|
Gray's Anatomy For Students
''Gray's Anatomy for Students'' is an anatomy textbook inspired by the famous '' Gray's Anatomy'' (Grey's Anatomy) and aimed primarily at medical students A medical school is a tertiary educational institution, or part of such an institution, that teaches medicine, and awards a professional degree for physicians. Such medical degrees include the Bachelor of Medicine, Bachelor of Surgery (MBBS, MB .... The textbook has been praised for its innovative illustration style, which emphasizes clarity and a conceptual approach to learning. The text aims to display the basic concepts for chiropractic, dental, medical, and physical therapy students. ''Gray's Anatomy'' was used as the major reference, both for the text and the illustrations.''Gray's Anatomy for Students'', page xi, paragraph 3. References Anatomy books Gray's Anatomy Medical manuals Medical students 2004 books {{med-book-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Wales to its west and Scotland to its north. The Irish Sea lies northwest and the Celtic Sea to the southwest. It is separated from continental Europe by the North Sea to the east and the English Channel to the south. The country covers five-eighths of the island of Great Britain, which lies in the North Atlantic, and includes over 100 smaller islands, such as the Isles of Scilly and the Isle of Wight. The area now called England was first inhabited by modern humans during the Upper Paleolithic period, but takes its name from the Angles, a Germanic tribe deriving its name from the Anglia peninsula, who settled during the 5th and 6th centuries. England became a unified state in the 10th century and has had a significant cultural and legal impact on the wider world since the Age of Discovery, which began during the 15th century. The English language, the Anglican Church, and Engli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
English Language
English is a West Germanic language of the Indo-European language family, with its earliest forms spoken by the inhabitants of early medieval England. It is named after the Angles, one of the ancient Germanic peoples that migrated to the island of Great Britain. Existing on a dialect continuum with Scots, and then closest related to the Low Saxon and Frisian languages, English is genealogically West Germanic. However, its vocabulary is also distinctively influenced by dialects of France (about 29% of Modern English words) and Latin (also about 29%), plus some grammar and a small amount of core vocabulary influenced by Old Norse (a North Germanic language). Speakers of English are called Anglophones. The earliest forms of English, collectively known as Old English, evolved from a group of West Germanic (Ingvaeonic) dialects brought to Great Britain by Anglo-Saxon settlers in the 5th century and further mutated by Norse-speaking Viking settlers starting in the 8 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
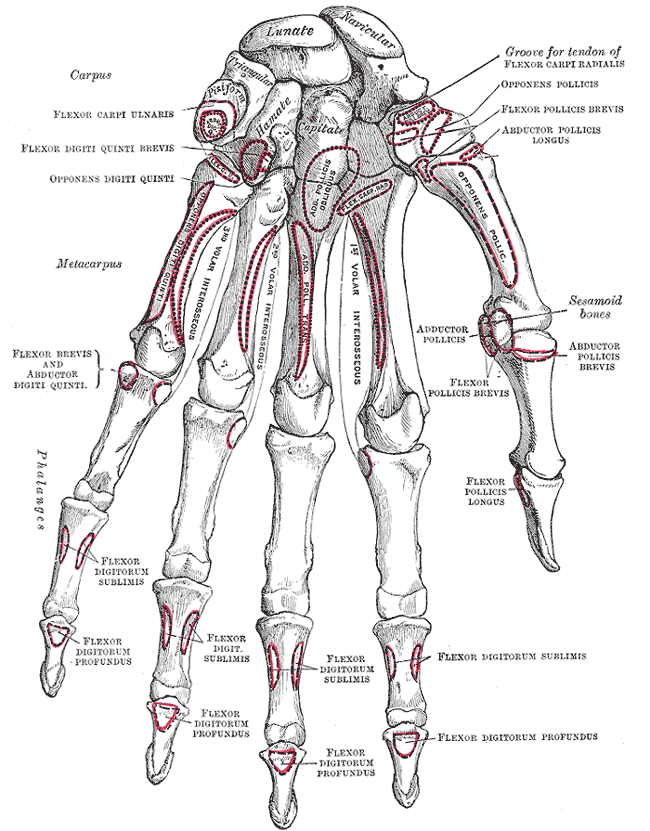
Human Anatomy
The human body is the structure of a human being. It is composed of many different types of cells that together create tissues and subsequently organ systems. They ensure homeostasis and the viability of the human body. It comprises a head, hair, neck, trunk (which includes the thorax and abdomen), arms and hands, legs and feet. The study of the human body involves anatomy, physiology, histology and embryology. The body varies anatomically in known ways. Physiology focuses on the systems and organs of the human body and their functions. Many systems and mechanisms interact in order to maintain homeostasis, with safe levels of substances such as sugar and oxygen in the blood. The body is studied by health professionals, physiologists, anatomists, and by artists to assist them in their work. Composition The human body is composed of elements including hydrogen, oxygen, carbon, calcium and phosphorus. These elements reside in trillions of cells and non-cellular c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Churchill Livingstone
Churchill Livingstone is an academic publisher. It was formed in 1971 from the merger of Longman's medical list, E & S Livingstone (Edinburgh, Scotland) and J & A Churchill (London, England) and was owned by Pearson PLC, Pearson. Harcourt (publisher), Harcourt acquired Churchill Livingstone in 1997. It is now integrated as an imprint (trade name), imprint in Elsevier's health science division after Elsevier acquired Harcourt in 2001. In the past it published a number of classic medical texts, including Sir William Osler's textbook ''The Principles and Practice of Medicine, Gray's Anatomy,'' and ''Margaret Myles, Myles' Textbook for Midwives.'' In the 1980s, in addition to new texts in all areas of clinical medicine, it published an extensive list of medical and nursing textbooks in low-cost editions for low-income countries supported by the UK-funded Educational Low Priced Book Scheme (ELBS). [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gray's Anatomy
