|
Geological History Of Mars
The geological history of Mars follows the physical evolution of Mars as substantiated by observations, indirect and direct measurements, and various inference techniques. Methods dating back to 17th century techniques developed by Nicholas Steno, including the so-called law of superposition and stratigraphy, used to estimate the geological histories of Earth and the Moon, are being actively applied to the data available from several Martian observational and measurement resources. These include the landers, orbiting platforms, Earth-based observations, and Martian meteorites. Observations of the surfaces of many Solar System bodies reveal important clues about their evolution. For example, a lava flow that spreads out and fills a large impact crater is likely to be younger than the crater. On the other hand, a small crater on top of the same lava flow is likely to be younger than both the lava and the larger crater since it can be surmised to have been the product of a later, un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mars
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun and the second-smallest planet in the Solar System, only being larger than Mercury. In the English language, Mars is named for the Roman god of war. Mars is a terrestrial planet with a thin atmosphere (less than 1% that of Earth's), and has a crust primarily composed of elements similar to Earth's crust, as well as a core made of iron and nickel. Mars has surface features such as impact craters, valleys, dunes and polar ice caps. It has two small and irregularly shaped moons, Phobos and Deimos. Some of the most notable surface features on Mars include Olympus Mons, the largest volcano and highest known mountain in the Solar System and Valles Marineris, one of the largest canyons in the Solar System. The Borealis basin in the Northern Hemisphere covers approximately 40% of the planet and may be a large impact feature. Days and seasons on Mars are comparable to those of Earth, as the planets have a similar rotation period ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Absolute Dating
Absolute dating is the process of determining an age on a specified chronology in archaeology and geology. Some scientists prefer the terms chronometric or calendar dating, as use of the word "absolute" implies an unwarranted certainty of accuracy. Absolute dating provides a numerical age or range, in contrast with relative dating, which places events in order without any measure of the age between events. In archaeology, absolute dating is usually based on the physical, chemical, and life properties of the materials of artifacts, buildings, or other items that have been modified by humans and by historical associations with materials with known dates (such as coins and historical records). For example, coins found in excavations may have their production date written on them, or there may be written records describing the coin and when it was used, allowing the site to be associated with a particular calendar year. Absolute dating techniques include radiocarbon dating of wood o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
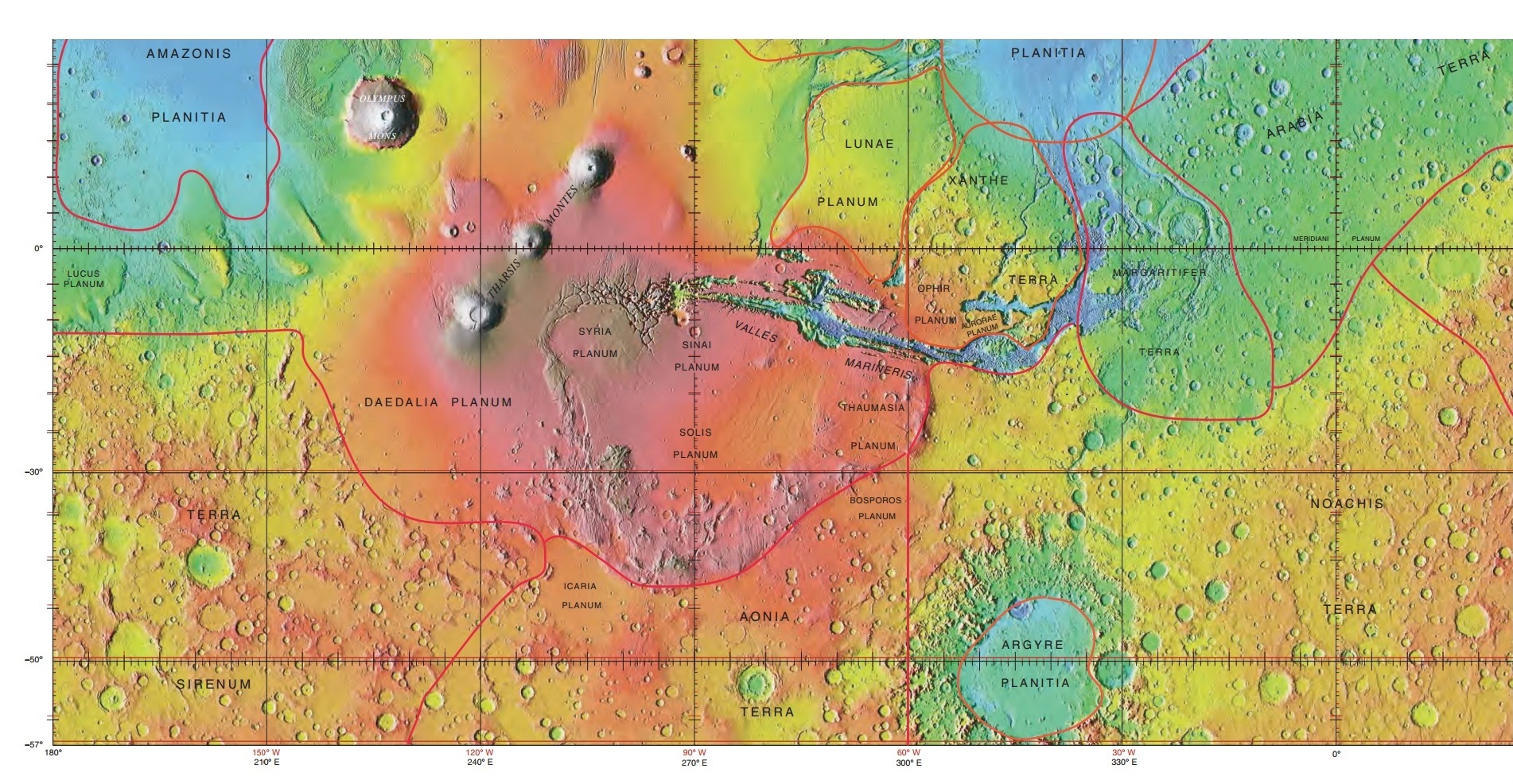
Tharsis Bulge
Tharsis () is a vast volcanic plateau centered near the equator in the western hemisphere of Mars. The region is home to the largest volcanoes in the Solar System, including the three enormous shield volcanoes Arsia Mons, Pavonis Mons, and Ascraeus Mons, which are collectively known as the Tharsis Montes. The tallest volcano on the planet, Olympus Mons, is often associated with the Tharsis region but is actually located off the western edge of the plateau. The name Tharsis is the Greco-Latin transliteration of the biblical Tarshish, the land at the western extremity of the known world. Location and size Tharsis can have many meanings depending on historical and scientific context. The name is commonly used in a broad sense to represent a continent-sized region of anomalously elevated terrain centered just south of the equator around longitude 265°E.Carr, M.H. (2006). ''The Surface of Mars;'' Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, p. 46. . Called the Tharsis bulge or Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Noachis Terra
Noachis Terra (; lit. "Land of Noah") is an extensive southern landmass (''terra'') of the planet Mars. It lies west of the giant Hellas impact basin, roughly between the latitudes −20° and −80° and longitudes 30° west and 30° east, centered on . It is in the Noachis quadrangle. The term " Noachian epoch" is derived from this region. Gallery Dunes of Mars.jpg, A crater in Noachis Terra. The dunes here are linear, thought to be due to shifting wind directions. Image:Exhumed crater in Noachis.JPG, Crater that was buried in another age and is now being exposed by erosion, as seen by the Mars Global Surveyor, under the MOC Public Targeting Program. Image:24396floor.jpg, Floor of crater in Noachis quadrangle, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program. ESP 035632 1490noachiscraterfloor.jpg, Erosion forms on floor of crater, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program WikidarkdunesS0101212context.jpg, Context for image of dark dunes in next image. Picture taken with Mars Global ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Noachian
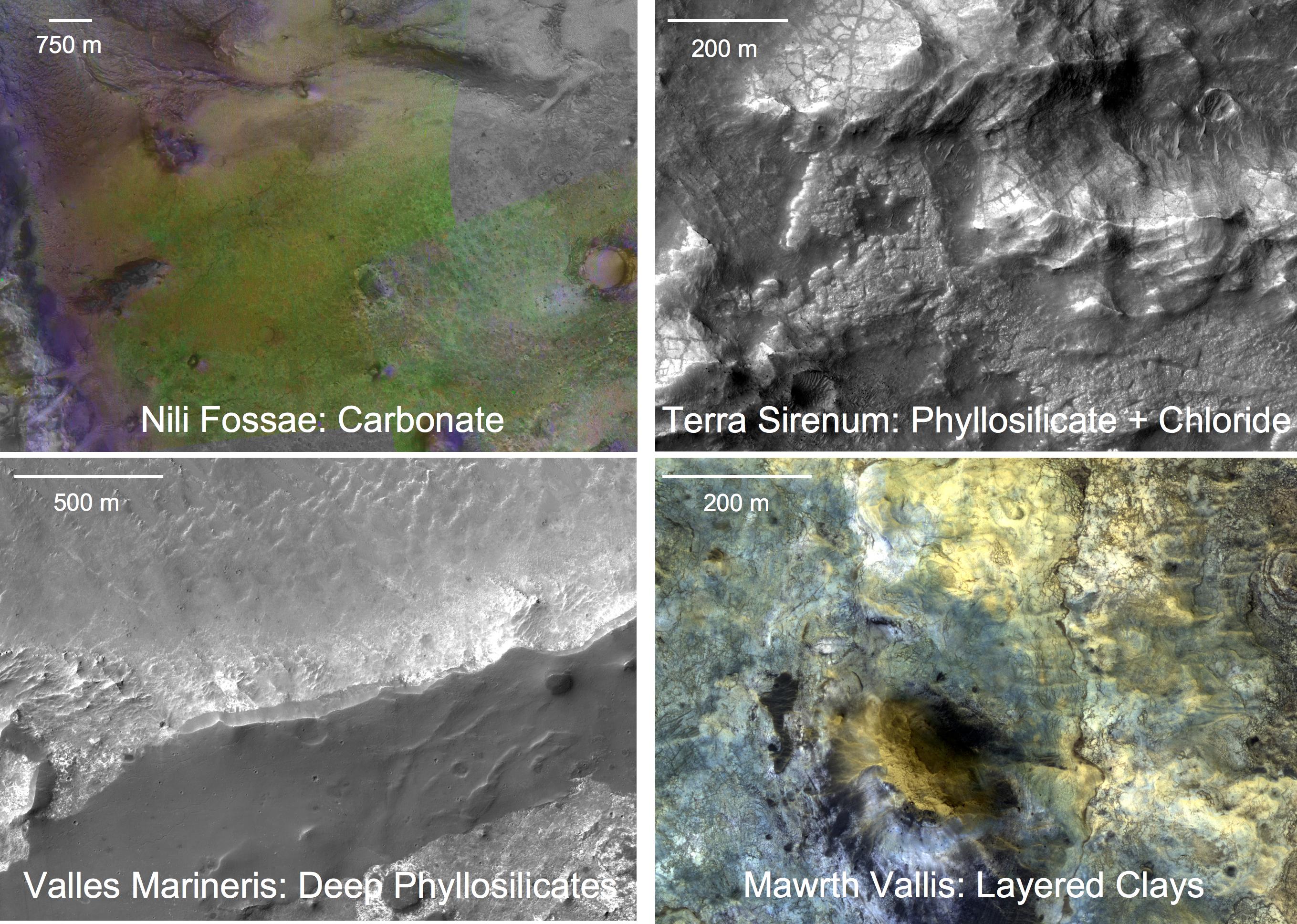
The Noachian is a geologic system and early time period on the planet Mars characterized by high rates of meteorite and asteroid impacts and the possible presence of abundant surface water. The absolute age of the Noachian period is uncertain but probably corresponds to the lunar Pre-Nectarian to Early Imbrian periods of 4100 to 3700 million years ago, during the interval known as the Late Heavy Bombardment. Many of the large impact basins on the Moon and Mars formed at this time. The Noachian Period is roughly equivalent to the Earth's Hadean and early Archean eons when the first life forms likely arose. Noachian-aged terrains on Mars are prime spacecraft landing sites to search for fossil evidence of life. During the Noachian, the atmosphere of Mars was denser than it is today, and the climate possibly warm enough to allow rainfall. Large lakes and rivers were present in the southern hemisphere, and an ocean may have covered the low-lying northern plains. Extensive volcanism ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isidis Planitia
Isidis Planitia is a plain located within a giant impact basin on Mars, located partly in the Syrtis Major quadrangle and partly in the Amenthes quadrangle. At approximately in diameter, it is the third-largest obvious impact structure on the planet, after the Hellas and Argyre basins. Isidis was likely the last major basin to be formed on Mars, having formed approximately 3.9 billion years ago during the Noachian period. Due to dust coverage, it typically appears bright in telescopic views, and was mapped as a classical albedo feature, Isidis Regio, visible by telescope in the pre-spacecraft era. A study reported in ''Icarus'' described the complex geologic history of parts of Isidis, especially areas near the Deuteronilus contact. This contact is the supposed edge of a vast Martian ocean. The researchers found evidence of a Late Hesperian/Early Amazonian Sea in the area. The sea would have quickly frozen over. Eskers formed under the ice. Just to the west of Isidis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Argyre Planitia
Argyre Planitia is a plain located within the impact basin Argyre in the southern highlands of Mars. Its name comes from a map produced by Giovanni Schiaparelli in 1877; it refers to Argyre, a mythical island of silver in Greek mythology. Argyre is centered at and lies between 35° and 61° S and 27° and 62° W in the Argyre quadrangle. The basin is approximately wide and drops below the surrounding plains; it is the second deepest impact basin on Mars after Hellas. The crater Galle, located on the east rim of Argyre at , strongly resembles a smiley face. The basin was formed by a giant impact during the Late Heavy Bombardment of the early Solar System, approximately 3.9 billion years ago, and may be one of the best preserved ancient impact basins from that period. Argyre is surrounded by rugged massifs which form concentric and radial patterns around the basin. Several mountain ranges are present, some of these mountain ranges include Charitum and Nereidum Montes. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Martian Dichotomy
The most conspicuous feature of Mars is a sharp contrast, known as the Martian dichotomy, between the Southern and the Northern hemispheres. The two hemispheres' geography differ in elevation by 1 to 3 km. The average thickness of the Martian crust is 45 km, with 32 km in the northern lowlands region, and 58 km in the southern highlands. The boundary between the two regions is quite complex in places. One distinctive type of topography is called fretted terrain. It contains mesas, knobs, and flat-floored valleys having walls about a mile high. Around many of the mesas and knobs are lobate debris aprons that have been shown to be rock glaciers. Many large valleys formed by the lava erupted from the volcanoes of Mars cut through the dichotomy. The Martian dichotomy boundary includes the regions called Deuteronilus Mensae, Protonilus Mensae, and Nilosyrtis Mensae. All three regions have been studied extensively because they contain landforms believed to ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hellas Planitia
Hellas Planitia is a plain located within the huge, roughly circular impact basin Hellas located in the southern hemisphere of the planet Mars. Hellas is the third- or fourth-largest known impact crater in the Solar System. The basin floor is about deep, deeper than the Moon's South Pole-Aitken basin, and extends about east to west.The part below zero datum, see Geography of Mars#Zero elevation It is centered at Hellas Planitia spans the boundary between the Hellas quadrangle and the Noachis quadrangle. Description With a diameter of about , it is the largest unambiguous impact structure on the planet; the obscured Utopia Planitia is slightly larger (the Borealis Basin, if it proves to be an impact crater, is considerably larger). Hellas Planitia is thought to have been formed during the Late Heavy Bombardment period of the Solar System, approximately 4.1 to 3.8 billion years ago, when a protoplanet or large asteroid hit the surface. The altitude difference between ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geological Timescale
The geologic time scale, or geological time scale, (GTS) is a representation of time based on the rock record of Earth. It is a system of chronological dating that uses chronostratigraphy (the process of relating strata to time) and geochronology (scientific branch of geology that aims to determine the age of rocks). It is used primarily by Earth scientists (including geologists, paleontologists, geophysicists, geochemists, and paleoclimatologists) to describe the timing and relationships of events in geologic history. The time scale has been developed through the study of rock layers and the observation of their relationships and identifying features such as lithologies, paleomagnetic properties, and fossils. The definition of standardized international units of geologic time is the responsibility of the International Commission on Stratigraphy (ICS), a constituent body of the International Union of Geological Sciences (IUGS), whose primary objective is to precisely defin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Period (geology)
The geologic time scale, or geological time scale, (GTS) is a representation of time based on the rock record of Earth. It is a system of chronological dating that uses chronostratigraphy (the process of relating strata to time) and geochronology (scientific branch of geology that aims to determine the age of rocks). It is used primarily by Earth scientists (including geologists, paleontologists, geophysicists, geochemists, and paleoclimatologists) to describe the timing and relationships of events in geologic history. The time scale has been developed through the study of rock layers and the observation of their relationships and identifying features such as lithologies, paleomagnetic properties, and fossils. The definition of standardized international units of geologic time is the responsibility of the International Commission on Stratigraphy (ICS), a constituent body of the International Union of Geological Sciences (IUGS), whose primary objective is to precisely de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

_with_poles_HiRes.jpg)