|
Geophilus Alaskanus
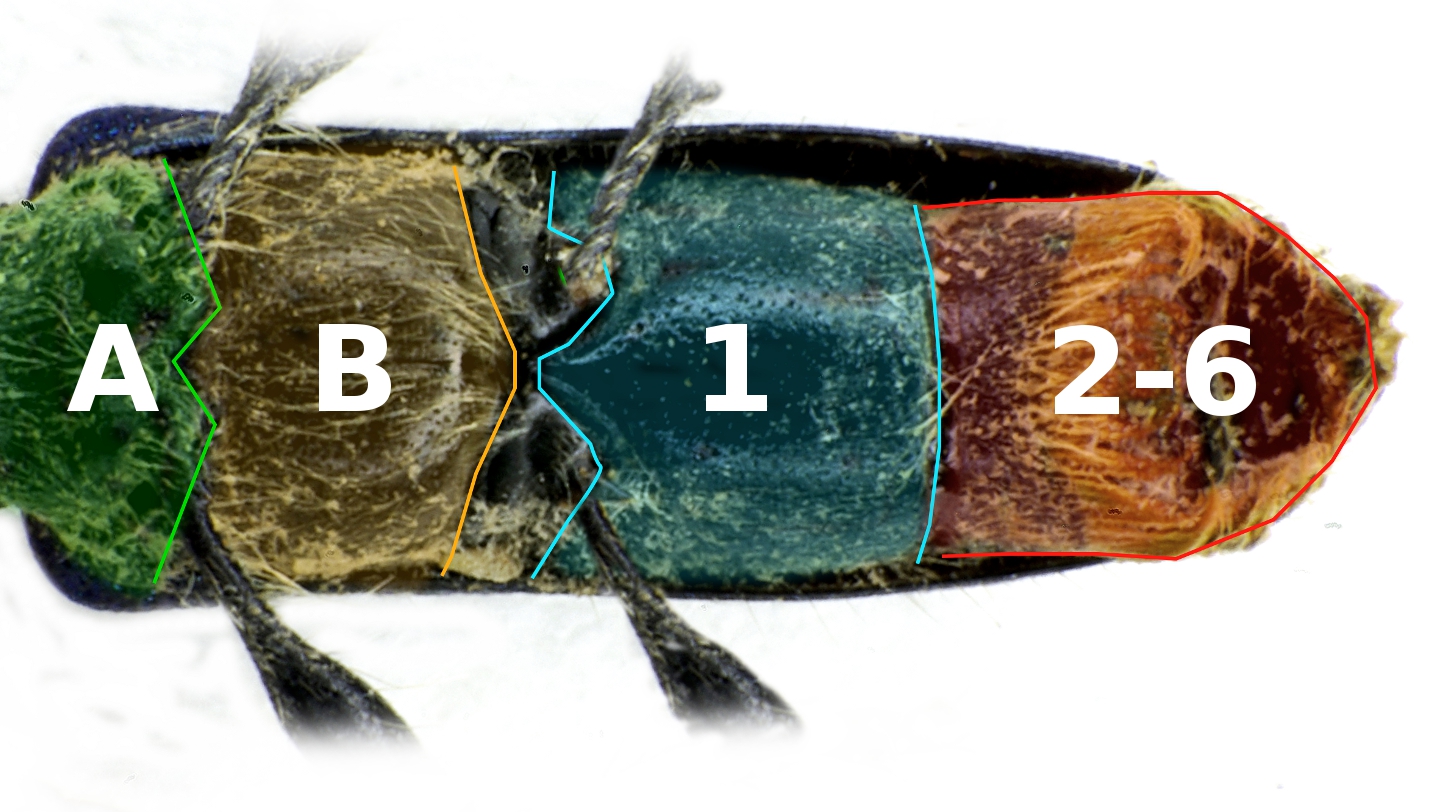
''Geophilus alaskanus'' is a species of soil centipede in the family Geophilidae found in Alaska. It bears similarities to '' Mecistocephalus attenuatus'', however unlike ''M. attenuatus'', it has oblong cephalic lamina, unarmed coxae, and unarmed claw at base. ''G. alaskanus'' is dull orange-brown in color, grows to about 30 millimeters, and has 53 leg pairs (in male specimens) with the first pair being very small and the last pair being distinctly larger than the others. It also possesses coalesced frontal lamina, unexposed basal lamina broader than the cephalic, a prehensorial sternum that's broader than it is long, distinct lateral grooves, obsolete prosternal teeth, a smooth, bare dorsal surface except for two faint impressed lines, and a small pleurae The pulmonary pleurae (''sing.'' pleura) are the two opposing layers of serous membrane overlying the lungs and the inside of the surrounding chest walls. The inner pleura, called the visceral pleura, covers the surface o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orator F
An orator, or oratist, is a public speaker, especially one who is eloquent or skilled. Etymology Recorded in English c. 1374, with a meaning of "one who pleads or argues for a cause", from Anglo-French ''oratour'', Old French ''orateur'' (14th century), Latin ''orator'' ("speaker"), from ''orare'' ("speak before a court or assembly; plead"), derived from a Proto-Indo-European base *''or-'' ("to pronounce a ritual formula"). The modern meaning of the word, "public speaker", is attested from c. 1430. History In ancient Rome, the art of speaking in public (''Ars Oratoria'') was a professional competence especially cultivated by politicians and lawyers. As the Greeks were still seen as the masters in this field, as in philosophy and most sciences, the leading Roman families often either sent their sons to study these things under a famous master in Greece (as was the case with the young Julius Caesar), or engaged a Greek teacher (under pay or as a slave). In the young revolution ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Species
In biology, a species is the basic unit of Taxonomy (biology), classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. A species is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate sexes or mating types can reproduction, produce Fertility, fertile offspring, typically by sexual reproduction. Other ways of defining species include their karyotype, DNA sequence, morphology (biology), morphology, behaviour or ecological niche. In addition, paleontologists use the concept of the chronospecies since fossil reproduction cannot be examined. The most recent rigorous estimate for the total number of species of eukaryotes is between 8 and 8.7 million. However, only about 14% of these had been described by 2011. All species (except viruses) are given a binomial nomenclature, two-part name, a "binomial". The first part of a binomial is the genus to which the species belongs. The second part is called the specifi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geophilomorpha
The centipedes or Chilopoda are divided into the following orders. Scutigeromorpha The Scutigeromorpha are anamorphic, reaching 15 leg-bearing segments in length. Also known as house centipedes, they are very fast creatures, and able to withstand falling at great speed: they reach up to 15 body lengths per second when dropped, surviving the fall. They are the only centipede group to retain their original compound eyes, within which a crystalline layer analogous to that seen in chelicerates and insects can be observed. They also bear long and multi-segmented antennae. Adaptation to a burrowing lifestyle has led to the degeneration of compound eyes in other orders; this feature is of great use in phylogenetic analysis. The group is the sole extant representative of the Notostigmophora, defined by having a single spiracle opening at the posterior of each dorsal plate. The more derived groups bear a plurality of spiracular openings on their sides, and are termed the Pleurostigmoph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Family (biology)
Family ( la, familia, plural ') is one of the eight major hierarchical taxonomic ranks in Linnaean taxonomy. It is classified between order and genus. A family may be divided into subfamilies, which are intermediate ranks between the ranks of family and genus. The official family names are Latin in origin; however, popular names are often used: for example, walnut trees and hickory trees belong to the family Juglandaceae, but that family is commonly referred to as the "walnut family". What belongs to a family—or if a described family should be recognized at all—are proposed and determined by practicing taxonomists. There are no hard rules for describing or recognizing a family, but in plants, they can be characterized on the basis of both vegetative and reproductive features of plant species. Taxonomists often take different positions about descriptions, and there may be no broad consensus across the scientific community for some time. The publishing of new data and opi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geophilidae
The Geophilidae are a polyphyletic, cosmopolitan family of soil centipedes in the superfamily Geophiloidea containing the mostly defunct clades Aphilodontidae, Dignathodontidae, Linotaeniidae, Chilenophilinae, and Macronicophilidae. Species in this family are characterized by mandibles with a single pectinate lamella, slender antennae, sternal pores with variable arrangement, a generally slightly or moderately elongate head, frequently undivided coxosternite with two paramedian sclerotized lines, claws without rows of filament, and female gonopods usually being an undivided lamina. Compared to most other families in the suborder Adesmata, this family features a modest number of leg-bearing segments (no more than 125) and limited variation in this number within each species. Two species in this family include centipedes with only 29 pairs of legs: '' Geophilus persephones'' (29 pairs in the only specimen, a male), and '' G. richardi'' (29 or 31 pairs in the males and 33 pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arthropod Leg
The arthropod leg is a form of jointed appendage of arthropods, usually used for walking. Many of the terms used for arthropod leg segments (called podomeres) are of Latin origin, and may be confused with terms for bones: ''coxa'' (meaning hip, plural ''coxae''), ''trochanter'', ''femur'' (plural ''femora''), ''tibia'' (plural ''tibiae''), ''tarsus'' (plural ''tarsi''), ''ischium'' (plural ''ischia''), ''metatarsus'', ''carpus'', ''dactylus'' (meaning finger), ''patella'' (plural ''patellae''). Homologies of leg segments between groups are difficult to prove and are the source of much argument. Some authors posit up to eleven segments per leg for the most recent common ancestor of extant arthropods but modern arthropods have eight or fewer. It has been argued that the ancestral leg need not have been so complex, and that other events, such as successive loss of function of a ''Hox''-gene, could result in parallel gains of leg segments. In arthropods, each of the leg segments ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sternum (arthropod Anatomy)
The sternum (pl. "sterna") is the ventral portion of a segment of an arthropod thorax or abdomen. In insects, the sterna are usually single, large sclerites, and external. However, they can sometimes be divided in two or more, in which case the subunits are called sternites, and may also be modified on the terminal abdominal segments so as to form part of the functional genitalia, in which case they are frequently reduced in size and development, and may become internalized and/or membranous. For a detailed explanation of the terminology, see Kinorhynchs have tergal and sternal plates too, though seemingly not homologous with those of arthropods.Sørensen, M. V. et al. Phylogeny of Kinorhyncha based on morphology and two molecular loci. PLoS One 10, 1–33 (2015). Ventrites are externally visible sternites. Usually the first sternite is covered up, so that vertrite numbers do not correspond to sternid numbers. The term is also used in other arthropod groups such as crustacea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prothorax
The prothorax is the foremost of the three segments in the thorax of an insect, and bears the first pair of legs. Its principal sclerites (exoskeletal plates) are the pronotum (dorsal), the prosternum (ventral), and the propleuron (lateral) on each side. The prothorax never bears wings in extant insects (except in some cases of atavism), though some fossil groups possessed wing-like projections. All adult insects possess legs on the prothorax, though in a few groups (e.g., the butterfly family Nymphalidae) the forelegs are greatly reduced. In many groups of insects, the pronotum is reduced in size, but in a few it is hypertrophied, such as in all beetles (Coleoptera). In most treehoppers (family Membracidae, order Hemiptera), the pronotum is expanded into often fantastic shapes that enhance their camouflage or mimicry. Similarly, in the Tetrigidae, the pronotum is extended backward to cover the flight wings, supplanting the function of the tegmina. See also *Glossary of en ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sclerite
A sclerite ( Greek , ', meaning " hard") is a hardened body part. In various branches of biology the term is applied to various structures, but not as a rule to vertebrate anatomical features such as bones and teeth. Instead it refers most commonly to the hardened parts of arthropod exoskeletons and the internal spicules of invertebrates such as certain sponges and soft corals. In paleontology, a scleritome is the complete set of sclerites of an organism, often all that is known from fossil invertebrates. Sclerites in combination Sclerites may occur practically isolated in an organism, such as the sting of a cone shell. Also, they can be more or less scattered, such as tufts of defensive sharp, mineralised bristles as in many marine Polychaetes. Or, they can occur as structured, but unconnected or loosely connected arrays, such as the mineral "teeth" in the radula of many Mollusca, the valves of Chitons, the beak of Cephalopod, or the articulated exoskeletons of Arthropoda. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geophilus
''Geophilus '' is a large, heterogeneous genus of soil centipedes in the family Geophilidae largely considered to be synonymous with '' Brachygeophilus''. It is a mostly holarctic genus characterized by a claw-shaped ultimate pretarsus, anterior porefields, complete or nearly complete coxo-pleural sutures at the prosternum, and incomplete chitin-lines. The generic name first appeared in Brewster's Edinburgh Encyclopaedia in 1814 as ''Geophilus electricus''. Although centipedes in this genus can have as many as 89 pairs of legs, most species have a much smaller number of leg pairs. For example, two species in this genus include centipedes with only 29 pairs of legs, the lowest number found in the family Geophilidae: '' G. persephones'' (29 pairs in the only specimen, a male) and '' G. richardi'' (29 or 31 pairs in males and 33 pairs in females). This genus also includes other species with notably few legs, for example, ''G. hadesi'' (33 pairs in both males and females) and ''G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fauna Of Alaska
The wildlife of Alaska is both diverse and abundant. The Alaskan Peninsula provides an important habitat for fish, mammals, reptiles, and birds. At the top of the food chain are the bears. Alaska contains about 70% of the total North American brown bear population and the majority of the grizzly bears. as well as black bears and Kodiak bears. In winter, polar bears can be found in the Kuskokwim Delta, St. Matthew Island, and at the southernmost portion of St. Lawrence Island. There are also moose and caribou, bison, wolves and wolverines, foxes, otters and beavers. Fish species are extensive, including: salmon, graylings, char, rainbow and lake trout, northern pike, halibut, pollock, and burbot. The bird population consists of hundreds of species, including: bald eagles, owls, falcons, ravens, ducks, geese, swans, and the passerines. Sea lions, seals, sea otters, and migratory whales are often found close to shore and in offshore waters. The Alaskan waters are home to two ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)