analysts group metaphors with other types of figurative language, such as antithesis, hyperbole, metonymy, and simile. According to Grammarly, "Figurative language examples include similes, metaphors, personification, hyperbole, allusions, and idioms." One of the most commonly cited examples of a metaphor in English literature comes from the "All the world's a stage" monologue from ''As You Like It'': All the world's a stage, And all the men and women merely players; They have their exits and their entrances And one man in his time plays many parts, His Acts being seven ages. At first, the infant... :—William Shakespeare, ''As You Like It'', 2/7 This quotation expresses a metaphor because the w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hedgehogs In Popular Culture
A hedgehog is a spiny mammal of the subfamily Erinaceinae, in the eulipotyphlan family Erinaceidae. There are 17 species of hedgehog in five genera found throughout parts of Europe, Asia, and Africa, and in New Zealand by introduction. There are no hedgehogs native to Australia and no living species native to the Americas. However, the extinct genus ''Amphechinus'' was once present in North America. Hedgehogs share distant ancestry with shrews (family Soricidae), with gymnures possibly being the intermediate link, and they have changed little over the last 15 million years. Like many of the first mammals, they have adapted to a nocturnal way of life. Their spiny protection resembles that of porcupines, which are rodents, and echidnas, a type of monotreme. Etymology The name ''hedgehog'' came into use around the year 1450, derived from the Middle English , from , , because it frequents hedgerows, and , , from its piglike snout. Other names that are used are ''urchin'' and ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dilemmas
A dilemma () is a problem offering two possibilities, neither of which is unambiguously acceptable or preferable. The possibilities are termed the ''horns'' of the dilemma, a clichéd usage, but distinguishing the dilemma from other kinds of predicament as a matter of usage. Terminology The term ''dilemma'' is attributed by Gabriel Nuchelmans to Lorenzo Valla in the 15th century, in later versions of his logic text traditionally called ''Dialectica''. Valla claimed that it was the appropriate Latin equivalent of the Greek ''dilemmaton''. Nuchelmans argued that his probable source was a logic text of of George of Trebizond. He also concluded that Valla had reintroduced to the Latin West a type of argument that had fallen into disuse. Valla's neologism did not immediately take hold, preference being given to the established Latin term ''complexio'', used by Cicero, with ''conversio'' applied to the upsetting of dilemmatic reasoning. With the support of Juan Luis Vives, however ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interpersonal Relationships
In social psychology, an interpersonal relation (or interpersonal relationship) describes a social association, connection, or affiliation between two or more people. It overlaps significantly with the concept of social relations, which are the fundamental unit of analysis within the social sciences. Relations vary in degrees of intimacy, self-disclosure, duration, reciprocity, and power distribution. The main themes or trends of the interpersonal relations are: family, kinship, friendship, love, marriage, business, employment, clubs, neighborhoods, ethical values, support and solidarity. Interpersonal relations may be regulated by law, custom, or mutual agreement, and form the basis of social groups and societies. They appear when people communicate or act with each other within specific social contexts, and they thrive on equitable and reciprocal compromises. Interdisciplinary analysis of relationships draws heavily upon the other social sciences, including, but ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philosophy Of Arthur Schopenhauer
Philosophy ('love of wisdom' in Ancient Greek) is a systematic study of general and fundamental questions concerning topics like existence, reason, knowledge, value, mind, and language. It is a rational and critical inquiry that reflects on its methods and assumptions. Historically, many of the individual sciences, such as physics and psychology, formed part of philosophy. However, they are considered separate academic disciplines in the modern sense of the term. Influential traditions in the history of philosophy include Western, Arabic–Persian, Indian, and Chinese philosophy. Western philosophy originated in Ancient Greece and covers a wide area of philosophical subfields. A central topic in Arabic–Persian philosophy is the relation between reason and revelation. Indian philosophy combines the spiritual problem of how to reach enlightenment with the exploration of the nature of reality and the ways of arriving at knowledge. Chinese philosophy focuses principally on pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |