|
Gary Becker Milton Friedman Institute For Research In Economics
The Gary Becker Milton Friedman Institute for Research in Economics is a collaborative, cross-disciplinary center for research in economics. The institute was established at the University of Chicago in June 2011. It brought together the activities of two formerly independent economic research centers at the university: the Milton Friedman Institute for Research in Economics and the Becker Center on Chicago Price Theory. The institute is named for two globally influential economists: Gary S. Becker (1930–2014) and his mentor, Milton Friedman (1912-2006), both winners of the Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences. While they pursued different scholarly paths, Becker and Friedman shared a fundamental belief that economics, grounded in empirical research, is a powerful tool to understand human behavior. While Friedman is known for his lasting contributions to macroeconomics and monetary economics, Becker is recognized for extending microeconomic analysis to a wide range of f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harris School Of Public Policy
The University of Chicago Harris School of Public Policy is the public policy graduate school of the University of Chicago in Chicago, Illinois, United States. It is located on the University of Chicago's main campus in Hyde Park. The school is named after Irving B. Harris, who made a donation in 1986 that established the Harris School of Public Policy, which was later founded in 1988. In addition to policy studies and policy analysis, the school requires students to pursue training in economics and statistics as part of its rigorouCore Curriculum Harris offers joint degrees with the Booth School of Business, Law School, Crown Family School of Social Work, Policy, and Practice, and the Graduate Division of the Social Sciences. Harris is ranked third among policy analysis schools in the United States by '' U.S. News & World Report'', and listed as the fourth best public policy institution globally in the field of economics research by RePEc. History The Harris School of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Research Institutes Of The University Of Chicago
Research is creative and systematic work undertaken to increase the stock of knowledge. It involves the collection, organization, and analysis of evidence to increase understanding of a topic, characterized by a particular attentiveness to controlling sources of bias and error. These activities are characterized by accounting and controlling for biases. A research project may be an expansion of past work in the field. To test the validity of instruments, procedures, or experiments, research may replicate elements of prior projects or the project as a whole. The primary purposes of basic research (as opposed to applied research) are documentation, discovery, interpretation, and the research and development (R&D) of methods and systems for the advancement of human knowledge. Approaches to research depend on epistemologies, which vary considerably both within and between humanities and sciences. There are several forms of research: scientific, humanities, artistic, economic, s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Michael Greenstone
Michael Greenstone is an American economist and the Milton Friedman Distinguished Service Professor in Economics at the Harris School of Public Policy of the University of Chicago. He serves as director of the Energy Policy Institute at the University of Chicago (EPIC), director of the Becker Friedman Institute, and co-chair of the Energy and Environment sector at Abdul Latif Jameel Poverty Action Lab (J-PAL). Under the first Obama administration, he served as chief economist on the Council of Economic Advisors. His research interests focus on the nexus between development economics and environmental economics. Biography Born in the United States, Michael Greenstone earned a B.A. in economics with High Honors from Swarthmore College in 1991, where he starred and lettered for the men's basketball team, and a Ph.D. in economics from Princeton University in 1998. Thereafter, he worked as a Robert Wood Johnson Scholar at the University of California, Berkeley (UCB, 1998–2000) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Economics Of The Family
Economics () is a behavioral science that studies the production, distribution, and consumption of goods and services. Economics focuses on the behaviour and interactions of economic agents and how economies work. Microeconomics analyses what is viewed as basic elements within economies, including individual agents and markets, their interactions, and the outcomes of interactions. Individual agents may include, for example, households, firms, buyers, and sellers. Macroeconomics analyses economies as systems where production, distribution, consumption, savings, and investment expenditure interact; and the factors of production affecting them, such as: labour, capital, land, and enterprise, inflation, economic growth, and public policies that impact these elements. It also seeks to analyse and describe the global economy. Other broad distinctions within economics include those between positive economics, describing "what is", and normative economics, advocating "what ought ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Policy Uncertainty
Policy uncertainty (also called regime uncertainty) is a class of economic risk where the future path of government policy is uncertain, raising risk premia and leading businesses and individuals to delay spending and investment until this uncertainty has been resolved. Policy uncertainty may refer to uncertainty about monetary or fiscal policy, the tax or regulatory regime, or uncertainty over electoral outcomes that will influence political leadership. The Great Recession During the Great Recession of the late 2000s and the years following it, many academics, policymakers, and business leaders have asserted that levels of policy uncertainty had risen dramatically and had contributed to the depth of the recession and the weakness of the following recovery. United States Much of the policy uncertainty in the United States has revolved around fiscal policy as well as uncertainty over the tax code. This is best exemplified by partisan fights in the United States Congress over the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Systemic Risk
In finance, systemic risk is the risk of collapse of an entire financial system or entire market, as opposed to the risk associated with any one individual entity, group or component of a system, that can be contained therein without harming the entire system.Banking and currency crises and systemic risk George G. Kaufman (World Bank), Internet Archive It can be defined as "financial ''system'' instability, potentially catastrophic, caused or exacerbated by idiosyncratic events or conditions in financial intermediaries". It refers to the risks imposed by ''interlinkages'' and ''interdependencies'' in a system or market, where the failure of a single entity or cluster of entities can cause a casca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fiscal Imbalance
Fiscal imbalance is a mismatch in the revenue powers and expenditure responsibilities of a government. Fiscal imbalances as differences in net fiscal benefits A fiscal imbalance emerges when sub-national governments have different abilities to raise funds from their tax bases and to provide services. This creates differences in ‘net fiscal benefits’, which are a combination of levels of taxation and public services. It is these NFBs which are the main cause of horizontal fiscal disparities that in turn generate the need for equalization grants. Prominent among the objectives commonly attributed to intergovernmental fiscal transfers is ‘equalization’ of fiscal capacities or resolution of fiscal imbalances. Thus, the transfer system can promote efficiency in the public sector and can level the field for intergovernmental competition. The discussion of fiscal imbalance and equalisation was of particular importance in the drafting of the new Iraqi constitution. It was a stick ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
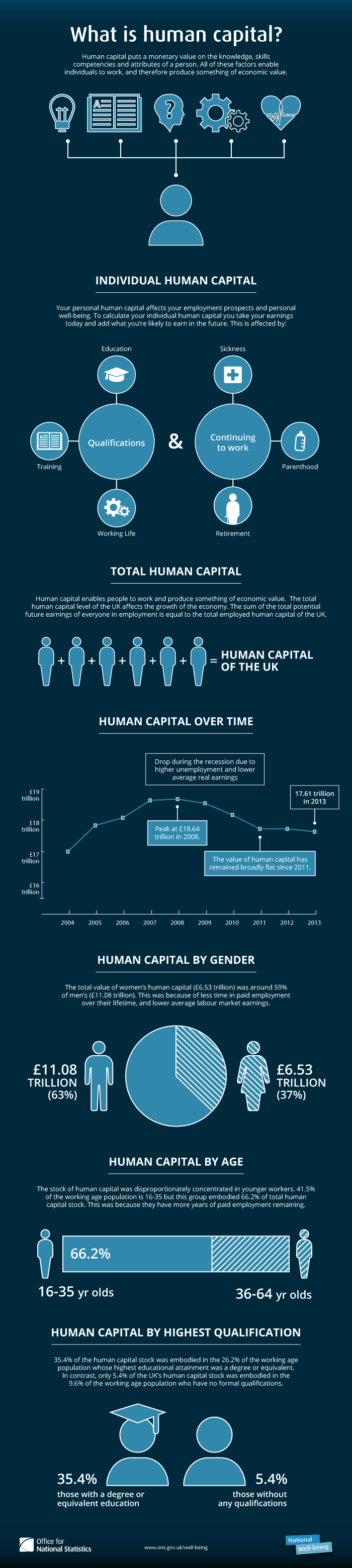
Human Capital
Human capital or human assets is a concept used by economists to designate personal attributes considered useful in the production process. It encompasses employee knowledge, skills, know-how, good health, and education. Human capital has a substantial impact on individual earnings. Research indicates that human capital investments have high economic returns throughout childhood and young adulthood. Companies can invest in human capital; for example, through education and training, improving levels of quality and production. History Adam Smith included in his definition of Capital (economics), capital "the acquired and useful abilities of all the inhabitants or members of the society". The first use of the term "human capital" may be by Irving Fisher. An early discussion with the phrase "human capital" was from Arthur Cecil Pigou: But the term only found widespread use in economics after its popularization by economists of the Chicago School of economics, Chicago School, in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Law And Economics
Law and economics, or economic analysis of law, is the application of microeconomic theory to the analysis of law. The field emerged in the United States during the early 1960s, primarily from the work of scholars from the Chicago school of economics such as Aaron Director, George Stigler, and Ronald Coase. The field uses economics concepts to explain the effects of laws, assess which legal rules are economically efficient, and predict which legal rules will be promulgated. There are two major branches of law and economics; one based on the application of the methods and theories of neoclassical economics to the positive and normative analysis of the law, and a second branch which focuses on an institutional analysis of law and legal institutions, with a broader focus on economic, political, and social outcomes, and overlapping with analyses of the institutions of politics and governance. History Origin The historical antecedents of law and economics can be traced back to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Price Theory
Microeconomics is a branch of economics that studies the behavior of individuals and firms in making decisions regarding the allocation of scarce resources and the interactions among these individuals and firms. Microeconomics focuses on the study of individual markets, sectors, or industries as opposed to the economy as a whole, which is studied in macroeconomics. One goal of microeconomics is to analyze the market mechanisms that establish relative prices among goods and services and allocate limited resources among alternative uses. Microeconomics shows conditions under which free markets lead to desirable allocations. It also analyzes market failure, where markets fail to produce efficient results. While microeconomics focuses on firms and individuals, macroeconomics focuses on the total of economic activity, dealing with the issues of growth, inflation, and unemployment—and with national policies relating to these issues. Microeconomics also deals with the effects o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Chicago Law School
The University of Chicago Law School is the Law school in the United States, law school of the University of Chicago, a Private university, private research university in Chicago, Illinois. It employs more than 180 full-time and part-time faculty and hosts more than 600 students in its Juris Doctor program, while also offering the degree programs in Master of Laws, Master of Studies in Law, and Doctor of Juridical Science. The law school was originally housed in Stuart Hall, a Gothic-style limestone building on the campus's main quadrangles. Since 1959, it has been housed in an Eero Saarinen-designed building across the Midway Plaisance from the main campus of the University of Chicago. The building was expanded in 1987 and again in 1998. It was renovated in 2008, preserving most of Saarinen's original structure. Members of the faculty have included Cass Sunstein, Richard Posner, and Richard Epstein, three of the most-cited legal scholars of the 20th and early 21st centuries. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |