|
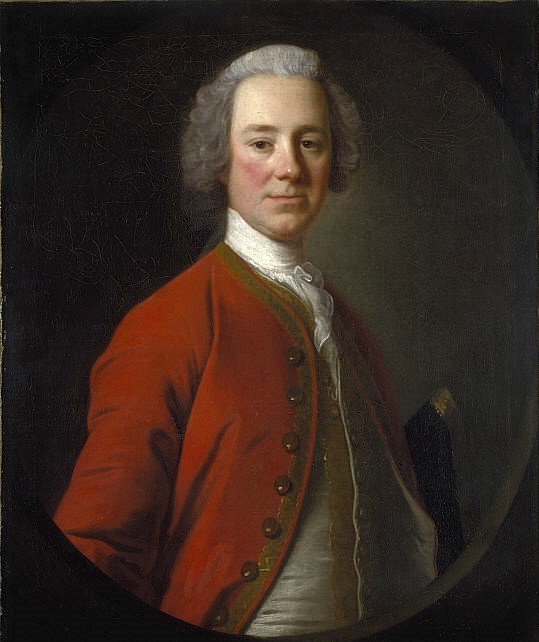
François Gaston De Lévis
François-Gaston de Lévis, Duke of Lévis (20 August 1719 – 20 November 1787), styled as the Chevalier de Lévis until 1785, was a nobleman and a Marshal of France. He served with distinction in the War of the Polish Succession and the War of the Austrian Succession. During the Seven Years' War, he was second-in-command to Louis-Joseph de Montcalm in the defense of New France and then, after the surrender of New France in 1760, he served in Europe. After the war, he was appointed Governor of Artois, and in 1783 he was made a Marshal of France. North American military service In 1756, the Marquis de Vaudreuil was informed that King Louis XV of France was sending the Marquis Louis-Joseph de Montcalm to take over French forces in North America, with Lévis as second in command. Vaudreuil wrote back that there was no need to send another general, as Vaudreuil disliked the tactics of most "municipal" French generals. When Montcalm arrived despite Vaudreuil's protest, the two ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duke Of Lévis
Duke is a male title either of a monarch ruling over a duchy, or of a member of royalty, or nobility. As rulers, dukes are ranked below emperors, kings, grand princes, grand dukes, and sovereign princes. As royalty or nobility, they are ranked below princess nobility and grand dukes. The title comes from French ''duc'', itself from the Latin ''dux'', 'leader', a term used in republican Rome to refer to a military commander without an official rank (particularly one of Germanic or Celtic origin), and later coming to mean the leading military commander of a province. In most countries, the word ''duchess'' is the female equivalent. Following the reforms of the emperor Diocletian (which separated the civilian and military administrations of the Roman provinces), a ''dux'' became the military commander in each province. The title ''dux'', Hellenised to ''doux'', survived in the Eastern Roman Empire where it continued in several contexts, signifying a rank equivalent to a capt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
War Of The Polish Succession
The War of the Polish Succession ( pl, Wojna o sukcesję polską; 1733–35) was a major European conflict sparked by a Polish civil war over the succession to Augustus II of Poland, which the other European powers widened in pursuit of their own national interests. France and Spain, the two Bourbon powers, attempted to test the power of the Austrian Habsburgs in Western Europe, as did the Kingdom of Prussia, whilst Saxony and Russia mobilized to support the eventual Polish victor. The fighting in Poland resulted in the accession of Augustus III, who in addition to Russia and Saxony, was politically supported by the Habsburgs. The war's major military campaigns and battles occurred outside of Poland. The Bourbons, supported by Charles Emmanuel III of Sardinia, moved against isolated Habsburg territories. In the Rhineland, France successfully took the Duchy of Lorraine, and in Italy, Spain regained control over the kingdoms of Naples and Sicily lost in the War of the Spani ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pierre François De Rigaud, Marquis De Vaudreuil-Cavagnal
Pierre de Rigaud de Vaudreuil de Cavagnial, marquis de Vaudreuil (22 November 1698 – 4 August 1778) was a Canadian-born colonial governor of French Canada in North America. He was governor of French Louisiana (1743–1753) and in 1755 became the last Governor-General of New France. In 1759 and 1760 the British conquered the colony in the Seven Years' War (known in the United States as the French and Indian War). Life and work He was born to the Governor-General of New France, Philippe de Rigaud Vaudreuil and his wife, Louise-Élisabeth, the daughter of Pierre de Joybert de Soulanges et de Marson, in Quebec. He was the uncle of Louis-Philippe de Vaudreuil. Vaudreuil rose quickly through the New France military and civil service, in part owing to his father's patronage but also due to his own innate ability. Commissioned an officer of the French army while still a youth, in 1733 he was appointed governor of Trois-Rivières, and in 1742 of French Louisiana, serving th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louis-Joseph De Montcalm
Louis-Joseph de Montcalm-Grozon, Marquis de Montcalm de Saint-Veran (28 February 1712 – 14 September 1759) was a French soldier best known as the commander of the forces in North America during the Seven Years' War (whose North American theatre is also referred to as the French and Indian War). Montcalm was born near Nîmes in France to a noble family, and entered military service early in life. He saw service in the War of the Polish Succession and the War of the Austrian Succession, where his distinguished service led to promotion to brigadier general. In 1756 King Louis XV sent him to New France to lead its defence against the British in the Seven Years' War. Montcalm met with notable successes in 1756, 1757 and 1758, but British mobilisation of large numbers of troops against New France led to military setbacks in 1758 and 1759 (when, in January, he was promoted to lieutenant general), culminating in Montcalm's death at the Battle of the Plains of Abraham. Montcalm' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
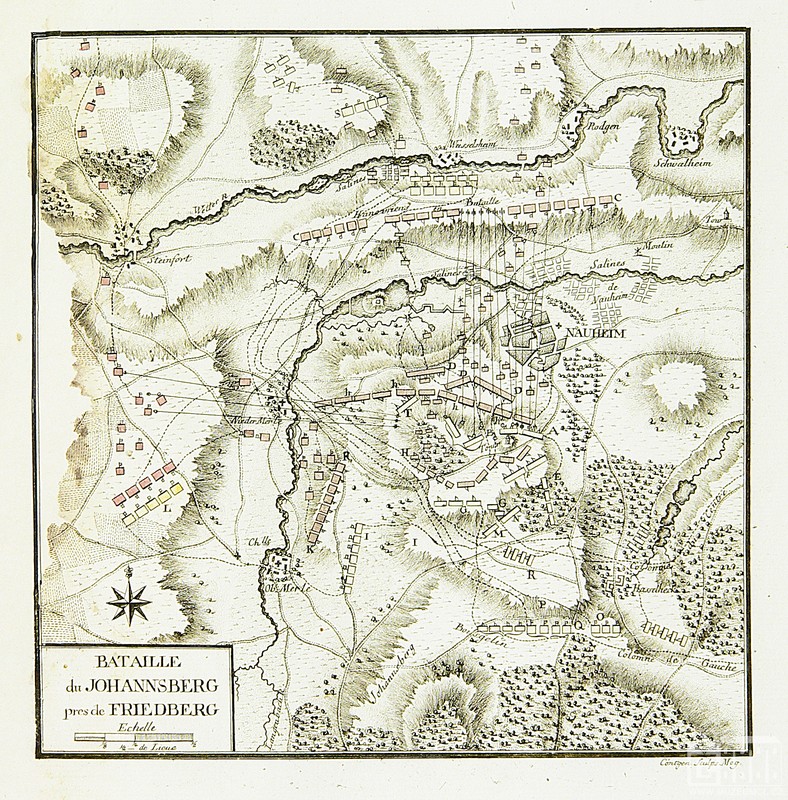
Battle Of Nauheim
The Battle of Nauheim (also known as the Battle of the Johannisberg or Johannesberg) was a battle of the Seven Years' War fought near Nauheim in the Landgraviate of Hessen-Kassel on 30 August 1762. French troops under the command of Louis Joseph, Prince of Condé defeated Hanoverian and British troops under the command of Duke Ferdinand of Brunswick. ReferencesBiography of the Marquis of Granby*Jomini, Henri; Traité des grandes opérations militaires, 2ème édition, 4ème partie, Magimel, Paris: 1811, pp. 182–183 *Mauvillon, I.; Geschichte Ferdinands Herzogs von Braunschweig-Lüneburg, Part 2, Leipzig: 1794, pp. 245–249 *Pajol, Charles P. V., Les Guerres sous Louis XV, vol. V, Paris, 1891, pp. 421–426 * Nauheim Battles of the Seven Years' War Battles involving France Battles involving Great Britain Nauheim Nauheim is a municipality in Groß-Gerau district in Hesse, Germany. Nauheim is located southwest of Frankfurt am Main and is part of the me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Montreal Campaign
The Montreal Campaign, also known as the Fall of Montreal, was a British three-pronged offensive against Montreal which took place from July 2 to 8 September 1760 during the French and Indian War as part of the global Seven Years' War. The campaign, pitted against an outnumbered and outsupplied French army, led to the capitulation and occupation of Montreal, the largest remaining city in French Canada. Under the overall direction of Jeffery Amherst, British forces numbering around 18,000 men converged on Montreal starting in July from three separate directions. One under Amherst moved in from Lake Ontario, the other under James Murray moved from Québec and the third under William Haviland moved from Fort Crown Point. After capturing French positions and outposts along the way all three forces met up and surrounded Montreal. Many Canadiens deserted or surrendered their arms to British forces while the native allies of the French began to negotiate peace treaties and alliances ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
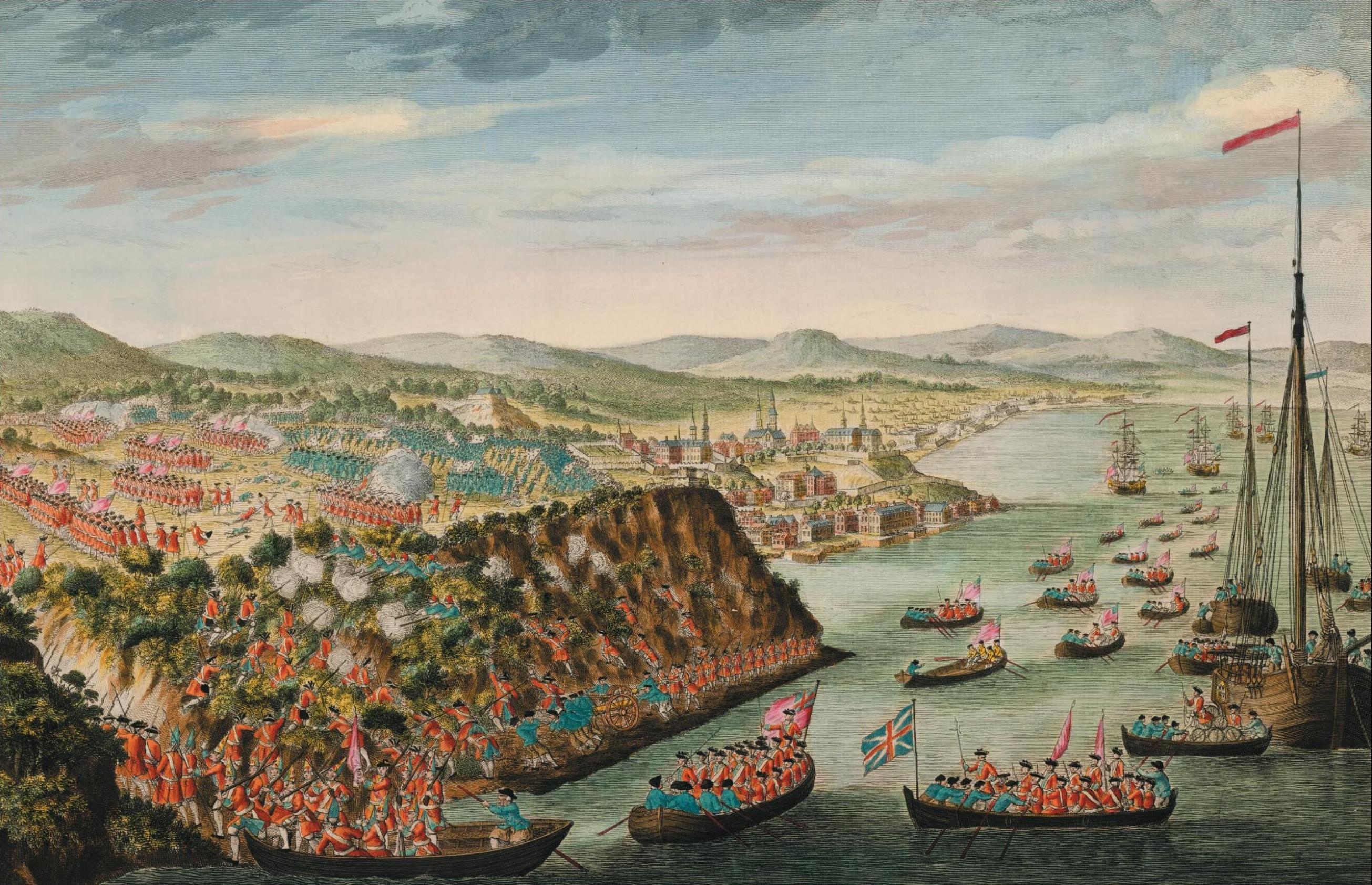
Siege Of Quebec (1760)
The Siege of Quebec, also known as the Second Siege of Quebec, was a French attempt to retake Quebec City, in New France, which had been captured by Britain the previous year. The siege lasted from 29 April to 15 May, when British ships arrived to relieve the city and compelled the French commander, Francis de Gaston, Chevalier de Lévis, to break off the siege and to retreat. The British launched the Montreal Campaign a few months later, which resulted in the city's capture. French resistance ceased, and the British Conquest of Canada was complete, as was confirmed in 1763 by the Treaty of Paris. Background In 1759, a British expedition, led by James Wolfe, had sailed up the St Lawrence River and laid siege to Quebec. After an initial failure at the Battle of Beauport, Wolfe managed to defeat the French field army under Louis-Joseph de Montcalm at the Battle of the Plains of Abraham on 13 September 1759. After Montcalm's death during the battle, the French armies outside Qu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Sainte-Foy
The Battle of Sainte-Foy (french: Bataille de Sainte-Foy) sometimes called the Battle of Quebec (french: Bataille du Quebec), was fought on April 28, 1760 near the British-held town of Quebec in the French province of Canada during the Seven Years' War (called the French and Indian War in the United States). It was a victory for the French under the Chevalier de Lévis over the British army under General Murray. The battle was notably bloodier than the Battle of the Plains of Abraham of the previous September, with 833 French casualties to 1,124 British casualties. At first the British had some success, but the advance masked their artillery, while the infantry became bogged down in the mud and melting snowdrifts of the late spring. The battle turned into a two-hour fight at close range; eventually, as more French soldiers joined the fray, the French turned the British flanks, forcing Murray to realize his mistake and to recall the British back to Quebec without their guns ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Beauport
The Battle of Beauport, also known as the Battle of Montmorency, fought on 31 July 1759, was an important confrontation between the British and French Armed Forces during the Seven Years' War (also known as the French and Indian War and the War of Conquest) of the French province of Canada. The attack conducted by the British against the French defense line of Beauport, some east of Quebec was checked, and the British soldiers of General James Wolfe retreated with 443 casualties and losses. Background The French and Indian War campaigns of 1758 were mostly successful for the British, who had sent more than 40,000 men against New France and made key gains by capturing Louisbourg and destroying Fort Frontenac, although their primary thrust was stopped by French general Louis-Joseph de Montcalm in the Battle of Carillon. William Pitt continued the aggressive policy in 1759, again organizing large campaigns aimed at the heartland of New France, the Canadien communities of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Carillon
The Battle of Carillon, also known as the 1758 Battle of Ticonderoga, Chartrand (2000), p. 57 was fought on July 8, 1758, during the French and Indian War (which was part of the global Seven Years' War). It was fought near Fort Carillon (now known as Fort Ticonderoga) on the shore of Lake Champlain in the frontier area between the British colony of New York and the French colony of New France. In the battle, which took place primarily on a rise about three-quarters of a mile (one km) from the fort itself, a French army of about 3,600 men under General Marquis de Montcalm and the Chevalier de Levis defeated a numerically superior force of British troops under General James Abercrombie, which frontally assaulted an entrenched French position without using field artillery, a lack that left the British and their allies vulnerable and allowed the French to win a complete victory. The battle was the bloodiest of the American theater of the war, with over 3,000 casualties s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Fort William Henry
The siege of Fort William Henry (3–9 August 1757, french: Bataille de Fort William Henry) was conducted by a French and Indian force led by Louis-Joseph de Montcalm against the British-held Fort William Henry. The fort, located at the southern end of Lake George, on the frontier between the British Province of New York and the French Province of Canada, was garrisoned by a poorly supported force of British regulars and provincial militia led by Lieutenant Colonel George Monro. After several days of bombardment, Monro surrendered to Montcalm, whose force included nearly 2,000 Indians from various tribes. The terms of surrender included the withdrawal of the garrison to Fort Edward, with specific terms that the French military protect the British from the Indians as they withdrew from the area. In one of the most notorious incidents of the French and Indian War, Montcalm's Indian allies violated the agreed terms of surrender and attacked the departing British column, whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seven Years' War
The Seven Years' War (1756–1763) was a global conflict that involved most of the European Great Powers, and was fought primarily in Europe, the Americas, and Asia-Pacific. Other concurrent conflicts include the French and Indian War (1754–1763), the Carnatic Wars and the Anglo-Spanish War (1762–1763). The opposing alliances were led by Great Britain and France respectively, both seeking to establish global pre-eminence at the expense of the other. Along with Spain, France fought Britain both in Europe and overseas with land-based armies and naval forces, while Britain's ally Prussia sought territorial expansion in Europe and consolidation of its power. Long-standing colonial rivalries pitting Britain against France and Spain in North America and the West Indies were fought on a grand scale with consequential results. Prussia sought greater influence in the German states, while Austria wanted to regain Silesia, captured by Prussia in the previous war, and to conta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |