|
Germanos III Of Old Patras
Germanos III of Old Patras ( el, Παλαιών Πατρών Γερμανός Γʹ; 1771–1826), born Georgios Gotzias, was an Orthodox Metropolitan of Patras. He played an important role in the Greek Revolution of 1821, having diplomatic and political activity. Germanos was born in Dimitsana, northwestern Arcadia, Peloponnese. Before his consecration as Metropolitan of Patras by Patriarch Gregory V, he had served as a priest and Protosyngellus in Smyrna. Greek Revolution According to tradition and several written sources, on March 25 (6 April, Greg.Calendar), the Feast of Annunciation, 1821, Bishop Germanos proclaimed the national uprising against the Ottoman Empire and blessed the flag of the revolution at the Monastery of Agia Lavra. Earlier, another revolt of the Greek War of Independence The Greek War of Independence, also known as the Greek Revolution or the Greek Revolution of 1821, was a successful war of independence by Greek revolutionaries against the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agia Lavra
Agia Lavra ("Holy Lavra") is a monastery near Kalavryta, Achaea, Greece. It was built in 961 AD, on Chelmos Mountain, at an altitude of 961 meters, and can be described as the symbolic birthplace of modern Greece. It stands as one of the oldest monasteries in the Peloponnese. It was burnt to the ground in 1585 by the Turks. It was rebuilt in 1600 while the frescoes by Anthimos were completed in 1645. It was burnt again in 1715 and in 1826 by the armies of Ibrahim Pasha of Egypt. In 1850 after the rebirth of modern Greece, the building was completely rebuilt. The monastery was burned down by German forces in 1943. It is famously linked with the Greek War of Independence, since it was here that the call for ''Eleftheria I Thanatos'' (Ελευθερία ή θάνατος) was first heard on 25 March 1821, launching the revolution against the Ottoman Empire. That day, Bishop Germanos of Patras performed a doxology and administered an oath to the Peloponnesian fighters. The revolution ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
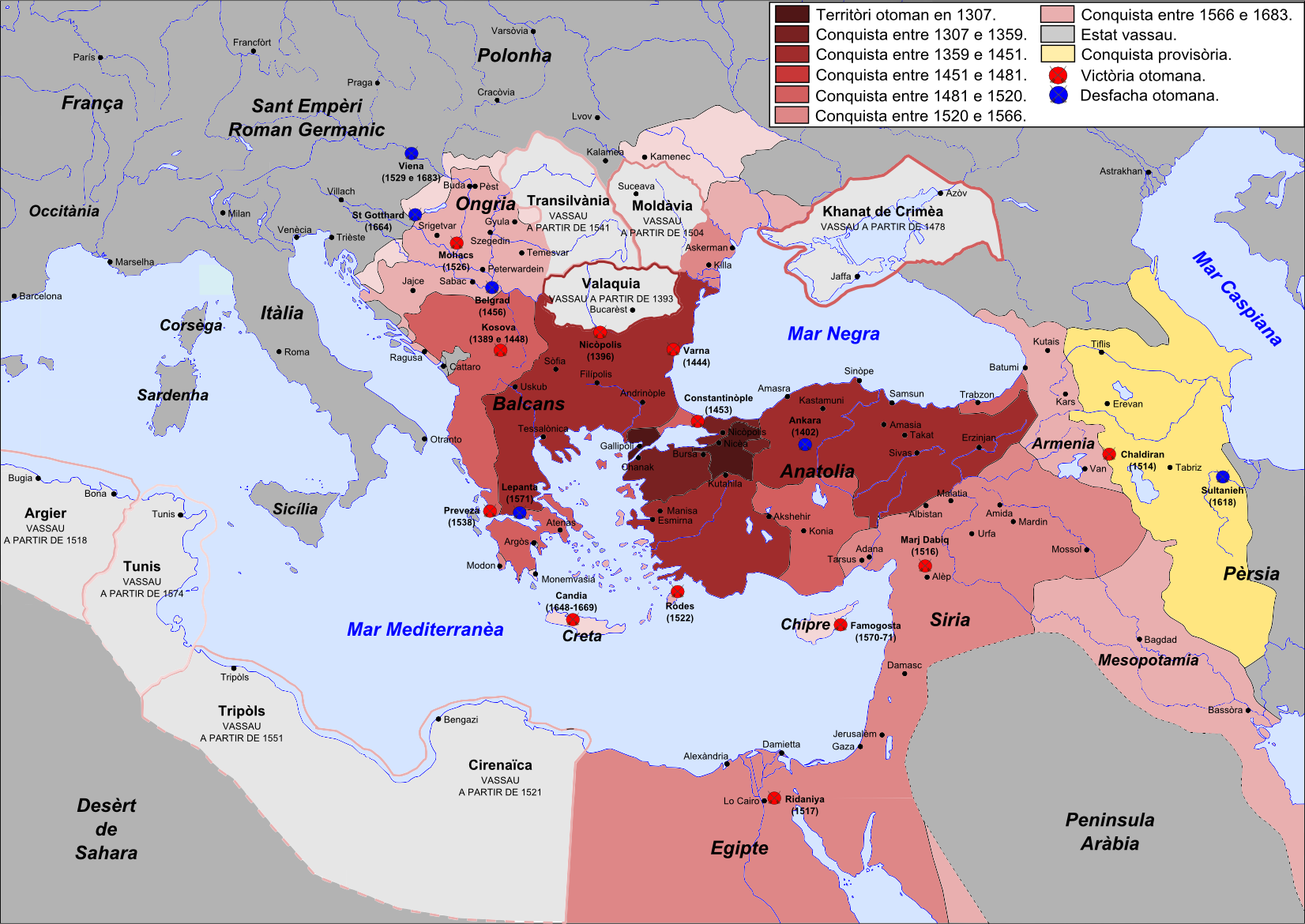
Ottoman Greece
Most of the areas which today are within modern Greece's borders were at some point in the past part of the Ottoman Empire. This period of Ottoman rule in Greece, lasting from the mid-15th century until the successful Greek War of Independence that broke out in 1821 and the proclamation of the First Hellenic Republic in 1822 (preceded by the creation of the autonomous Septinsular Republic in 1800), is known in Greek as ''Tourkokratia'' ( el, Τουρκοκρατία, "Turkish rule"; en, "Turkocracy"). Some regions, however, like the Ionian islands, various temporary Venetian possessions of the Stato da Mar, or Mani peninsula in Peloponnese did not become part of the Ottoman administration, although the latter was under Ottoman suzerainty. The Eastern Roman Empire, the remnant of the ancient Roman Empire which ruled most of the Greek-speaking world for over 1100 years, had been fatally weakened since the sacking of Constantinople by the Latin Crusaders in 1204. The Ottoma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greek People Of The Greek War Of Independence
Greek may refer to: Greece Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe: *Greeks, an ethnic group. *Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family. **Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor of all known varieties of Greek. **Mycenaean Greek, most ancient attested form of the language (16th to 11th centuries BC). **Ancient Greek, forms of the language used c. 1000–330 BC. **Koine Greek, common form of Greek spoken and written during Classical antiquity. **Medieval Greek or Byzantine Language, language used between the Middle Ages and the Ottoman conquest of Constantinople. **Modern Greek, varieties spoken in the modern era (from 1453 AD). *Greek alphabet, script used to write the Greek language. *Greek Orthodox Church, several Churches of the Eastern Orthodox Church. *Ancient Greece, the ancient civilization before the end of Antiquity. * Old Greek, the language as spoken from Late Antiquity to around 1500 AD. Other uses * ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greek Bishops
Greek may refer to: Greece Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe: * Greeks, an ethnic group. * Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family. ** Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor of all known varieties of Greek. ** Mycenaean Greek, most ancient attested form of the language (16th to 11th centuries BC). ** Ancient Greek, forms of the language used c. 1000–330 BC. ** Koine Greek, common form of Greek spoken and written during Classical antiquity. ** Medieval Greek or Byzantine Language, language used between the Middle Ages and the Ottoman conquest of Constantinople. ** Modern Greek, varieties spoken in the modern era (from 1453 AD). * Greek alphabet, script used to write the Greek language. * Greek Orthodox Church, several Churches of the Eastern Orthodox Church. * Ancient Greece, the ancient civilization before the end of Antiquity. * Old Greek, the language as spoken from Late Antiquity to around 1500 AD. Ot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
19th-century Eastern Orthodox Bishops
The 19th (nineteenth) century began on 1 January 1801 ( MDCCCI), and ended on 31 December 1900 ( MCM). The 19th century was the ninth century of the 2nd millennium. The 19th century was characterized by vast social upheaval. Slavery was abolished in much of Europe and the Americas. The First Industrial Revolution, though it began in the late 18th century, expanding beyond its British homeland for the first time during this century, particularly remaking the economies and societies of the Low Countries, the Rhineland, Northern Italy, and the Northeastern United States. A few decades later, the Second Industrial Revolution led to ever more massive urbanization and much higher levels of productivity, profit, and prosperity, a pattern that continued into the 20th century. The Islamic gunpowder empires fell into decline and European imperialism brought much of South Asia, Southeast Asia, and almost all of Africa under colonial rule. It was also marked by the collapse of the la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |