|
Heat Meter
A heat meter attached to a heat exchanger in a District heating substation in a residential neighborhood. Right in white-blue: the calculator; in the center in bronze: the ultrasonic flow meter A heat meter, thermal energy meter or energy meter is a device which measures thermal energy provided by a heater, source or delivered to a heat sink, sink, by measuring the flow rate of the heat transfer fluid and the change in its temperature ( ΔT) between the outflow and return legs of the system. It is typically used in industrial plants for measuring boiler output and heat taken by process, and for district heating systems to measure the heat delivered to consumers. It can be used to measure the heat output of say a heating boiler, or the cooling output from a chiller unit. In Europe heat meters have to comply with the measuring instruments directive MID Annex VI MI-004 if the meters are used for custody transfer. Elements A heat meter consists of # a fluid flow meter - typica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heater
Heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC ) is the use of various technologies to control the temperature, humidity, and purity of the air in an enclosed space. Its goal is to provide thermal comfort and acceptable indoor air quality. HVAC system design is a subdiscipline of mechanical engineering, based on the principles of thermodynamics, fluid mechanics, and heat transfer. "Refrigeration" is sometimes added to the field's abbreviation as HVAC&R or HVACR, or "ventilation" is dropped, as in HACR (as in the designation of HACR-rated circuit breakers). HVAC is an important part of residential structures such as single family homes, apartment buildings, hotels, and senior living facilities; medium to large industrial and office buildings such as skyscrapers and hospitals; vehicles such as cars, trains, airplanes, ships and submarines; and in marine environments, where safe and healthy building conditions are regulated with respect to temperature and humidity, using fre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heat Sink
A heat sink (also commonly spelled heatsink) is a passive heat exchanger that transfers the heat generated by an electronic or a mechanical device to a fluid medium, often air or a liquid coolant, where it is thermal management (electronics), dissipated away from the device, thereby allowing regulation of the device's temperature. In computers, heat sinks computer cooling, are used to cool central processing unit, CPUs, graphics processing unit, GPUs, and some chipsets and RAM modules. Heat sinks are used with other high-power semiconductor devices such as Transistor#Other transistor types, power transistors and optoelectronics such as lasers and light-emitting diodes (LEDs), where the heat dissipation ability of the component itself is insufficient to moderate its temperature. A heat sink is designed to maximize its surface area in contact with the cooling medium surrounding it, such as the air. Air velocity, choice of material, protrusion design and surface treatment are fact ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
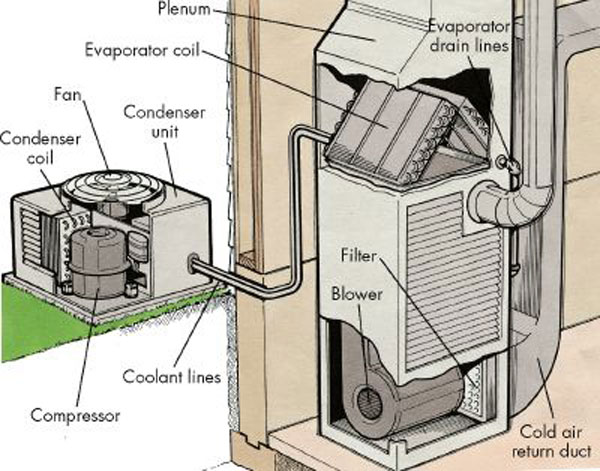
Coolant
A coolant is a substance, typically liquid, that is used to reduce or regulate the temperature of a system. An ideal coolant has high thermal capacity, low viscosity, is low-cost, non-toxic, chemically inert and neither causes nor promotes corrosion of the cooling system. Some applications also require the coolant to be an electrical insulator. While the term "coolant" is commonly used in automotive and HVAC applications, in industrial processing heat-transfer fluid is one technical term more often used in high temperature as well as low-temperature manufacturing applications. The term also covers cutting fluids. Industrial cutting fluid has broadly been classified as water-soluble coolant and neat cutting fluid. Water-soluble coolant is oil in water emulsion. It has varying oil content from nil oil (synthetic coolant). This coolant can either keep its phase and stay liquid or gaseous, or can undergo a phase transition, with the latent heat adding to the cooling efficiency. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psychrometrics
Psychrometrics (or psychrometry, ; also called hygrometry) is the field of engineering concerned with the physical and thermodynamic properties of gas-vapor mixtures. History With the inventions of the hygrometer and thermometer, the theories of combining the two began to emerge during the sixteenth and seventeenth centuries. In 1818, a German inventor, Ernst Ferdinand August (1795-1870), patented the term “psychrometer”, from the Greek language meaning “cold measure”. The psychrometer is a hygrometer, hygrometric instrument based on the principle that dry air enhances evaporation, unlike wet air, which slows it. Common applications Although the principles of psychrometry apply to any physical system consisting of gas-vapor mixtures, the most common system of interest is the mixture of water vapor and air, because of its application in HVAC, heating, ventilation, and air-conditioning and meteorology. In human terms, our thermal comfort is in large part a consequence ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
District Heating
District heating (also known as heat networks) is a system for distributing heat generated in a centralized location through a system of insulated pipes for residential and commercial heating requirements such as space heater, space heating and water heating. The heat is often obtained from a cogeneration plant burning fossil fuels or biomass, but heating plant, heat-only boiler stations, geothermal heating, heat pumps and central solar heating are also used, as well as heat waste from factories and nuclear power electricity generation. District heating plants can provide higher efficiencies and better pollution control than localized boilers. According to some research, district heating with combined heat and power (CHPDH) is the cheapest method of cutting carbon emissions, and has one of the lowest carbon footprints of all fossil generation plants. District heating is ranked number 27 in Drawdown (climate), Project Drawdown's 100 solutions to climate change, global warming. His ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Measuring Instruments Directive
The Measuring Instruments Directive 2014/32/EU, formerly 2004/22/EC, is a directive by the European Union, which seeks to harmonise many aspects of legal metrology across all member states of the EU. Retrieved 25 March 2014 Its most prominent tenet is that all kinds of meters which receive a MID approval may be used in all countries across the EU. Measuring Instruments Directive 2004/22/EC The MID covers these measuring instruments: * Water meters * Gas meters and volume conversion devices * Active electrical energy meters * Heat meters * Measuring systems for the continuous and dynamic measurement of quantities of liquids other than water * Automatic weighing instruments * Taximeters * Material measures * Dimensioning systems * Exhaust gas analys ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
District Heating
District heating (also known as heat networks) is a system for distributing heat generated in a centralized location through a system of insulated pipes for residential and commercial heating requirements such as space heater, space heating and water heating. The heat is often obtained from a cogeneration plant burning fossil fuels or biomass, but heating plant, heat-only boiler stations, geothermal heating, heat pumps and central solar heating are also used, as well as heat waste from factories and nuclear power electricity generation. District heating plants can provide higher efficiencies and better pollution control than localized boilers. According to some research, district heating with combined heat and power (CHPDH) is the cheapest method of cutting carbon emissions, and has one of the lowest carbon footprints of all fossil generation plants. District heating is ranked number 27 in Drawdown (climate), Project Drawdown's 100 solutions to climate change, global warming. His ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heat Cost Allocator
Heat cost allocators are devices attached to individual radiators in buildings that measure the total heat output of the individual radiator. Heat cost allocators can be either electronic, where one or two electronic thermosensors and a microcontroller are used to calculate the heat consumption of radiator by the temperature difference between the radiator and the air in room, or evaporative, where a special, calibrated liquid in a capillary tube records the total heat absorbed from the air (for which an average allowance is made) in addition to that output by the radiator. Tubes filled with methyl benzoate according to DIN EN 835 can be used by checking the color change. Working principle As the radiator heats up, the back section also heats up. The temperature (or the temperature difference to room temperature for electronic two-sensor devices) is integrated over the heating period (one year according to the heating costs ordinance) and thus forms the measured value. Since the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heating System
A heating system is a mechanism designed to regulate and maintain a desired temperature within a space by utilizing thermal energy. It is a fundamental component of Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning (HVAC) systems, providing warmth to residential, commercial, and industrial buildings. Heating systems are classified into two main types: central heating and distributed heating. Central heating systems generate heat (electrically or by burning gas/coal) in a single location and distribute the heat through ducts pipes or radiators. Distributed heating systems involve localized heat sources, such as space heaters or electric radiators. Distributed heating systems do not rely on the use of ducts, pipes or radiators. These systems are critical to ensure indoor comfort especially in colder regions. Types and uses Central heating systems: These systems produce heat in one central location and distribute it throughout the building. This category includes furnaces, boilers, and heat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermometer
A thermometer is a device that measures temperature (the hotness or coldness of an object) or temperature gradient (the rates of change of temperature in space). A thermometer has two important elements: (1) a temperature sensor (e.g. the bulb of a mercury-in-glass thermometer or the pyrometric sensor in an infrared thermometer) in which some change occurs with a change in temperature; and (2) some means of converting this change into a numerical value (e.g. the visible scale that is marked on a mercury-in-glass thermometer or the digital readout on an infrared model). Thermometers are widely used in technology and industry to monitor processes, in meteorology, in medicine (''medical thermometer''), and in scientific research. A standard scale While an individual thermometer is able to measure degrees of hotness, the readings on two thermometers cannot be compared unless they conform to an agreed scale. Today there is an absolute thermodynamic temperature scale. Internat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |