|
Gas-checks In British RML Heavy Guns
Gas-checks were attachments to ammunition that revolutionised the performance of RML heavy guns. The first generation of RML heavy guns began entering service in about 1865. They all had Woolwich rifling and relied on studs on the projectiles for rotation. Gas-checks were first introduced in 1878 or soon after. They significantly reduced wear on the guns while also increasing their range and accuracy. Before long, studless ammunition was being manufactured for these guns, using gas-checks for projectile rotation. Gas-checks also facilitated a switch to the second generation of RML guns which used polygroove rifling and only supported studless ammunition. Introduction The first RML heavy guns were introduced into British service in about 1865. By 1878, 11 models of Woolwich rifled guns had been introduced, ranging from 7 inches to 12.5 inches. Unfortunately, Woolwich rifling had a major defect, namely, that hot powder gas escaping around the ammunition ("Windage Windage is a term ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muzzle-loading Rifle
A muzzle-loading rifle is a muzzle-loaded small arm or artillery piece that has a rifled barrel rather than a smoothbore. The term " rifled muzzle loader" typically is used to describe a type of artillery piece, although it is technically accurate for small arms as well. A shoulder arm is typically just called a "rifle", as almost all small arms were rifled by the time breechloading became prevalent. Muzzle and breechloading artillery served together for several decades, making a clear distinction more important. In the case of artillery, the abbreviation " RML" is often prefixed to the guns designation; a Rifled breech loader would be "RBL", or often just "BL", since smoothbore breechloading artillery is almost nonexistent (except in tank guns). A muzzle loading weapon is loaded through the muzzle, or front of the barrel (or "tube" in artillery terms). This is the opposite of a breech-loading weapon or rifled breechloader (RBL), which is loaded from the breech-end of the barrel. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RML 10 Inch 18 Ton Gun
The RML 10-inch guns Mk I – Mk II were large rifled muzzle-loading guns designed for British battleships and monitors in the 1860s to 1880s. They were also fitted to the and flat-iron gunboats. They were also used for fixed coastal defences around the United Kingdom and around the British Empire until the early years of the 20th century. Design The 10-inch gun was a standard "Woolwich" design (characterised by having a steel A tube with relatively few broad, rounded and shallow rifling grooves) developed in 1868, based on the successful Mk III 9-inch gun, itself based on the "Fraser" system. The Fraser system was an economy measure applied to the successful Armstrong design for heavy muzzle-loaders, which were expensive to produce. It retained the Armstrong steel barrel surrounded by wrought-iron coils under tension, but replaced the multiple thin wrought-iron coils shrunk around it by a single larger coil (10 inch Mark I) or 2 coils (Mark II); the trunnion ring was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Victorian-era Weapons Of The United Kingdom
In the history of the United Kingdom and the British Empire, the Victorian era was the period of Queen Victoria's reign, from 20 June 1837 until her death on 22 January 1901. The era followed the Georgian period and preceded the Edwardian period, and its later half overlaps with the first part of the ''Belle Époque'' era of Continental Europe. There was a strong religious drive for higher moral standards led by the nonconformist churches, such as the Methodists and the evangelical wing of the established Church of England. Ideologically, the Victorian era witnessed resistance to the rationalism that defined the Georgian period, and an increasing turn towards romanticism and even mysticism in religion, social values, and arts. This era saw a staggering amount of technological innovations that proved key to Britain's power and prosperity. Doctors started moving away from tradition and mysticism towards a science-based approach; medicine advanced thanks to the adoption o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artillery Of The United Kingdom
Artillery is a class of heavy military ranged weapons that launch munitions far beyond the range and power of infantry firearms. Early artillery development focused on the ability to breach defensive walls and fortifications during sieges, and led to heavy, fairly immobile siege engines. As technology improved, lighter, more mobile field artillery cannons developed for battlefield use. This development continues today; modern self-propelled artillery vehicles are highly mobile weapons of great versatility generally providing the largest share of an army's total firepower. Originally, the word "artillery" referred to any group of soldiers primarily armed with some form of manufactured weapon or armor. Since the introduction of gunpowder and cannon, "artillery" has largely meant cannons, and in contemporary usage, usually refers to shell-firing guns, howitzers, and mortars (collectively called ''barrel artillery'', ''cannon artillery'', ''gun artillery'', or - a layman term - ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coastal Artillery
Coastal artillery is the branch of the armed forces concerned with operating anti-ship artillery or fixed gun batteries in coastal fortifications. From the Middle Ages until World War II, coastal artillery and naval artillery in the form of cannons were highly important to military affairs and generally represented the areas of highest technology and capital cost among materiel. The advent of 20th-century technologies, especially military aviation, naval aviation, jet aircraft, and guided missiles, reduced the primacy of cannons, battleships, and coastal artillery. In countries where coastal artillery has not been disbanded, these forces have acquired amphibious capabilities. In littoral warfare, mobile coastal artillery armed with surface-to-surface missiles can still be used to deny the use of sea lanes. It was long held as a rule of thumb that one shore-based gun equaled three naval guns of the same caliber, due to the steadiness of the coastal gun which allowed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RML 7 Inch Gun
The RML 7-inch guns were various designs of medium-sized rifled muzzle-loading guns used to arm small to medium-sized British warships in the late 19th century, and some were used ashore for coast defence. Design and history These guns were the first to incorporate the new "Woolwich" rifling system, a modification of the French system, of from 3 – 9 broad shallow grooves after Britain abandoned the Armstrong "shunt" rifling system in May 1865 : "...M.L. 7-inch guns in course of manufacture were rifled on this principle, upon which all of our heavy pieces since have been rifled. The 7-inch referred to, and introduced into the service in 1865, were the first of the so-called Woolwich guns, which then meant "''wrought iron M.L. guns built up on Sir W. Armstrong's principle, improved upon by hooking the coils over one another, and having solid ended steel barrels, rifled on the system shown above, for studded projectiles''". All versions were constructed of a steel A tube surroun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RML 8 Inch Howitzer
The RML 8-inch howitzer was a British Rifled, Muzzle Loading (RML) Howitzer manufactured in England in the 19th century, which fired a projectile weighing approximately . It was used in siege batteries and in fortifications. Design and manufacture The gun consisted of an 'A' tube of toughened steel, over which was shrunk a 'B' tube of wrought iron and jacket. A cascable was fitted at the end. The original 46 cwt howitzer was rifled on the "Woolwich" pattern with 4 spiral grooves in which studs protruding from the projectile engaged to impart spin; the later 70 cwt howitzer was rifled on the "Polygroove" pattern with 24 grooves and projectiles had " Automatic gas-checks" attached to the base which engaged the grooves. Three planes were machined on the upper surface of the Howitzer, for use with quadrants enabling it to be elevated to 30 degrees. This enabled the gun to be sighted for indirect, or direct fire. Ammunition 46- and 70 cwt guns differed in number and type of ri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RML 8 Inch 9 Ton Gun
The British RML 8-inch 9-ton guns Mark I – Mark III were medium rifled muzzle-loading guns used to arm smaller ironclad warships and coast defence batteries in the later 19th century. Design In common with other Royal Ordnance RML designs of the 1860s, Mark I used the strong but expensive Armstrong system of a steel tube surrounded by a complex system of multiple wrought-iron coils, which was progressively simplified in Marks II and III to reduce costs : Mark III consisted only of A tube, B tube, breech coil and cascabel screw. Rifling was of the "Woolwich" pattern of a small number of broad shallow grooves: 4 grooves with twist increasing from 0 to 1 turn in 40 calibres (i.e. in 320 inches) at the muzzle. Ammunition The ammunition was mainly studded, with the studs engaging in the Woolwich rifling grooves. However, a studless pointed common shell with automatic gas-check also became available later in the gun's life.Gas-checks in British RML heavy guns See also * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RML 9 Inch 12 Ton Gun
The RML 9-inch guns Mark I – Mark VIMark I – Mark VI = Mark 1 through to Mark 6. Britain used Roman numerals to denote Marks (models) of ordnance until after World War II. Hence this article describes the six models of RML 9-inch guns. were large rifled muzzle-loading guns of the 1860s used as primary armament on smaller British ironclad battleships and secondary armament on larger battleships, and also ashore for coast defence. It should not be confused with the RML 9-inch Armstrong Gun, used by the Dutch navy, the Spanish Navy, and other navies. Design The rifling was the Woolwich pattern of a relatively small number of broad, rounded shallow grooves : there were 6 grooves, increasing from 0 to 1 turn in 45 calibres (i.e. 405 inches). Mark I, introduced in 1865, incorporated the strong but expensive Armstrong method of a steel A tube surrounded by multiple thin wrought-iron coils which maintained the central A tube under compression, and a forged steel breech-piece. 190 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
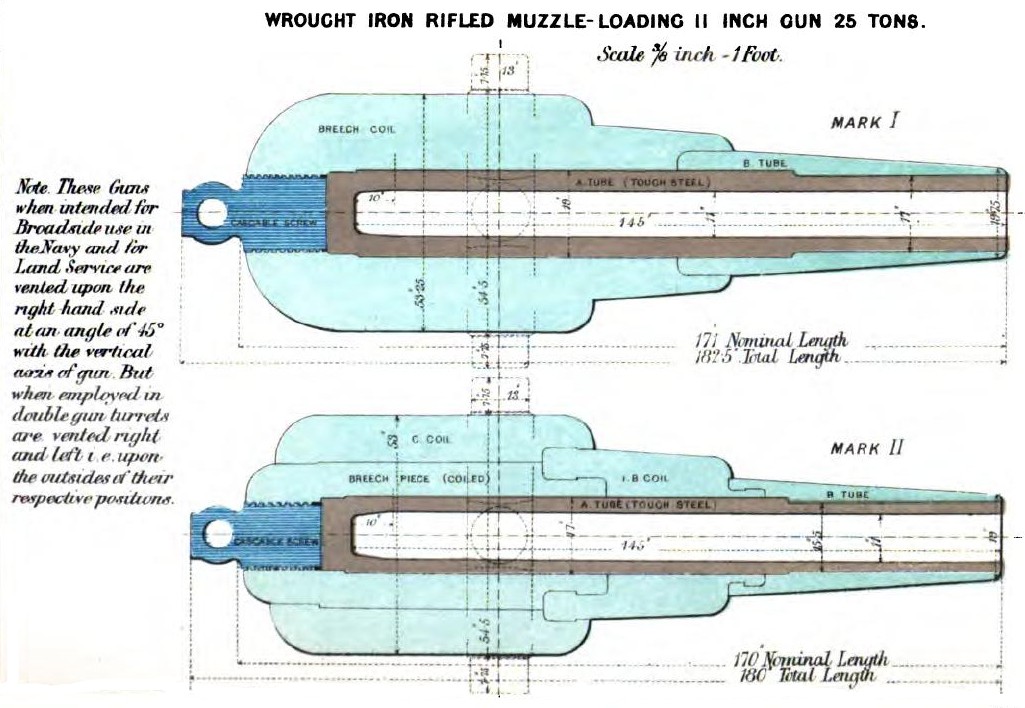
RML 11 Inch 25 Ton Gun
RML 11-inch 25-ton guns were large rifled muzzle-loading guns used as primary armament on British battleships and for coastal defence. They were effectively the same gun as the RML 12-inch 25-ton gun, bored to 11 inches instead of 12. Design Mark I was introduced in 1867. Mark II was introduced in 1871 using the simpler and cheaper "Fraser" gun construction method which had proved successful with the RML 9-inch 12-ton Mk IV gun. In 1874 the process of development made a "New Eighty-one Ton Gun" available in Woolwich. Naval service Guns were mounted on: * HMS ''Alexandra'', commissioned 1877. * HMS ''Temeraire'', commissioned 1877. Ammunition When the gun was first introduced projectiles had several rows of "studs" which engaged with the gun's rifling to impart spin. Sometime after 1878, " attached gas-checks" were fitted to the bases of the studded shells, reducing wear on the guns and improving their range and accuracy. Subsequently, " automatic gas-checks" were de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Howitzer
A howitzer () is a long- ranged weapon, falling between a cannon (also known as an artillery gun in the United States), which fires shells at flat trajectories, and a mortar, which fires at high angles of ascent and descent. Howitzers, like other artillery equipment, are usually organized in a group called a battery. Howitzers, together with long-barreled guns, mortars, and rocket artillery, are the four basic types of modern artillery. Mortars fire at angles of elevation greater than 45°, and are useful for mountain warfare because the projectile could go over obstacles. Cannons fire at low angles of elevation (<45°), and the projectile lands much faster at its target than it would in the case of a mortar. But the cannon is not useful if there is an obstacle like a hill/wall in front of its target. Etymology The English word ''howitzer'' comes from the Czech word , from , 'crowd', and is in turn a borrowing from the Middle High German word or (mod ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RML 12 Inch 25 Ton Gun
The RML 12-inch 25-ton guns were large rifled muzzle-loading guns of mid-late 1800s used as primary armament on British ironclad turret battleships and coastal monitors, and also ashore for coast defence. They were the shorter and less powerful of the two 12-inch (305-mm) British RML guns, the other being the 35-ton gun. Design Mark I Four guns were first made in 1866 with a toughened mild steel tube surrounded by multiple wrought iron coils on the original Armstrong pattern. Mark II While strong, the multiple coils were considered too expensive for construction in quantity. From 1867 guns were built on the simplified and hence cheaper "Fraser" system involving fewer but larger coils similar to the 10-inch (254-mm) Mk II gun. The guns were not considered a success, with the rifling twist of 1 in 100 increasing to 1 in 50 considered insufficient for accuracy, and guns were retubed in 11-inch (279-mm) calibre when their bores wore out.Treatise on Construction of Service ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |