|
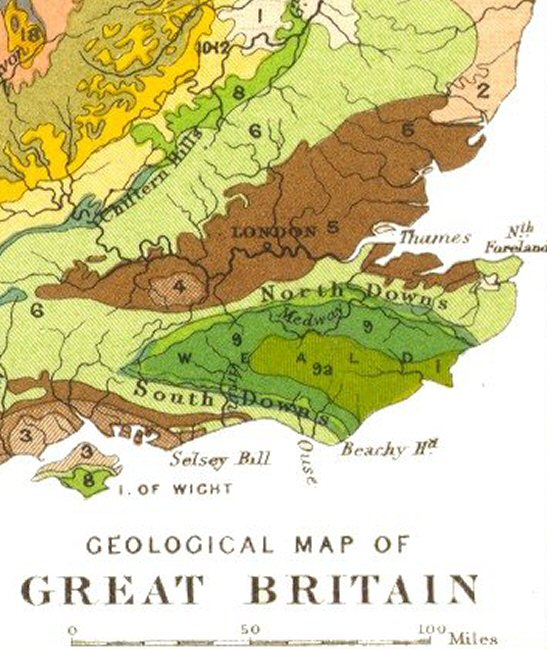
Gault Clay
The Gault Formation is a geological formation of stiff blue clay deposited in a calm, fairly deep-water marine environment during the Lower Cretaceous Period (Upper and Middle Albian). It is well exposed in the coastal cliffs at Copt Point in Folkestone, Kent, England, where it overlays the Lower Greensand formation, and underlies the Upper Greensand Formation. These represent different facies, with the sandier parts probably being deposited close to the shore and the clay in quieter water further from the source of sediment; both are believed to be shallow-water deposits. The etymology of the name is uncertain and probably of local origin. Distribution It is found in exposure on the south side of the North Downs and the north side of the South Downs. It is also to be found beneath the scarp of the Berkshire Downs, in the Vale of White Horse, in Oxfordshire, England, and on the Isle of Wight where it is known as Blue Slipper. Gault underlies the chalk beneath the Londo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beachy Head
Beachy Head is a chalk headland in East Sussex, England. It is situated close to Eastbourne, immediately east of the Seven Sisters. Beachy Head is located within the administrative area of Eastbourne Borough Council which owns the land, forming part of the Eastbourne Downland Estate. The cliff is the highest chalk sea cliff in Britain, rising to above sea level. The peak allows views of the south east coast towards Dungeness in the east, and to the Isle of Wight in the west. Geology The chalk was formed in the Late Cretaceous epoch, between 66 and 100 million years ago, when the area was under the sea. During the Cenozoic Era, the chalk was uplifted (see Cenozoic Era). When the last ice age ended, sea levels rose and the English Channel formed, cutting into the chalk to form the dramatic cliffs along the Sussex coast. Wave action contributes towards the erosion of cliffs around Beachy Head, which experience frequent small rock falls. Since chalk forms in layers separate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triassic
The Triassic ( ) is a geologic period and system (stratigraphy), system which spans 50.6 million years from the end of the Permian Period 251.902 million years ago (Year#Abbreviations yr and ya, Mya), to the beginning of the Jurassic Period 201.36 Mya. The Triassic is the first and shortest period of the Mesozoic, Mesozoic Era. Both the start and end of the period are marked by major extinction events. The Triassic Period is subdivided into three epochs: Early Triassic, Middle Triassic and Late Triassic. The Triassic began in the wake of the Permian–Triassic extinction event, which left the Earth's biosphere impoverished; it was well into the middle of the Triassic before life recovered its former diversity. Three categories of organisms can be distinguished in the Triassic record: survivors from the extinction event, new groups that flourished briefly, and other new groups that went on to dominate the Mesozoic Era. Reptiles, especially archosaurs, were the chief terrestrial vert ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxfordshire
Oxfordshire is a ceremonial and non-metropolitan county in the north west of South East England. It is a mainly rural county, with its largest settlement being the city of Oxford. The county is a centre of research and development, primarily due to the work of the University of Oxford and several notable science parks. These include the Harwell Science and Innovation Campus and Milton Park, both situated around the towns of Didcot and Abingdon-on-Thames. It is a landlocked county, bordered by six counties: Berkshire to the south, Buckinghamshire to the east, Wiltshire to the south west, Gloucestershire to the west, Warwickshire to the north west, and Northamptonshire to the north east. Oxfordshire is locally governed by Oxfordshire County Council, together with local councils of its five non-metropolitan districts: City of Oxford, Cherwell, South Oxfordshire, Vale of White Horse, and West Oxfordshire. Present-day Oxfordshire spanning the area south of the Thames wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
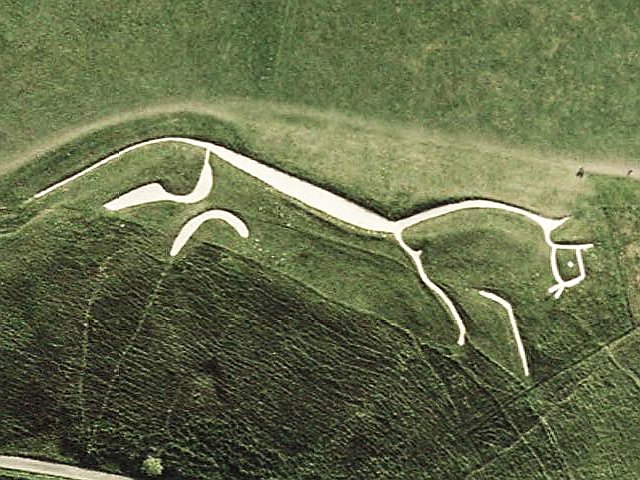
Vale Of White Horse
The Vale of White Horse is a local government district of Oxfordshire in England. It was historically a north-west projection of Berkshire. The area is commonly referred to as the 'Vale of ''the'' White Horse'. It is crossed by the Ridgeway National Trail in its far south, across the North Wessex Downs AONB at the junction of four counties. The northern boundary is defined by the River Thames. The name refers to Uffington White Horse, a prehistoric hill figure. History The area has been long settled as a productive fertile chalklands above well-drained clay valleys and well-farmed with many small woodlands and hills between the Berkshire Downs and the River Thames on its north and east sides. It is named after the prominent and large Bronze Age-founded Uffington White Horse hill figure. The name "Vale of the White Horse" predates the present-day local authority district, having been described, for example, in the 1870-72 ''Imperial Gazetteer of England and Wales''. The dis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Berkshire Downs
The Berkshire Downs are a range of chalk downland hills in South east England split between the counties of Berkshire and Oxfordshire. They are part of the North Wessex Downs Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty. The western parts of the downs are also known as the Lambourn Downs. Geography The Berkshire Downs run east–west, with their scarp slope facing north into the Vale of White Horse and their dip slope bounded by the course of the River Kennet. Geologically they are continuous with the Marlborough Downs to the west and the Chilterns to the east. In the east they are divided from the Chilterns by Goring Gap on the River Thames. In the west their boundary is generally taken to be the border between Berkshire and Wiltshire, although the downs in Wiltshire between the Berkshire border and the valley of the River Og are sometimes considered to be part of the Berkshire Downs. History English downland has attracted human habitation since prehistoric times. The ancient ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Escarpment
An escarpment is a steep slope or long cliff that forms as a result of faulting or erosion and separates two relatively level areas having different elevations. The terms ''scarp'' and ''scarp face'' are often used interchangeably with ''escarpment''. Some sources differentiate the two terms, with ''escarpment'' referring to the margin between two landforms, and ''scarp'' referring to a cliff or a steep slope. In this usage an escarpment is a ridge which has a gentle slope on one side and a steep scarp on the other side. More loosely, the term ''scarp'' also describes a zone between a coastal lowland and a continental plateau which shows a marked, abrupt change in elevation caused by coastal erosion at the base of the plateau. Formation and description Scarps are generally formed by one of two processes: either by differential erosion of sedimentary rocks, or by movement of the Earth's crust at a geologic fault. The first process is the more common type: the escarpment is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Downs
The South Downs are a range of chalk hills that extends for about across the south-eastern coastal counties of England from the Itchen valley of Hampshire in the west to Beachy Head, in the Eastbourne Downland Estate, East Sussex, in the east. The Downs are bounded on the northern side by a steep escarpment, from whose crest there are extensive views northwards across the Weald. The South Downs National Park forms a much larger area than the chalk range of the South Downs and includes large parts of the Weald. The South Downs are characterised by rolling chalk downland with close-cropped turf and dry valleys, and are recognised as one of the most important chalk landscapes in England. The range is one of the four main areas of chalk downland in southern England. The South Downs are relatively less populated compared to South East England as a whole, although there has been large-scale urban encroachment onto the chalk downland by major seaside resorts, including most notabl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North Downs
The North Downs are a ridge of chalk hills in south east England that stretch from Farnham in Surrey to the White Cliffs of Dover in Kent. Much of the North Downs comprises two Areas of Outstanding Natural Beauty (AONBs): the Surrey Hills and the Kent Downs. The North Downs Way National Trail runs along the North Downs from Farnham to Dover. The highest point in the North Downs is Botley Hill, Surrey ( above sea level). The ''County Top'' of Kent is Betsom's Hill ( above sea level), which is less than 1 km from Westerham Heights, Bromley, the highest point in Greater London at an elevation of . Etymology 'Downs' is from Old English ''dun'', meaning, amongst other things, "hill". The word acquired the sense of "elevated rolling grassland" around the 14th century. The name contains "North" to distinguish them from a similar range of hills – the South Downs – which runs roughly parallel to them but some to the south. Geography The narrow spine of the Hog's B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Facies
In geology, a facies ( , ; same pronunciation and spelling in the plural) is a body of rock with specified characteristics, which can be any observable attribute of rocks (such as their overall appearance, composition, or condition of formation), and the changes that may occur in those attributes over a geographic area. A facies encompasses all of the characteristics of a rock including its chemical, physical, and biological features that distinguish it from adjacent rock. The term facies was introduced by the Swiss geologist Amanz Gressly in 1838 and was part of his significant contribution to the foundations of modern stratigraphy, which replaced the earlier notions of Neptunism. Types of facies Sedimentary facies Ideally, a sedimentary facies is a distinctive rock unit that forms under certain conditions of sedimentation, reflecting a particular process or environment. Sedimentary facies are either descriptive or interpretative. Sedimentary facies are bodies of sediment ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lower Greensand
The Lower Greensand Group is a geological unit present across large areas of Southern England. It was deposited during the Aptian and Albian stages of the Early Cretaceous. It predominantly consists of sandstone and unconsolidated sand that were deposited in shallow marine conditions. Lithology The Lower Greensand typically comprises loose, unconsolidated sandstone (termed rubblestone/rubble in construction) and sands of varying grain size with subordinate amounts of siltstones, mudstones (containing smectites and similar) and limestones. The name "greensand" is derived from the presence of the green coloured mineral glauconite, which forms in shallow marine conditions. In the Weald of East Sussex the lowermost part of the group is recognised by green glauconitic clays with a basal bed of phosphate nodules. These clays are overlain by green sandy clays and silts and finally homogeneous fine grained sands.Lake, R.D. & Shepard-Thorn, E.R. (1987) ''Geology of the country around ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kent
Kent is a county in South East England and one of the home counties. It borders Greater London to the north-west, Surrey to the west and East Sussex to the south-west, and Essex to the north across the estuary of the River Thames; it faces the French department of Pas-de-Calais across the Strait of Dover. The county town is Maidstone. It is the fifth most populous county in England, the most populous non-Metropolitan county and the most populous of the home counties. Kent was one of the first British territories to be settled by Germanic tribes, most notably the Jutes, following the withdrawal of the Romans. Canterbury Cathedral in Kent, the oldest cathedral in England, has been the seat of the Archbishops of Canterbury since the conversion of England to Christianity that began in the 6th century with Saint Augustine. Rochester Cathedral in Medway is England's second-oldest cathedral. Located between London and the Strait of Dover, which separates England from m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Copt Point
Copts ( cop, ⲛⲓⲣⲉⲙⲛ̀ⲭⲏⲙⲓ ; ar, الْقِبْط ) are a Christian ethnoreligious group indigenous to North Africa who have primarily inhabited the area of modern Egypt and Sudan since antiquity. Most ethnic Copts are Coptic Oriental Orthodox Christians. They are the largest Christian denomination in Egypt and the Middle East, as well as in Sudan and Libya. Copts have historically spoken the Coptic language, a direct descendant of the Demotic Egyptian that was spoken in late antiquity. Originally referring to all Egyptians at first, the term ''Copt'' became synonymous with native Christians in light of Egypt's Islamization and Arabization after the Muslim conquest of Egypt in the 7th century. Copts in Egypt account for roughly 5–20 percent of the Egyptian population, although the exact percentage is unknown; Copts in Sudan account for 1 percent of the Sudanese population while Copts in Libya similarly account for 1 percent of the Libyan po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)