|
Gattermann Reaction
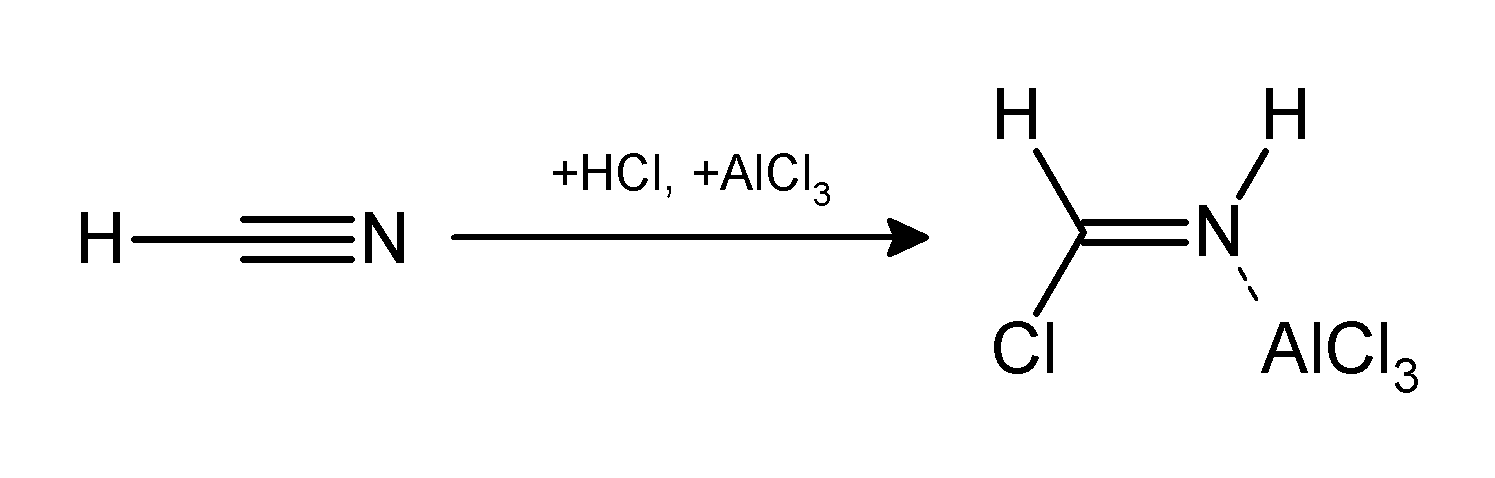
The Gattermann reaction, (also known as the Gattermann formylation and the Gattermann salicylaldehyde synthesis) is a chemical reaction in which aromatic compounds are formylated by a mixture of hydrogen cyanide (HCN) and hydrogen chloride (HCl) in the presence of a Lewis acid catalyst such as AlCl3. It is named for the German chemist Ludwig Gattermann and is similar to the Friedel–Crafts reaction. Modifications have shown that it is possible to use sodium cyanide or cyanogen bromide in place of hydrogen cyanide. The reaction can be simplified by replacing the HCN/AlCl3 combination with zinc cyanide. Although it is also highly toxic, Zn(CN)2 is a solid, making it safer to work with than gaseous HCN. The Zn(CN)2 reacts with the HCl to form the key HCN reactant and Zn(Cl)2 that serves as the Lewis-acid catalyst ''in-situ''. An example of the Zn(CN)2 method is the synthesis of mesitaldehyde from mesitylene. Gattermann–Koch reaction The Gattermann–Koch reaction, named ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ludwig Gattermann
Ludwig Gattermann (20 April 1860 – 20 June 1920) was a German chemist who contributed significantly to both organic and inorganic chemistry. Early life Ludwig Gatterman was born on 20 April 1860 in Goslar, an old mining town north of the Harz mountains. Two of his three siblings died at a young age. During his time in the Realschule he started experimenting. In 1880, he wanted to study at the University of Leipzig, but he had to complete his compulsory military service before he could start. He started his studies in 1881. After one year with Robert Bunsen at the University of Leipzig, he visited Liebermann for one semester at the University of Berlin to improve his skills in organic chemistry. Gattermann chose the University of Göttingen, which was close to Goslar for his further studies. He started his thesis under the supervision of Hans Hübner, who died in 1884, and finished his Ph.D. in 1885. As successor of Hans Hübner, Victor Meyer came to Göttingen and some ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemische Berichte
''Chemische Berichte'' (usually abbreviated as ''Ber.'' or ''Chem. Ber.'') was a German-language scientific journal of all disciplines of chemistry founded in 1868. It was one of the oldest scientific journals in chemistry, until it merged with ''Recueil des Travaux Chimiques des Pays-Bas'' to form ''Chemische Berichte/Recueil'' in 1997. ''Chemische Berichte/Recueil'' was then merged with other European journals in 1998 to form '' European Journal of Inorganic Chemistry''. History Founded in 1868 as ''Berichte der Deutschen Chemischen Gesellschaft'' (, CODEN BDCGAS), it operated under this title until 1928 (Vol. 61). The journal was then split into: * ''Berichte der Deutschen Chemischen Gesellschaft, A: Vereins-Nachrichten'' (, CODEN BDCAAS), and * ''Berichte der Deutschen Chemischen Gesellschaft, B: Abhandlungen'' (, CODEN BDCBAD). Vol. 78 and 79 (1945–1946) were omitted and not published due to World War II. The journal was renamed ''Chemische Berichte'' (, CODEN CHBEAM) i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Formylation Reactions
In biochemistry, the addition of a formyl functional group is termed formylation. A formyl functional group consists of a carbonyl bonded to hydrogen. When attached to an R group, a formyl group is called an aldehyde. Formylation has been identified in several critical biological processes. Methionine was first discovered to be formylated in ''E. coli'' by Marcker and Sanger in 1964 and was later identified to be involved in the initiation of protein synthesis in bacteria and organelles. The formation of ''N''-formylmethionine is catalyzed by the enzyme methionyl-tRNA transformylase. Additionally, two formylation reactions occur in the de novo biosynthesis of purines. These reactions are catalyzed by the enzymes glycinamide ribonucleotide (GAR) transformylase and 5-aminoimidazole-4-carboxyamide ribotide (AICAR) transformylase. More recently, formylation has been discovered to be a histone modification, which may modulate gene expression. General formylation reaction Formyla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Name Reactions
A name reaction is a chemical reaction named after its discoverers or developers. Among the tens of thousands of organic reactions that are known, hundreds of such reactions are well-known enough to be named after people. Well-known examples include the Grignard reaction, the Sabatier reaction, the Wittig reaction, the Claisen condensation, the Friedel-Crafts acylation, and the Diels-Alder reaction. Books have been published devoted exclusively to name reactions;Alfred Hassner, C. Stumer. ''Organic syntheses based on name reactions''. Elsevier, 2002. Li, Jie Jack. ''Name Reactions: A Collection of Detailed Reaction Mechanisms''. Springer, 2003. the Merck Index, a chemical encyclopedia, also includes an appendix on name reactions. As organic chemistry developed during the 20th century, chemists started associating synthetically useful reactions with the names of the discoverers or developers; in many cases, the name is merely a mnemonic. Some cases of reactions that were not r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Substitution Reactions
A substitution reaction (also known as single displacement reaction or single substitution reaction) is a chemical reaction during which one functional group in a chemical compound is replaced by another functional group. Substitution reactions are of prime importance in organic chemistry. Substitution reactions in organic chemistry are classified either as electrophilic or nucleophilic depending upon the reagent involved, whether a reactive intermediate involved in the reaction is a carbocation, a carbanion or a free radical, and whether the substrate is aliphatic or aromatic. Detailed understanding of a reaction type helps to predict the product outcome in a reaction. It also is helpful for optimizing a reaction with regard to variables such as temperature and choice of solvent. A good example of a substitution reaction is halogenation. When chlorine gas (Cl2) is irradiated, some of the molecules are split into two chlorine radicals (Cl•), whose free electrons are strongly n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stephen Aldehyde Synthesis
Stephen aldehyde synthesis, a named reaction in chemistry, was invented by Henry Stephen ( OBE/ MBE). This reaction involves the preparation of aldehydes (R-CHO) from nitriles (R-CN) using tin(II) chloride (SnCl2), hydrochloric acid (HCl) and quenching the resulting iminium salt ( -CH=NH2sup>+Cl−) with water (H2O). During the synthesis, ammonium chloride is also produced. Mechanism The following scheme shows the reaction mechanism: By addition of hydrogen chloride the used nitrile (1) reacts to its corresponding salt (2). It is believed that this salt is reduced by a single electron transfer by the tin(II) chloride (3a and 3b). The resulting salt (4) precipitates after some time as aldimine tin chloride (5). Hydrolysis of 5 produces a hemi aminal (6) from which an aldehyde (7) is formed. Substitutes that increase the electron density promote the formation of the aldimine-tin chloride adduct. With electron withdrawing substituents, the formation of an amide chlo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Houben–Hoesch Reaction
The Hoesch reaction or Houben–Hoesch reaction is an organic reaction in which a nitrile reacts with an arene compound to form an aryl ketone. The reaction is a type of Friedel-Crafts acylation with hydrogen chloride and a Lewis acid catalyst. The synthesis of 2,4,6-Trihydroxyacetophenone (THAP) from phloroglucinol is representative: If two-equivalents are added, 2,4-Diacetylphloroglucinol is the product. : An imine can be isolated as an intermediate reaction product. The attacking electrophile is possibly a species of the type R-C+=NHCl−. The arene must be electron-rich i.e. phenol or aniline type. A related reaction is the Gattermann reaction in which hydrocyanic acid not a nitrile is used. The reaction is named after Kurt Hoesch and Josef Houben''Über die Kern-Kondensation von Phenolen und Phenol-äthern mit Nitrilen zu Phenol- und Phenol-äther-Ketimiden und -Ketonen (I.)'' Berichte der deutschen chemischen Gesellschaft (A and B Series) Volume 59, Issue 11, Date: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nickel(II) Chloride
Nickel(II) chloride (or just nickel chloride) is the chemical compound NiCl2. The anhydrous salt is yellow, but the more familiar hydrate NiCl2·6H2O is green. Nickel(II) chloride, in various forms, is the most important source of nickel for chemical synthesis. The nickel chlorides are deliquescent, absorbing moisture from the air to form a solution. Nickel salts have been shown to be carcinogenic to the lungs and nasal passages in cases of long-term inhalation exposure. Production and syntheses The largest scale production of nickel chloride involves the extraction with hydrochloric acid of nickel matte and residues obtained from roasting refining nickel-containing ores. Nickel chloride is not usually prepared in the laboratory because it is inexpensive and has a long shelf-life. Heating the hexahydrate in the range 66–133.°C gives the yellowish dihydrate, NiCl2·2H2O. The hydrates convert to the anhydrous form upon heating in thionyl chloride or by heating under a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Copper(I) Chloride
Copper(I) chloride, commonly called cuprous chloride, is the lower chloride of copper, with the formula CuCl. The substance is a white solid sparingly soluble in water, but very soluble in concentrated hydrochloric acid. Impure samples appear green due to the presence of copper(II) chloride (CuCl2). History Copper(I) chloride was first prepared by Robert Boyle in the mid-seventeenth century from mercury(II) chloride ("Venetian sublimate") and copper metal: :HgCl2 + 2 Cu → 2 CuCl + Hg In 1799, J.L. Proust characterized the two different chlorides of copper. He prepared CuCl by heating CuCl2 at red heat in the absence of air, causing it to lose half of its combined chlorine followed by removing residual CuCl2 by washing with water. An acidic solution of CuCl was formerly used for analysis of carbon monoxide content in gases, for example in Hempel's gas apparatus. This application was significant during the nineteenth and early twentieth centuries when coal gas was wid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ether
In organic chemistry, ethers are a class of compounds that contain an ether group—an oxygen atom connected to two alkyl or aryl groups. They have the general formula , where R and R′ represent the alkyl or aryl groups. Ethers can again be classified into two varieties: if the alkyl or aryl groups are the same on both sides of the oxygen atom, then it is a simple or symmetrical ether, whereas if they are different, the ethers are called mixed or unsymmetrical ethers. A typical example of the first group is the solvent and anaesthetic diethyl ether, commonly referred to simply as "ether" (). Ethers are common in organic chemistry and even more prevalent in biochemistry, as they are common linkages in carbohydrates and lignin. Structure and bonding Ethers feature bent C–O–C linkages. In dimethyl ether, the bond angle is 111° and C–O distances are 141 pm. The barrier to rotation about the C–O bonds is low. The bonding of oxygen in ethers, alcohols, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phenol
Phenol (also called carbolic acid) is an aromatic organic compound with the molecular formula . It is a white crystalline solid that is volatile. The molecule consists of a phenyl group () bonded to a hydroxy group (). Mildly acidic, it requires careful handling because it can cause chemical burns. Phenol was first extracted from coal tar, but today is produced on a large scale (about 7 billion kg/year) from petroleum-derived feedstocks. It is an important industrial commodity as a precursor to many materials and useful compounds. It is primarily used to synthesize plastics and related materials. Phenol and its chemical derivatives are essential for production of polycarbonates, epoxies, Bakelite, nylon, detergents, herbicides such as phenoxy herbicides, and numerous pharmaceutical drugs. Properties Phenol is an organic compound appreciably soluble in water, with about 84.2 g dissolving in 1000 mL (0.895 M). Homogeneous mixtures of phenol and water a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

_complexes_in_aqueous_solution.jpg)
_Chloride_Precipitate.jpg)