''Gray's Anatomy'' is a reference book of human anatomy written by Henry Gray, illustrated by Henry Vandyke Carter, and first published in London in 1858. It has gone through multiple revised editions and the current edition, the 42nd (October 2020), remains a standard reference, often considered "the doctors' bible". Earlier editions were called ''Anatomy: Descriptive and Surgical'', ''Anatomy of the Human Body'' and ''Gray's Anatomy: Descriptive and Applied'', but the book's name is commonly shortened to, and later editions are titled, ''Gray's Anatomy''. The book is widely regarded as an extremely influential work on the subject. Publication history Origins The English anatomist Henry Gray was born in 1827. He studied the development of the endocrine glands and spleen and in 1853 was appointed Lecturer on Anatomy at St George's Hospital Medical School in London. In 1855, he approached his colleague Henry Vandyke Carter with his idea to produce an inexpensive and a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medical Students
A medical school is a tertiary educational institution, or part of such an institution, that teaches medicine, and awards a professional degree for physicians. Such medical degrees include the Bachelor of Medicine, Bachelor of Surgery (MBBS, MBChB, MBBCh, BMBS), Master of Medicine (MM, MMed), Doctor of Medicine (MD), or Doctor of Osteopathic Medicine (DO). Many medical schools offer additional degrees, such as a Doctor of Philosophy (PhD), master's degree (MSc) or other post-secondary education. Medical schools can also carry out medical research and operate teaching hospitals. Around the world, criteria, structure, teaching methodology, and nature of medical programs offered at medical schools vary considerably. Medical schools are often highly competitive, using standardized entrance examinations, as well as grade point averages and leadership roles, to narrow the selection criteria for candidates. In most countries, the study of medicine is completed as an undergraduate degre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anatomy Books
Anatomy () is the branch of biology concerned with the study of the structure of organisms and their parts. Anatomy is a branch of natural science that deals with the structural organization of living things. It is an old science, having its beginnings in prehistoric times. Anatomy is inherently tied to developmental biology, embryology, comparative anatomy, evolutionary biology, and phylogeny, as these are the processes by which anatomy is generated, both over immediate and long-term timescales. Anatomy and physiology, which study the structure and function of organisms and their parts respectively, make a natural pair of related disciplines, and are often studied together. Human anatomy is one of the essential basic sciences that are applied in medicine. The discipline of anatomy is divided into macroscopic and microscopic. Macroscopic anatomy, or gross anatomy, is the examination of an animal's body parts using unaided eyesight. Gross anatomy also includes the branch o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medical Manuals
Medicine is the science and practice of caring for a patient, managing the diagnosis, prognosis, prevention, treatment, palliation of their injury or disease, and promoting their health. Medicine encompasses a variety of health care practices evolved to maintain and restore health by the prevention and treatment of illness. Contemporary medicine applies biomedical sciences, biomedical research, genetics, and medical technology to diagnose, treat, and prevent injury and disease, typically through pharmaceuticals or surgery, but also through therapies as diverse as psychotherapy, external splints and traction, medical devices, biologics, and ionizing radiation, amongst others. Medicine has been practiced since prehistoric times, and for most of this time it was an art (an area of skill and knowledge), frequently having connections to the religious and philosophical beliefs of local culture. For example, a medicine man would apply herbs and say prayers for healing, or an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medical Students
A medical school is a tertiary educational institution, or part of such an institution, that teaches medicine, and awards a professional degree for physicians. Such medical degrees include the Bachelor of Medicine, Bachelor of Surgery (MBBS, MBChB, MBBCh, BMBS), Master of Medicine (MM, MMed), Doctor of Medicine (MD), or Doctor of Osteopathic Medicine (DO). Many medical schools offer additional degrees, such as a Doctor of Philosophy (PhD), master's degree (MSc) or other post-secondary education. Medical schools can also carry out medical research and operate teaching hospitals. Around the world, criteria, structure, teaching methodology, and nature of medical programs offered at medical schools vary considerably. Medical schools are often highly competitive, using standardized entrance examinations, as well as grade point averages and leadership roles, to narrow the selection criteria for candidates. In most countries, the study of medicine is completed as an undergraduate degre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |