|
Greek Passport
Greek passports () are issued to Greek citizens for the purpose of international travel. Biometric passports have been issued since 26 August 2006, with old-style passports being declared invalid as of 1 January 2007. Since June 2009, the passport's RFID chip includes two index fingerprints as well as a high-resolution JPEG image of the passport holder. From 18 December 2023, issuance of the new generation of Greek passports was started by selected authorities and after 9 January 2024, only the new generation of passports are issued. Every Greek citizen is also a citizen of the European Union. The passport, along with the national identity card allows for free rights of movement and residence in any of the states of the European Union, European Economic Area, and Switzerland. https://www.consilium.europa.eu/prado/en/GRC-AO-04001/index.html Passport appearance The Greek passport follows the standard European Union passport design, with a burgundy red cover and the national em ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biometric Passport
A biometric passport (also known as an electronic passport, e-passport or a digital passport) is a passport that has an embedded electronic microprocessor chip, which contains biometrics, biometric information that can be used to authenticate the identity of the passport holder. It uses contactless smart card technology, including a microprocessor chip (computer chip) and antenna (for both power to the chip and communication) embedded in the front or back cover, or centre page, of the passport. The passport's critical information is printed on the data page of the passport, repeated on the Machine-readable passport, machine readable lines and stored in the chip. Public key infrastructure (PKI) is used to authenticate the data stored electronically in the passport chip, making it expensive and difficult to forge when all security mechanisms are fully and correctly implemented. Most countries are issuing biometric passports to their citizens. Malaysia was the first country to iss ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polycarbonate
Polycarbonates (PC) are a group of thermoplastic polymers containing carbonate ester, carbonate groups in their chemical structures. Polycarbonates used in engineering are strong, toughness, tough materials, and some grades are optically transparent. They are easily worked, injection molding, molded, and thermoforming, thermoformed. Because of these properties, polycarbonates find many applications. Polycarbonates do not have a unique resin identification code, resin identification code (RIC) and are identified as "Other", 7 on the RIC list. Products made from polycarbonate can contain the precursor monomer bisphenol A (BPA). Structure Carbonate esters have planar OC(OC)2 cores, which confer rigidity. The unique O=C bond is short (1.173 Å in the depicted example), while the C-O bonds are more ether-like (the bond distances of 1.326 Å for the example depicted). Polycarbonates received their name because they are polymers containing carbonate ester, carbonate groups (−O−( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
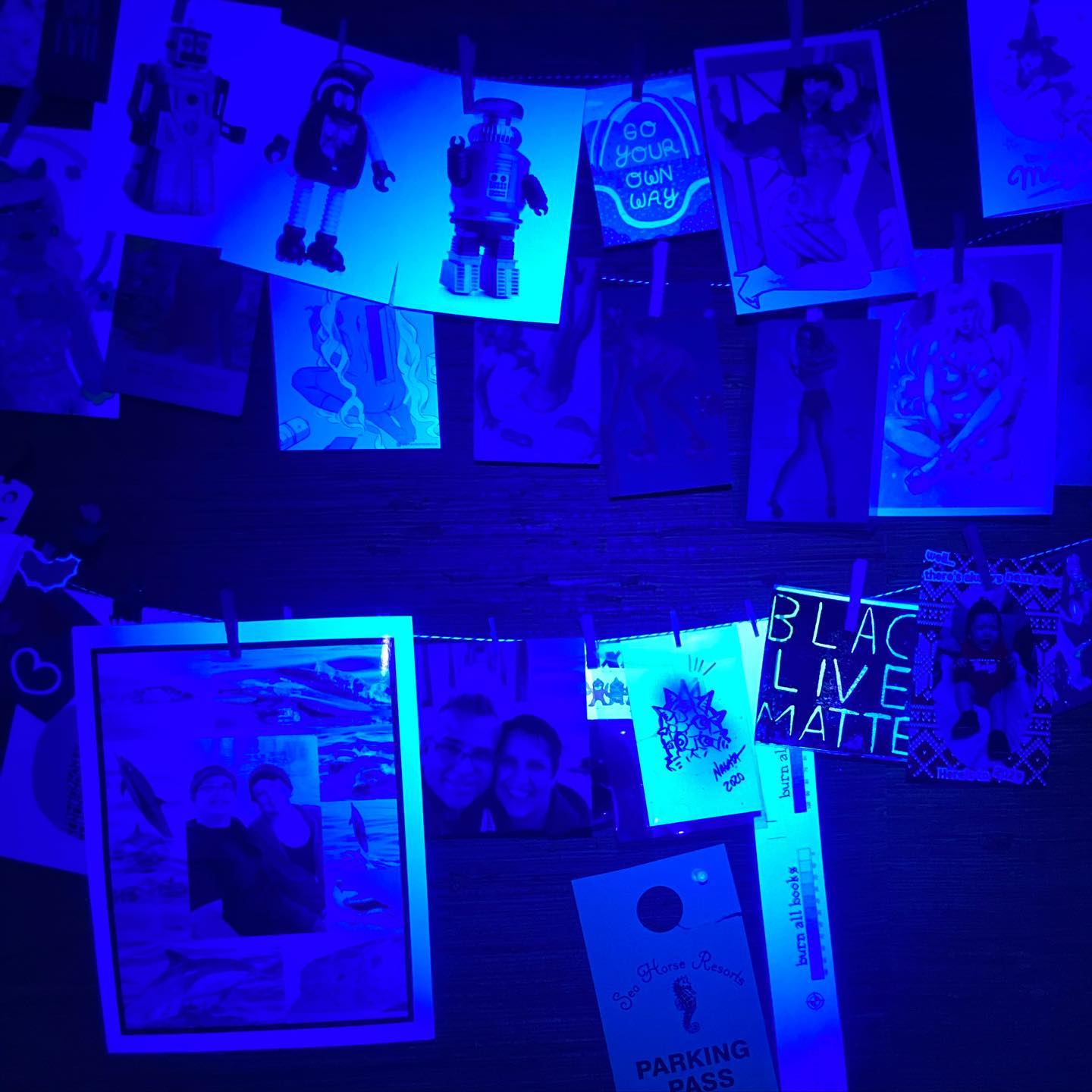
Greek Service ID And Greek Passport Under UV Light
Greek may refer to: Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe: *Greeks, an ethnic group *Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family **Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor of all known varieties of Greek **Mycenaean Greek, most ancient attested form of the language (16th to 11th centuries BC) **Ancient Greek, forms of the language used c. 1000–330 BC **Koine Greek, common form of Greek spoken and written during Classical antiquity **Medieval Greek or Byzantine Language, language used between the Middle Ages and the Ottoman conquest of Constantinople **Modern Greek, varieties spoken in the modern era (from 1453 AD) *Greek alphabet, script used to write the Greek language *Greek Orthodox Church, several Churches of the Eastern Orthodox Church *Ancient Greece, the ancient civilization before the end of Antiquity *Old Greek, the language as spoken from Late Antiquity to around 1500 AD *Greek mythology, a body of myths or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intaglio (printmaking)
Intaglio ( ; ) is the family of printing and printmaking techniques in which the image is incised into a surface and the incised line or sunken area holds the ink. It is the direct opposite of a relief print where the parts of the matrix that make the image stand ''above'' the main surface. Normally copper, or in recent times zinc, sheets called plates are used as a surface or matrix, and the incisions are created by etching, engraving, drypoint, aquatint or mezzotint, often in combination. Collagraphs may also be printed as intaglio plates. After the decline of the main relief technique of woodcut around 1550, the intaglio techniques dominated both artistic printmaking as well as most types of illustration and popular prints until the mid 19th century. The word "intaglio" describes prints created from plates where the ink-bearing regions are recessed beneath the plate's surface. Though brass, zinc, and other materials are occasionally utilized, copper is the most commo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ultraviolet
Ultraviolet radiation, also known as simply UV, is electromagnetic radiation of wavelengths of 10–400 nanometers, shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays. UV radiation is present in sunlight and constitutes about 10% of the total electromagnetic radiation output from the Sun. It is also produced by electric arcs, Cherenkov radiation, and specialized lights, such as mercury-vapor lamps, tanning lamps, and black lights. The photons of ultraviolet have greater energy than those of visible light, from about 3.1 to 12 electron volts, around the minimum energy required to ionize atoms. Although long-wavelength ultraviolet is not considered an ionizing radiation because its photons lack sufficient energy, it can induce chemical reactions and cause many substances to glow or fluoresce. Many practical applications, including chemical and biological effects, are derived from the way that UV radiation can interact with organic molecules. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Invisible Ink
Invisible ink, also known as security ink or sympathetic ink, is a substance used for writing, which is invisible either on application or soon thereafter, and can later be made visible by some means, such as heat or ultraviolet light. Invisible ink is one form of steganography. History One of the earliest writers to mention an invisible ink is Aeneas Tacticus, in the 4th century BC. He mentions it in discussing how to survive under siege but does not indicate the type of ink to be used. This was part of his list of the 20 different methods of secret communications in a book called ''On the Defense of Fortifications''. One of the techniques that involved steganography involved puncturing a tiny hole above or below letters in a document to spell out a secret message. This did not include an invisible ink but the Germans improved on the method during World War I and World War II. They used invisible ink and microdots instead of pinpricks. Philo of Byzantium may be the first write ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Security Thread
A security thread is a security feature of many banknotes to protect against counterfeiting. Introduced in United States banknotes in 1990, it consists of a thin ribbon that is woven through the note's paper. Usually, the ribbon runs vertically, and is "woven" into the paper, so that it at some places emerges on the front side and at the remaining places at the rear side of the paper. It is made of metal foil, but sometimes of plastic, and oftentimes it has some text or numbers (e.g., the denomination) engraved. Threads are embedded within the paper fiber and can be completely invisible or have a star burst effect, where the thread appears to weave in and out of the paper when viewed from one side, while the thread will always appear as a solid line when held up to the light. Features can be built into the thread material e.g., microprinting on a transparent plastic thread or adding materials so they fluoresce under ultraviolet light. The thread is a difficult feature to cou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Watermark
A watermark is an identifying image or pattern in paper that appears as various shades of lightness/darkness when viewed by transmitted light (or when viewed by reflected light, atop a dark background), caused by thickness or density variations in the paper. Watermarks have been used on postage stamps, currency, and other government documents to discourage counterfeiting. There are two main ways of producing watermarks in paper; the ''dandy roll process'', and the more complex ''cylinder mould process''. Watermarks vary greatly in their visibility; while some are obvious on casual inspection, others require some study to pick out. Various aids have been developed, such as ''watermark fluid'' that wets the paper without damaging it. A watermark is very useful in the questioned document examination, examination of paper because it can be used for dating documents and artworks, identifying sizes, mill trademarks and locations, and determining the quality of a sheet of paper. The wor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microprinting
Microprinting is the production of recognizable patterns or characters in a printed medium at a scale that typically requires magnification to read with the naked eye. To the unaided eye, the text may appear as a solid line. Attempts to reproduce by methods of photocopy, image scanning, or pantograph typically translate as a dotted or solid line, unless the reproduction method can identify and recreate patterns to such scale. Microprint is predominantly used as an anti-counterfeiting technique, due to its inability to be easily reproduced by widespread digital methods. While microphotography precedes microprint, microprint was significantly influenced by Albert Boni in 1934 when he was inspired by his friend, writer and editor Manuel Komroff, who was showing his experimentations related to the enlarging of photographs. It occurred to Boni that if he could reduce rather than enlarge photographs, this technology might enable publication companies and libraries to access much gre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Security Printing
Security printing is the field of the printing industry that deals with the printing of items such as banknotes, cheques, passports, tamper-evident labels, security tapes, product authentication, stock certificates, postage stamps, and identity cards. The main goal of security printing is to prevent forgery, tampering, or counterfeiting. More recently many of the techniques used to protect these high-value documents have become more available to commercial printers, whether they are using the more traditional offset printing, offset and flexography, flexographic presses or the newer digital platforms. Businesses are protecting their lesser-value documents such as transcripts, coupons and prescription pads by incorporating some of the features listed below to ensure that they cannot be forged or that alteration of the data cannot occur undetected. A number of technical methods are used in the security printing industry. Security printing is most often done on security paper, but it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optically Variable Ink
Optically variable ink (OVI) also called color shifting ink is an anti-counterfeiting measure used on many major modern banknotes, as well as on other official documents ( professional licenses, for example). The ink displays two distinct colors depending on the angle the bill is viewed at. The United States fifty-dollar bill, for example, uses color shifting ink for the numeral 50 so that it displays copper at one angle and bright green in another. OVI is particularly useful as an anti-counterfeiting measure as it is not widely available, and it is used on security printing. One major manufacturer is a Swiss company called SICPA (Société Industrielle et Commerciale de Produits pour l'Agriculture). Additional suppliers include German company Gleitsmann Security Inks, Sun Chemical (through their Brand Protection Division based in Manchester, UK), and the Swiss company Printcolor AG, located in Berikon, Switzerland. Color-shifting inks reflect various wavelengths in white ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optical Variable Device
An optical variable device or optically variable device (OVD) is an iridescent or non-iridescent security feature that exhibits different information, such as movement or colour changes, depending on the viewing and/or lighting conditions. The particular changes of appearance when rotating and tilting are reversible, predictable and reproducible. OVDs cannot be photocopied or scanned, nor can they be accurately replicated or reproduced. OVDs are often used as security devices and anti-counterfeiting measures on banknotes, government-issued identification documents, or credit cards. OVDs can be created through a combination of printing and embossing. OVDs are based on diffractive optical structures. This gives cards the appearance of having different patterns, colours, and designs depending on the amount of light striking the OVD and the angle the OVD is viewed at. Hologram Holography is a technique that allows a wavefront to be recorded and later reconstructed. It is bes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |