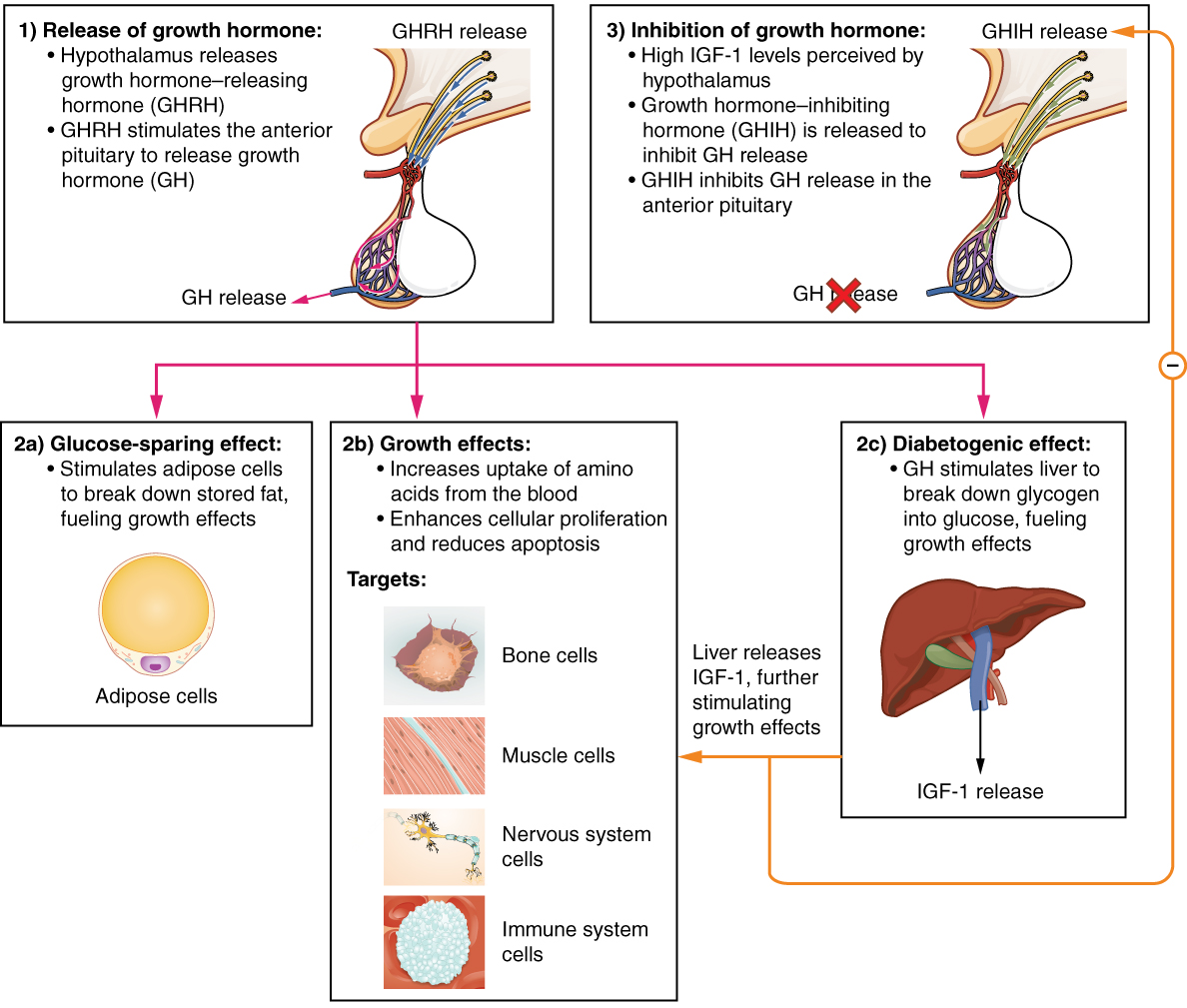
|
Growth-hormone-releasing Hormone Receptor
The growth-hormone-releasing hormone receptor (GHRHR) is a G-protein-coupled receptor that binds growth hormone-releasing hormone. The GHRHR activates a Gs protein that causes a cascade of cAMP via adenylate cyclase. GHRHR is distinct from the growth hormone secretagogue receptor (also known as the ghrelin receptor), where growth hormone releasing peptides act to release growth hormone. Function This gene, expressed in the pituitary, encodes a receptor for growth-hormone-releasing hormone. Binding of this hormone to the receptor leads to synthesis and release of growth hormone. Mutations in this gene have been associated with isolated growth-hormone deficiency (IGHD), also known as Dwarfism of Sindh, a disorder characterized by short stature. Many alternate transcriptional splice variants encoding different isoforms have been described, but only two have been characterized to date. Ligands Agonists * CJC-1295 * Dumorelin * GHRH (somatorelin) * Rismorelin * Sermoreli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
G-protein-coupled Receptor
G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs), also known as seven-(pass)-transmembrane domain receptors, 7TM receptors, heptahelical receptors, serpentine receptors, and G protein-linked receptors (GPLR), form a large protein family, group of evolutionarily related proteins that are cell surface receptors that detect molecules outside the cell (biology), cell and activate cellular responses. They are coupled with G proteins. They pass through the cell membrane seven times in the form of six loops (three extracellular loops interacting with ligand molecules, three intracellular loops interacting with G proteins, an N-terminus, N-terminal extracellular region and a C-terminal intracellular region) of amino acid residues, which is why they are sometimes referred to as seven-transmembrane receptors. Text was copied from this source, which is available under Attribution 2.5 Generic (CC BY 2.5) licence/ref> Ligands can bind either to the extracellular N-terminus and loops (e.g. glutama ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Growth Hormone-releasing Hormone
Growth may refer to: Biology * Auxology, the study of all aspects of human physical growth * Bacterial growth *Cell growth *Growth hormone, a peptide hormone that stimulates growth *Human development (biology) *Plant growth *Secondary growth, growth that thickens woody plants *A tumor or other such neoplasm Economics * Economic growth, the increase in the inflation-adjusted market value of the goods and services * Growth investing, a style of investment strategy focused on capital appreciation Mathematics * Exponential growth, also called geometric growth * Hyperbolic growth * Linear growth, refers to two distinct but related notions * Logistic growth, characterized as an S curve Social science * Developmental psychology * Erikson's stages of psychosocial development * Human development (humanity) * Personal development * Population growth Other uses * ''Growth'' (film), a 2010 American horror film * Izaugsme (''Growth''), a Latvian political party * ''Grown'' (album), by 2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gs Alpha Subunit
The Gs alpha subunit (Gαs, Gsα) is a subunit of the heterotrimeric G protein Gs that stimulates the cAMP-dependent pathway by activating adenylyl cyclase. Gsα is a GTPase that functions as a cellular signaling protein. Gsα is the founding member of one of the four families of heterotrimeric G proteins, defined by the alpha subunits they contain: the Gαs family, Gαi/Gαo family, Gαq family, and Gα12/Gα13 family. The Gs-family has only two members: the other member is Golf, named for its predominant expression in the olfactory system. In humans, Gsα is encoded by the GNAS complex locus, while Golfα is encoded by the GNAL gene. Function The general function of Gs is to activate intracellular signaling pathways in response to activation of cell surface G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs). GPCRs function as part of a three-component system of receptor-transducer-effector. The transducer in this system is a heterotrimeric G protein, composed of three subunits: a G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclic Adenosine Monophosphate
Cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP, cyclic AMP, or 3',5'-cyclic adenosine monophosphate) is a second messenger, or cellular signal occurring within cells, that is important in many biological processes. cAMP is a derivative of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and used for intracellular signal transduction in many different organisms, conveying the cAMP-dependent pathway. History Earl Sutherland of Vanderbilt University won a Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1971 "for his discoveries concerning the mechanisms of the action of hormones", especially epinephrine, via second messengers (such as cyclic adenosine monophosphate, cyclic AMP). Synthesis The synthesis of cAMP is stimulated by trophic hormones that bind to receptors on the cell surface. cAMP levels reach maximal levels within minutes and decrease gradually over an hour in cultured cells. Cyclic AMP is synthesized from ATP by adenylate cyclase located on the inner side of the plasma membrane and anchored at v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adenylate Cyclase
Adenylate cyclase (EC 4.6.1.1, also commonly known as adenyl cyclase and adenylyl cyclase, abbreviated AC) is an enzyme with systematic name ATP diphosphate-lyase (cyclizing; 3′,5′-cyclic-AMP-forming). It catalyzes the following reaction: :ATP = 3′,5′-cyclic AMP + diphosphate It has key regulatory roles in essentially all cells. It is the most polyphyletic known enzyme: six distinct classes have been described, all catalyzing the same reaction but representing unrelated gene families with no known sequence or structural homology. The best known class of adenylyl cyclases is class III or AC-III (Roman numerals are used for classes). AC-III occurs widely in eukaryotes and has important roles in many human tissues. All classes of adenylyl cyclase catalyse the conversion of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) to 3',5'-cyclic AMP (cAMP) and pyrophosphate. Magnesium ions are generally required and appear to be closely involved in the enzymatic mechanism. The cAMP produced by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Growth Hormone Secretagogue Receptor
Growth hormone secretagogue receptor(GHS-R), also known as ghrelin receptor, is a G protein-coupled receptor that binds growth hormone secretagogues (GHSs), such as ghrelin, the "hunger hormone". The role of GHS-R is thought to be in regulating energy homeostasis and body weight. In the brain, they are most highly expressed in the hypothalamus, specifically the ventromedial nucleus and arcuate nucleus. GSH-Rs are also expressed in other areas of the brain, including the ventral tegmental area, hippocampus, and substantia nigra. Outside the central nervous system, too, GSH-Rs are also found in the liver, in skeletal muscle, and even in the heart. Structure Two identified transcript variants are expressed in several tissues and are evolutionarily conserved in fish and swine. One transcript, 1a, excises an intron and encodes the functional protein; this protein is the receptor for the ghrelin ligand and defines a neuroendocrine pathway for growth hormone release. The second transcr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Growth Hormone
Growth hormone (GH) or somatotropin, also known as human growth hormone (hGH or HGH) in its human form, is a peptide hormone that stimulates growth, cell reproduction, and cell regeneration in humans and other animals. It is thus important in human development. GH also stimulates production of insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) and increases the concentration of glucose and free fatty acids. It is a type of mitogen which is specific only to the receptors on certain types of cells. GH is a 191-amino acid, single-chain polypeptide that is synthesized, stored and secreted by somatotropic cells within the lateral wings of the anterior pituitary gland. A recombinant form of HGH called somatropin ( INN) is used as a prescription drug to treat children's growth disorders and adult growth hormone deficiency. In the United States, it is only available legally from pharmacies by prescription from a licensed health care provider. In recent years in the United States, some health ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Splice Variant
Alternative splicing, alternative RNA splicing, or differential splicing, is an alternative splicing process during gene expression that allows a single gene to produce different splice variants. For example, some exons of a gene may be included within or excluded from the final RNA product of the gene. This means the exons are joined in different combinations, leading to different splice variants. In the case of protein-coding genes, the proteins translated from these splice variants may contain differences in their amino acid sequence and in their biological functions (see Figure). Biologically relevant alternative splicing occurs as a normal phenomenon in eukaryotes, where it increases the number of proteins that can be encoded by the genome. In humans, it is widely believed that ~95% of multi-exonic genes are alternatively spliced to produce functional alternative products from the same gene but many scientists believe that most of the observed splice variants are due to spli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CJC-1295
CJC-1295 DAC, also known as DAC:GRF (short for drug affinity complex:growth hormone-releasing factor), is a synthetic analogue of growth hormone-releasing hormone (GHRH) (also known as ''growth hormone-releasing factor'' (''GRF'')) and a growth hormone secretagogue (GHS) which was developed by ConjuChem Biotechnologies. It is a modified form of GHRH (1-29) with improved pharmacokinetics, especially in regard to half-life. Effects CJC-1295 may markedly increase plasma growth hormone (GH) and insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) levels in animals and humans. With a single injection, in human subjects, CJC-1295 DAC may increase plasma GH levels by 2- to 10-fold for 6 days or longer and plasma IGF-1 levels by 0.5- to 3-fold for 9 to 11 days. With the inclusion of the DAC additive, the drug has an estimated half-life of about 6 to 8 days in humans. With multiple doses of CJC-1295, IGF-1 levels were found to remain elevated in humans for up to 28 days. CJC-1295 has been shown to e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Growth Hormone-releasing Hormone
Growth may refer to: Biology * Auxology, the study of all aspects of human physical growth * Bacterial growth *Cell growth *Growth hormone, a peptide hormone that stimulates growth *Human development (biology) *Plant growth *Secondary growth, growth that thickens woody plants *A tumor or other such neoplasm Economics * Economic growth, the increase in the inflation-adjusted market value of the goods and services * Growth investing, a style of investment strategy focused on capital appreciation Mathematics * Exponential growth, also called geometric growth * Hyperbolic growth * Linear growth, refers to two distinct but related notions * Logistic growth, characterized as an S curve Social science * Developmental psychology * Erikson's stages of psychosocial development * Human development (humanity) * Personal development * Population growth Other uses * ''Growth'' (film), a 2010 American horror film * Izaugsme (''Growth''), a Latvian political party * ''Grown'' (album), by 2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |