|
Genetic Association
Genetic association is when one or more genotypes within a population co-occur with a phenotype, phenotypic trait association (statistics), more often than would be expected by chance occurrence. Studies of genetic association aim to test whether single-locus alleles or genotype frequencies or more generally, multilocus haplotype frequencies differ between two groups of individuals (usually treatment and control groups, diseased subjects and healthy controls). Genetic association studies are based on the principle that genotypes can be compared "directly", i.e. with the sequences of the actual genomes or exomes via whole genome sequencing or exome sequencing, whole exome sequencing. Before 2010, DNA sequencing methods were used. Description Genetic association can be between phenotypes, such as visible characteristics such as flower color or height, between a phenotype and a genetic polymorphism, such as a single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP), or between two genetic polymorphism ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genotype
The genotype of an organism is its complete set of genetic material. Genotype can also be used to refer to the alleles or variants an individual carries in a particular gene or genetic location. The number of alleles an individual can have in a specific gene depends on the number of copies of each chromosome found in that species, also referred to as ploidy. In diploid species like humans, two full sets of chromosomes are present, meaning each individual has two alleles for any given gene. If both alleles are the same, the genotype is referred to as Zygosity, homozygous. If the alleles are different, the genotype is referred to as heterozygous. Genotype contributes to phenotype, the observable traits and characteristics in an individual or organism. The degree to which genotype affects phenotype depends on the trait. For example, the petal color in a pea plant is exclusively determined by genotype. The petals can be purple or white depending on the alleles present in the pea plan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genetic Marker
A genetic marker is a gene or DNA sequence with a known location on a chromosome that can be used to identify individuals or species. It can be described as a variation (which may arise due to mutation or alteration in the genomic loci) that can be observed. A genetic marker may be a short DNA sequence, such as a sequence surrounding a single base-pair change ( single nucleotide polymorphism, SNP), or a long one, like minisatellites. Background For many years, gene mapping was limited to identifying organisms by traditional phenotypes markers. This included genes that encoded easily observable characteristics, such as blood types or seed shapes. The insufficient number of these types of characteristics in several organisms limited the possible mapping efforts. This prompted the development of gene markers, which could identify genetic characteristics that are not readily observable in organisms (such as protein variation). Types Some commonly used types of genetic markers ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
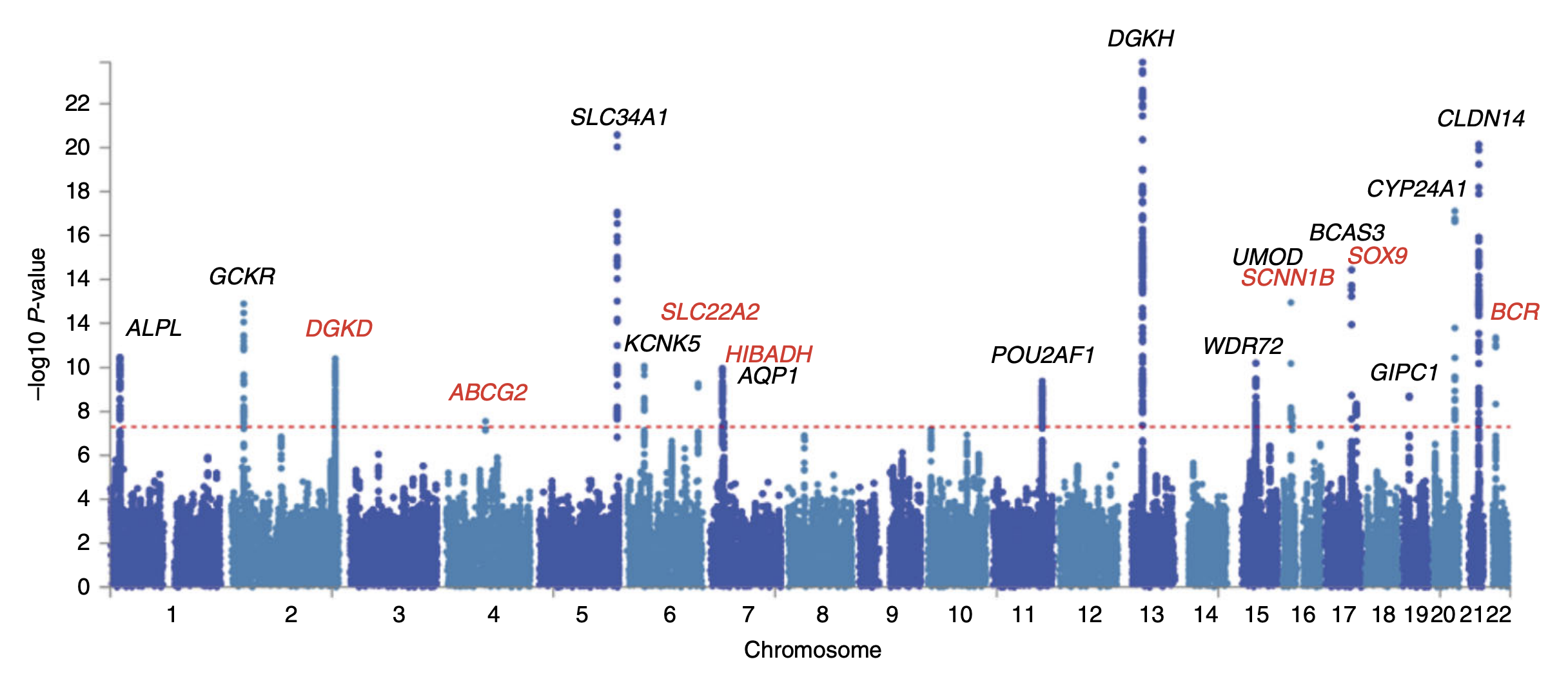
Genome-wide Association Study
In genomics, a genome-wide association study (GWA study, or GWAS), is an observational study of a genome-wide set of Single-nucleotide polymorphism, genetic variants in different individuals to see if any variant is associated with a trait. GWA studies typically focus on associations between single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) and traits like major human diseases, but can equally be applied to any other genetic variants and any other organisms. When applied to human data, GWA studies compare the DNA of participants having varying phenotypes for a particular trait or disease. These participants may be people with a disease (cases) and similar people without the disease (controls), or they may be people with different phenotypes for a particular trait, for example blood pressure. This approach is known as phenotype-first, in which the participants are classified first by their clinical manifestation(s), as opposed to Genotype-first approach, genotype-first. Each person gives a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genetic Linkage
Genetic linkage is the tendency of Nucleic acid sequence, DNA sequences that are close together on a chromosome to be inherited together during the meiosis phase of sexual reproduction. Two Genetic marker, genetic markers that are physically near to each other are unlikely to be separated onto different Chromatid, chromatids during chromosomal crossover, and are therefore said to be more ''linked'' than markers that are far apart. In other words, the nearer two Gene, genes are on a chromosome, the lower the chance of Genetic recombination, recombination between them, and the more likely they are to be inherited together. Markers on different chromosomes are perfectly ''unlinked'', although the penetrance of potentially deleterious alleles may be influenced by the presence of other alleles, and these other alleles may be located on other chromosomes than that on which a particular potentially deleterious allele is located. Genetic linkage is the most prominent exception to Gregor M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genetic Epidemiology
Genetic epidemiology is the study of the role of genetic factors in determining health and disease in families and in populations, and the interplay of such genetic factors with environmental factors. Genetic epidemiology seeks to derive a statistical and quantitative analysis of how genetics work in large groups. Definition The use of the term ''Genetic epidemiology'' emerged in the mid-1980s as a new scientific field. In formal language, genetic epidemiology was defined by Newton Morton, one of the pioneers of the field, as "a science which deals with the etiology, distribution, and control of disease in groups of relatives and with inherited causes of disease in populations". It is closely allied to both molecular epidemiology and statistical genetics, but these overlapping fields each have distinct emphases, societies and journals. One definition of the field closely follows that of behavior genetics, defining genetic epidemiology as "the scientific discipline that dea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Family Based QTL Mapping
Quantitative trait loci mapping or QTL mapping is the process of identifying genomic regions that potentially contain genes responsible for important economic, health or environmental characters. Mapping QTLs is an important activity that plant breeders and geneticists routinely use to associate potential causal genes with phenotypes of interest. Family-based QTL mapping is a variant of QTL mapping where multiple-families are used. Pedigree in humans and wheat Pedigree information include information about ancestry. Keeping pedigree records is a centuries-old tradition. Pedigrees can also be verified using gene-marker data. In plants The method has been discussed in the context of plant breeding populations. Pedigree records are kept by plants breeders and pedigree-based selection is popular in several plant species. Plant pedigrees are different from that of humans, particularly as plant are hermaphroditic – an individual can be male or female and mating can be performed in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Association Mapping
In genetics, association mapping, also known as "linkage disequilibrium mapping", is a method of mapping quantitative trait locus, quantitative trait loci (QTLs) that takes advantage of historic linkage disequilibrium to link phenotypes (observable characteristics) to genotypes (the genetic constitution of organisms), uncovering genetic associations. Theory Association mapping is based on the idea that traits that have entered a population only recently will still be linked to the surrounding genetic sequence of the original evolutionary ancestor, or in other words, will more often be found within a given haplotype, than outside of it. It is most often performed by scanning the entire genome for significant associations between a panel of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) (which, in many cases are spotted onto glass slides to create "SNP genotyping, SNP chips") and a particular phenotype. These associations must then be independently verified in order to show that they either (a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Disease Gene Identification
Disease gene identification is a process by which scientists identify the mutant genotypes responsible for an inherited genetic disorder. Mutations in these genes can include single nucleotide substitutions, single nucleotide additions/deletions, deletion of the entire gene, and other genetic abnormalities. Significance Knowledge of which genes (when non-functional) cause which disorders will simplify diagnosis of patients and provide insights into the functional characteristics of the mutation. The advent of modern-day high-throughput sequencing technologies combined with insights provided from the growing field of genomics is resulting in more rapid disease gene identification, thus allowing scientists to identify more complex mutations. Generic gene identification procedure Disease gene identification techniques often follow the same overall procedure. DNA is first collected from several patients who are believed to have the same genetic disease. Then, their DNA sample ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quantitative Trait Locus
A quantitative trait locus (QTL) is a locus (section of DNA) that correlates with variation of a quantitative trait in the phenotype of a population of organisms. QTLs are mapped by identifying which molecular markers (such as SNPs or AFLPs) correlate with an observed trait. This is often an early step in identifying the actual genes that cause the trait variation. Definition A quantitative trait locus (QTL) is a region of DNA which is associated with a particular phenotypic trait, which varies in degree and which can be attributed to polygenic effects, i.e., the product of two or more genes, and their environment. . These QTLs are often found on different chromosomes. The number of QTLs which explain variation in the phenotypic trait indicates the genetic architecture of a trait. It may indicate that plant height is controlled by many genes of small effect, or by a few genes of large effect. Typically, QTLs underlie continuous traits (those traits which vary continuou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haploid-relative-risk
The haplotype-relative-risk (HRR) method is a family-based method for determining gene allele genetic association, association to a disease in the presence of actual genetic linkage. nuclear family, Nuclear families with one affected child are sampled using the parental haplotypes not transmitted as a control. While similar to the genotype relative risk (RR), the HRR provides a solution to the problem of population stratification by only sampling within family trios. The HRR method was first proposed by Rubinstein in 1981 then detailed in 1987 by Rubinstein and Falk and is an important tool in genetic association studies. The original method proposed by Falk and Rubinstien fell under scrutiny in 1989, when Ott showed the equivalence of HRR to the classical RR method demonstrating that the HRR holds only when there is zero chance of Genetic recombination, recombination between a disease Locus (genetics), locus and its markers. Yet, even when the recombination factor for a locus and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transmission Disequilibrium Test
In genetics, the transmission disequilibrium test (TDT) was proposed by Spielman, McGinnis and Ewens (1993) as a family-based association test for the presence of genetic linkage between a genetic marker and a trait. It is an application of McNemar's test. A specificity of the TDT is that it will detect genetic linkage only in the presence of genetic association. While genetic association can be caused by population structure, genetic linkage will not be affected, which makes the TDT robust to the presence of population structure. The case of trios: one affected child per family Description of the test We first describe the TDT in the case where families consist of trios (two parents and one affected child). Our description follows the notations used in Spielman, McGinnis & Ewens (1993). The TDT measures the over-transmission of an allele from heterozygous parents to affected offsprings. The affected offsprings have parents. These can be represented by the transmitted a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Population Stratification
Population structure (also called genetic structure and population stratification) is the presence of a systematic difference in allele frequencies between subpopulations. In a randomly mating (or ''panmictic'') population, allele frequencies are expected to be roughly similar between groups. However, mating tends to be non-random to some degree, causing structure to arise. For example, a barrier like a river can separate two groups of the same species and make it difficult for potential mates to cross; if a mutation occurs, over many generations it can spread and become common in one subpopulation while being completely absent in the other. Genetic variants do not necessarily cause observable changes in organisms, but can be correlated by coincidence because of population structure—a variant that is common in a population that has a high rate of disease may erroneously be thought to cause the disease. For this reason, population structure is a common confounding variable in m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |