|
General Instrument
General Instrument (GI) was an American electronics manufacturer based in Horsham, Pennsylvania, specializing in semiconductors and cable television equipment. They formed in New York City in 1923 as an electronics manufacturer. During the 1950s, the company began a series of acquisitions under the direction of Moses Shapiro. Among the more notable purchases was General Transistor in 1960, which led to GI becoming a major producer of transistors, and later, integrated circuits (ICs). By the late 1960s, the company was mostly depending on sales into the television industry, which was further bolstered by the 1967 purchase of Jerrold Electronics. The company changed markets continually. Through the 1970s they focussed mostly on the off-track betting market through their purchase of American Totalisator, but this market faced significant competition in the late 1970s. At this time, GI became well known for their IC's including the CP1600 used in the Mattel Intellivision game console, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
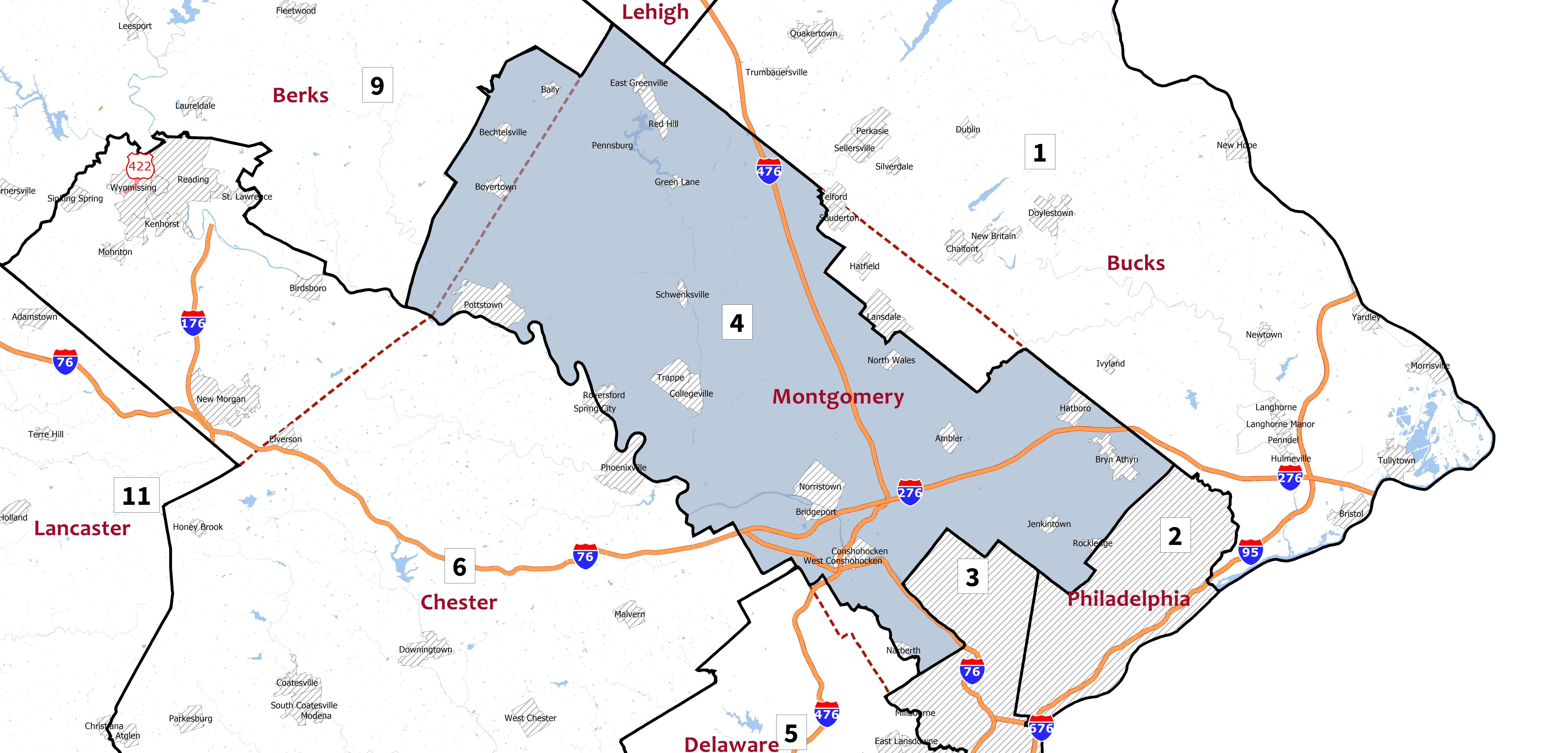
Montgomery County, Pennsylvania
Montgomery County is a county in the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania. It is the third-most populous county in Pennsylvania and the 73rd-most populous county in the United States. As of the 2020 census, the population of the county was 856,553, representing a 7.1% increase from the 799,884 residents enumerated in the 2010 census. Montgomery County is located adjacent to and northwest of Philadelphia. The county seat and largest city is Norristown. Montgomery County is geographically diverse, ranging from farms and open land in the extreme north of the county to densely populated suburban neighborhoods in the southern and central portions of the county. Montgomery County is included in the Philadelphia- Camden- Wilmington PA- NJ- DE- MD metropolitan statistical area, sometimes expansively known as the Delaware Valley. The county marks part of the Delaware Valley's northern border with the Lehigh Valley region of Pennsylvania. In 2010, Montgomery County was the 66th-wealthiest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
General Instrument CP1600
The CP1600 is a 16-bit microprocessor created in a partnership between General Instrument and Honeywell, introduced in February 1975. It is one of the first single-chip 16-bit processors. The overall design bore a strong resemblance to the PDP-11. Honeywell used the CP1600 in a number of process control computers and related systems, but its most widespread use was the CP1610 version in the Intellivision video game console. The system saw little other use due to General Instrument's marketing philosophy of seeking out customers only with very large orders and ignoring smaller customers. They also did not pursue a second source arrangement, which in the early days of microprocessor designs was a requirement for most potential customers. Description Physical implementation The CP1600 was implemented in enhancement mode nMOS and required +12, +5, -3 V power supplies; I/O connections except for the clocks were TTL (5 V) compatible. Each microstate or processor cycle use ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Control Data
Control Data Corporation (CDC) was a mainframe and supercomputer firm. CDC was one of the nine major United States computer companies through most of the 1960s; the others were IBM, Burroughs Corporation, DEC, NCR, General Electric, Honeywell, RCA, and UNIVAC. CDC was well-known and highly regarded throughout the industry at the time. For most of the 1960s, Seymour Cray worked at CDC and developed a series of machines that were the fastest computers in the world by far, until Cray left the company to found Cray Research (CRI) in the 1970s. After several years of losses in the early 1980s, in 1988 CDC started to leave the computer manufacturing business and sell the related parts of the company, a process that was completed in 1992 with the creation of Control Data Systems, Inc. The remaining businesses of CDC currently operate as Ceridian. Background and origins: World War II–1957 During World War II the U.S. Navy had built up a classified team of engineers to build codeb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Racetrack
A race track (racetrack, racing track or racing circuit) is a facility built for racing of vehicles, athletes, or animals (e.g. horse racing or greyhound racing). A race track also may feature grandstands or concourses. Race tracks are also used in the study of animal locomotion. A ''racetrack'' is a permanent facility or building. ''Racecourse'' is an alternate term for a horse racing track, found in countries such as the United Kingdom, India, Australia, Hong Kong, and the United Arab Emirates. Race tracks built for bicycles are known as ''velodromes''. ''Circuit'' is a common alternate term for race track, given the circuit configuration of most race tracks, allowing races to occur over several laps. Some race tracks may also be known as ''speedways'', or ''raceways''. A ''race course'', as opposed to a ''racecourse'', is a nonpermanent track for sports, particularly road running, water sports, road racing, or rallying. Many sports usually held on race tracks also can occ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conglomerate (company)
A conglomerate () is a multi-industry company – i.e., a combination of multiple business entities operating in entirely different industries under one corporate group, usually involving a parent company and many subsidiaries. Conglomerates are often large and multinational. United States The conglomerate fad of the 1960s During the 1960s, the United States was caught up in a "conglomerate fad" which turned out to be a form of speculative mania. Due to a combination of low interest rates and a repeating bear-bull market, conglomerates were able to buy smaller companies in leveraged buyouts (sometimes at temporarily deflated values). Famous examples from the 1960s include Ling-Temco-Vought,. ITT Corporation, Litton Industries, Textron, and Teledyne. The trick was to look for acquisition targets with solid earnings and much lower price–earnings ratios than the acquirer. The conglomerate would make a tender offer to the target's shareholders at a princely premium to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |