|
Gable Grip
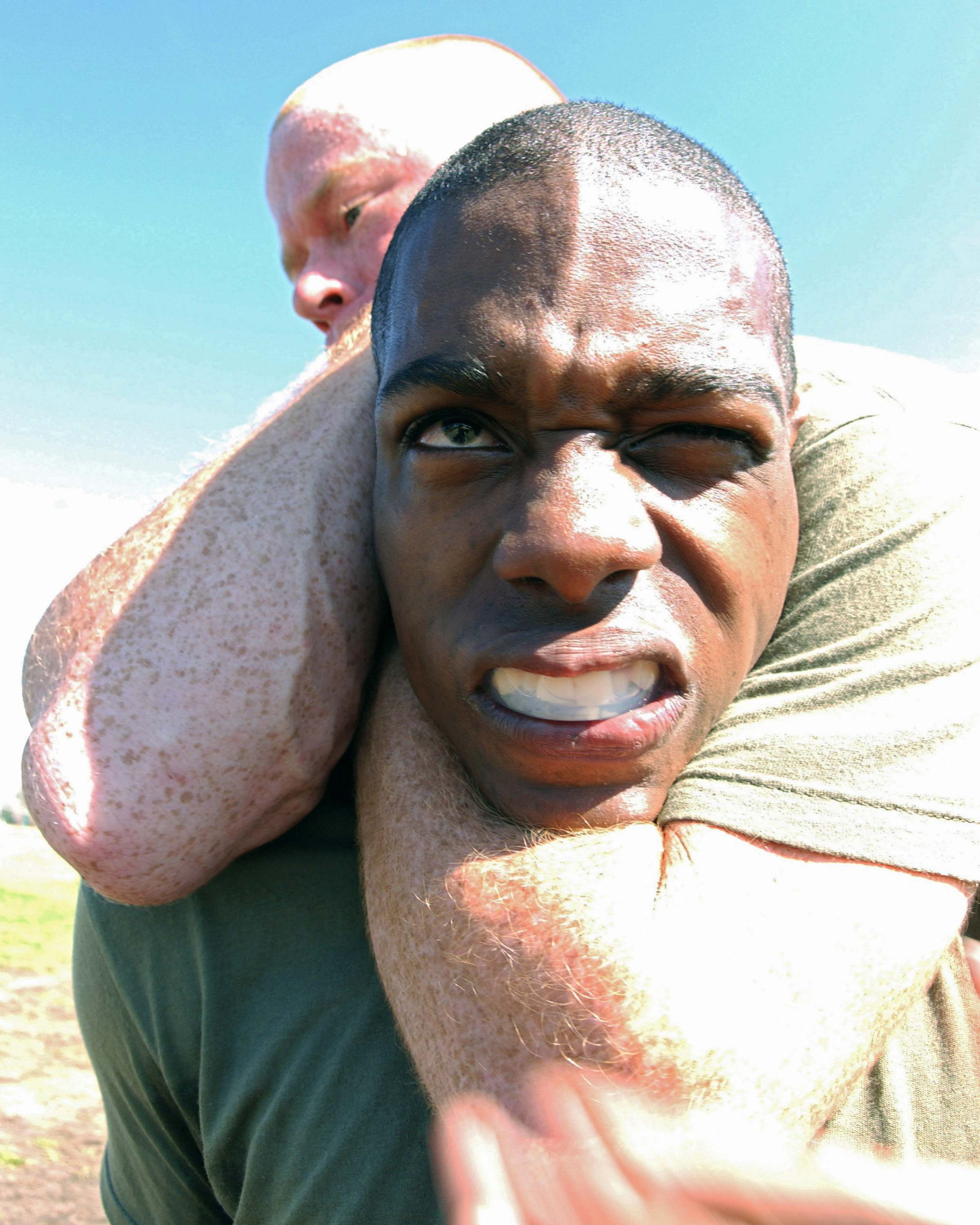
A chokehold, choke, stranglehold or, in Judo, shime-waza ( ja, 絞技, translation=constriction technique) is a general term for a grappling hold that critically reduces or prevents either air (choking)''The New Oxford Dictionary of English'' (1999). Oxford University press. . or blood (strangling) from passing through the neck of an opponent. The restriction may be of one or both and depends on the hold used and the reaction of the victim. While the time it takes for the choke to render an opponent unconscious varies depending on the type of choke, the average across all has been recorded as 9 seconds. The lack of blood or air often leads to unconsciousness or even death if the hold is maintained. Chokeholds are used in martial arts, combat sports, self-defense, law enforcement and in military hand to hand combat applications. They are considered superior to brute-force manual strangling, which generally requires a large disparity in physical strength to be effective.Jones, R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NCIS (TV Series)
''NCIS'' is an American police procedural television series, revolving around a fictional team of special agents from the Naval Criminal Investigative Service combining elements of the military drama and police procedural genres. The concept and characters were initially introduced in two episodes of the CBS series '' JAG'' ( season eight episodes 20 and 21: " Ice Queen" and "Meltdown"). A spin-off from ''JAG'', the series premiered on September 23, 2003, on CBS. To date it has entered into the twentieth full season and has gone into broadcast syndication on the USA Network. Donald P. Bellisario and Don McGill are co-creators and executive producers of the premiere member of the ''NCIS'' franchise. , ''NCIS'' is the third-longest-running scripted, non-animated U.S. primetime TV series currently airing, surpassed only by '' Law & Order: Special Victims Unit'' (1999–present) and '' Law & Order'' (1990–2010; 2022–present); it is the 7th-longest-running scripted U.S. p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Figure-four (grappling Hold)
A figure-four is a catch wrestling term for a joint-lock that resembles the number "4". A keylock or toe hold can be referred to as a figure-four hold, when it involves a figure-four formation with the legs or arms. If the figure-four involves grabbing the wrists with both hands, it is called a double wrist lock; known as kimura in MMA circles. A figure-four hold done with the legs around the neck and (usually) arm of an opponent is called figure-four (leg-)choke, better known as a triangle choke these days, and is a common submission Deference (also called submission or passivity) is the condition of submitting to the espoused, legitimate influence of one's superior or superiors. Deference implies a yielding or submitting to the judgment of a recognized superior, out of re ... in modern mixed martial arts, Submission wrestling and Brazilian jiu jitsu, and of course Catch wrestling. In addition to Lancashire, or catch-as-catch-can wrestling, the move was also found in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rear Naked Choke
The rear naked choke (RNC) is a chokehold in martial arts applied from an opponent's back. The word "naked" in this context suggests that, unlike other strangulation techniques found in jujutsu/judo, this hold does not require the use of a keikogi ("gi") or training uniform. The choke has two variations: in one version, the attacker's arm encircles the opponent's neck and then grabs their own biceps on the other arm (see below for details); in the second version, the attacker clasps their hands together instead after encircling the opponent's neck. Recent studies have shown that the rear-naked choke takes an average of 8.9 seconds to render an opponent unconscious regardless of the grip that is used. "Figure four" or "short" variation This variant is considered to be a "'' blood choke''" because it restricts blood flow to the brain via the carotid arteries. When applied correctly, it can cause temporary unconsciousness in a few seconds. The following is a description of this t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypoxia (medical)
Hypoxia is a condition in which the body or a region of the body is deprived of adequate oxygen supply at the tissue level. Hypoxia may be classified as either '' generalized'', affecting the whole body, or ''local'', affecting a region of the body. Although hypoxia is often a pathological condition, variations in arterial oxygen concentrations can be part of the normal physiology, for example, during strenuous physical exercise.. Hypoxia differs from hypoxemia and anoxemia, in that hypoxia refers to a state in which oxygen present in a tissue or the whole body is insufficient, whereas hypoxemia and anoxemia refer specifically to states that have low or no oxygen in the blood. Hypoxia in which there is complete absence of oxygen supply is referred to as anoxia. Hypoxia can be due to external causes, when the breathing gas is hypoxic, or internal causes, such as reduced effectiveness of gas transfer in the lungs, reduced capacity of the blood to carry oxygen, compromised gene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cerebral Ischemia
Brain ischemia is a condition in which there is insufficient bloodflow to the brain to meet metabolic demand. This leads to poor oxygen supply or cerebral hypoxia and thus leads to the death of brain tissue or cerebral infarction/ischemic stroke. It is a sub-type of stroke along with subarachnoid hemorrhage and intracerebral hemorrhage. Ischemia leads to alterations in brain metabolism, reduction in metabolic rates, and energy crisis. There are two types of ischemia: focal ischemia, which is confined to a specific region of the brain; and global ischemia, which encompasses wide areas of brain tissue. The main symptoms of brain ischemia involve impairments in vision, body movement, and speaking. The causes of brain ischemia vary from sickle cell anemia to congenital heart defects. Symptoms of brain ischemia can include unconsciousness, blindness, problems with coordination, and weakness in the body. Other effects that may result from brain ischemia are stroke, cardiorespir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jugular Veins
The jugular veins are veins that take deoxygenated blood from the head back to the heart via the superior vena cava. The internal jugular vein descends next to the internal carotid artery and continues posteriorly to the sternocleidomastoid muscle. Structure and Function There are two sets of jugular veins: external and internal. The left and right external jugular veins drain into the subclavian veins. The internal jugular veins join with the subclavian veins more medially to form the brachiocephalic veins. Finally, the left and right brachiocephalic veins join to form the superior vena cava, which delivers deoxygenated blood to the right atrium of the heart. The Jugular veins help carry blood from the heart to and from the brain. An average human brain weighs about 3 pounds, and gets about 15%-20% of the blood that the heart pumps out. It is important for the brain to get enough blood for many reasons. The jugular ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carotid Arteries
In anatomy, the left and right common carotid arteries (carotids) ( in Merriam-Webster Online Dictionary '.) are that supply the head and neck with ; they divide in the neck to form the external and |
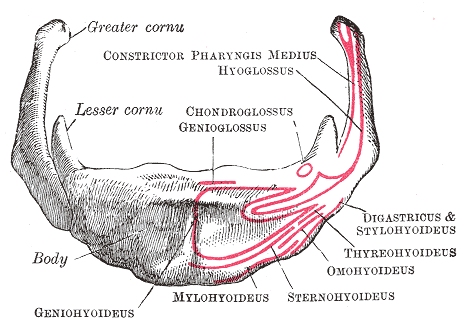
Hyoid Bone
The hyoid bone (lingual bone or tongue-bone) () is a horseshoe-shaped bone situated in the anterior midline of the neck between the chin and the thyroid cartilage. At rest, it lies between the base of the mandible and the third cervical vertebra. Unlike other bones, the hyoid is only distantly articulated to other bones by muscles or ligaments. It is the only bone in the human body that is not connected to any other bones nearby. The hyoid is anchored by muscles from the anterior, posterior and inferior directions, and aids in tongue movement and swallowing. The hyoid bone provides attachment to the muscles of the floor of the mouth and the tongue above, the larynx below, and the epiglottis and pharynx behind. Its name is derived . Structure The hyoid bone is classed as an irregular bone and consists of a central part called the body, and two pairs of horns, the greater and lesser horns. Body The body of the hyoid bone is the central part of the hyoid bone. *At the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Air Hunger
Shortness of breath (SOB), also medically known as dyspnea (in AmE) or dyspnoea (in BrE), is an uncomfortable feeling of not being able to breathe well enough. The American Thoracic Society defines it as "a subjective experience of breathing discomfort that consists of qualitatively distinct sensations that vary in intensity", and recommends evaluating dyspnea by assessing the intensity of its distinct sensations, the degree of distress and discomfort involved, and its burden or impact on the patient's activities of daily living. Distinct sensations include effort/work to breathe, chest tightness or pain, and "air hunger" (the feeling of not enough oxygen). The tripod position is often assumed to be a sign. Dyspnea is a normal symptom of heavy physical exertion but becomes pathological if it occurs in unexpected situations, when resting or during light exertion. In 85% of cases it is due to asthma, pneumonia, cardiac ischemia, interstitial lung disease, congestive heart failu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asphyxia
Asphyxia or asphyxiation is a condition of deficient supply of oxygen to the body which arises from abnormal breathing. Asphyxia causes generalized hypoxia, which affects primarily the tissues and organs. There are many circumstances that can induce asphyxia, all of which are characterized by the inability of a person to acquire sufficient oxygen through breathing for an extended period of time. Asphyxia can cause coma or death. In 2015, about 9.8 million cases of unintentional suffocation occurred which resulted in 35,600 deaths. The word asphyxia is from Ancient Greek "without" and , "squeeze" (throb of heart). Causes Situations that can cause asphyxia include but are not limited to: airway obstruction, the constriction or obstruction of airways, such as from asthma, laryngospasm, or simple blockage from the presence of foreign materials; from being in environments where oxygen is not readily accessible: such as underwater, in a low oxygen atmosphere, or in a vacuum; ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laryngopharynx
The pharynx (plural: pharynges) is the part of the throat behind the mouth and nasal cavity, and above the oesophagus and trachea (the tubes going down to the stomach and the lungs). It is found in vertebrates and invertebrates, though its structure varies across species. The pharynx carries food and air to the esophagus and larynx respectively. The flap of cartilage called the epiglottis stops food from entering the larynx. In humans, the pharynx is part of the digestive system and the conducting zone of the respiratory system. (The conducting zone—which also includes the nostrils of the nose, the larynx, trachea, bronchi, and bronchioles—filters, warms and moistens air and conducts it into the lungs). The human pharynx is conventionally divided into three sections: the nasopharynx, oropharynx, and laryngopharynx. It is also important in vocalization. In humans, two sets of pharyngeal muscles form the pharynx and determine the shape of its lumen. They are arranged as an in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Larynx
The larynx (), commonly called the voice box, is an organ in the top of the neck involved in breathing, producing sound and protecting the trachea against food aspiration. The opening of larynx into pharynx known as the laryngeal inlet is about 4–5 centimeters in diameter. The larynx houses the vocal cords, and manipulates pitch and volume, which is essential for phonation. It is situated just below where the tract of the pharynx splits into the trachea and the esophagus. The word ʻlarynxʼ (plural ʻlaryngesʼ) comes from the Ancient Greek word ''lárunx'' ʻlarynx, gullet, throat.ʼ Structure The triangle-shaped larynx consists largely of cartilages that are attached to one another, and to surrounding structures, by muscles or by fibrous and elastic tissue components. The larynx is lined by a ciliated columnar epithelium except for the vocal folds. The cavity of the larynx extends from its triangle-shaped inlet, to the epiglottis, and to the circular outlet at the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |