|
Focal Mechanism
The focal mechanism of an earthquake describes the deformation in the source region that generates the seismic waves. In the case of a fault-related event it refers to the orientation of the fault plane that slipped and the slip vector and is also known as a fault-plane solution. Focal mechanisms are derived from a solution of the moment tensor for the earthquake, which itself is estimated by an analysis of observed seismic waveforms. The focal mechanism can be derived from observing the pattern of "first motions", that is, whether the first arriving P waves break up or down. This method was used before waveforms were recorded and analysed digitally and this method is still used for earthquakes too small for easy moment tensor solution. Focal mechanisms are now mainly derived using semi-automatic analysis of the recorded waveforms. Moment tensor solutions The moment tensor solution is typically displayed graphically using a so-called ''beachball'' diagram. The pattern o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Focal Mechanism 01
Focal or FOCAL may refer to: *Focal (lexicographical website), an Irish lexicographical website *FOCAL (programming language), a programming language for the PDP-8 and similar machines *Focal (HP-41), for programming HP calculators *FOCAL (spacecraft), a proposed space telescope *FOCAL International, a trade body representing the film archive industry *Focal-JMLab, a French manufacturer of audio equipment *Focal Radio, a radio station based in Stoke-on-Trent, England *Focal neurologic signs See also *Focal point (other) Focal point may refer to: * Focus (optics) * Focus (geometry) * Conjugate points, also called focal points * Focal point (game theory) * Unicom Focal Point UNICOM Focal Point is a portfolio management and decision analysis tool used by the prod ... * Focus (other) * {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Focal Mechanism 02
Focal or FOCAL may refer to: *Focal (lexicographical website), an Irish lexicographical website *FOCAL (programming language), a programming language for the PDP-8 and similar machines *Focal (HP-41), for programming HP calculators *FOCAL (spacecraft), a proposed space telescope *FOCAL International, a trade body representing the film archive industry *Focal-JMLab, a French manufacturer of audio equipment *Focal Radio, a radio station based in Stoke-on-Trent, England *Focal neurologic signs See also *Focal point (other) Focal point may refer to: * Focus (optics) * Focus (geometry) * Conjugate points, also called focal points * Focal point (game theory) * Unicom Focal Point UNICOM Focal Point is a portfolio management and decision analysis tool used by the prod ... * Focus (other) * {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IRIS Consortium
IRIS (Incorporated Research Institutions for Seismology) is a university research consortium dedicated to exploring the Earth's interior through the collection and distribution of seismographic data. IRIS programs contribute to scholarly research, education, earthquake hazard mitigation, and the verification of a Comprehensive Nuclear-Test-Ban Treaty. Support for IRIS comes from the National Science Foundation, other federal agencies, universities, and private foundations. IRIS supports five major components, the Data Management Center (DMC), the Portable Array Seismic Studies of the Continental Lithosphere (PASSCAL), the Global Seismographic Network (GSN), the Transportable Array (USARRAY), and the Education and Public Outreach Program (EPO). IRIS maintains a Corporate Office in Washington, DC. IRIS's Education and Public Outreach Program provides resources for educators and the general public to advance awareness and understanding of seismology and earth science while inspiring ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seismic Moment
Seismic moment is a quantity used by seismologists to measure the size of an earthquake. The scalar seismic moment M_0 is defined by the equation M_0=\mu AD, where *\mu is the shear modulus of the rocks involved in the earthquake (in pascals (Pa), i.e. newtons per square meter) *A is the area of the rupture along the geologic fault where the earthquake occurred (in square meters), and *D is the average slip (displacement offset between the two sides of the fault) on A (in meters). M_0 thus has dimensions of torque, measured in newton meters. The connection between seismic moment and a torque is natural in the body-force equivalent representation of seismic sources as a double-couple (a pair of force couples with opposite torques): the seismic moment is the torque of each of the two couples. Despite having the same dimensions as energy, seismic moment is not a measure of energy. The relations between seismic moment, potential energy drop and radiated energy are indirect and appro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MATLAB
MATLAB (an abbreviation of "MATrix LABoratory") is a proprietary multi-paradigm programming language and numeric computing environment developed by MathWorks. MATLAB allows matrix manipulations, plotting of functions and data, implementation of algorithms, creation of user interfaces, and interfacing with programs written in other languages. Although MATLAB is intended primarily for numeric computing, an optional toolbox uses the MuPAD symbolic engine allowing access to symbolic computing abilities. An additional package, Simulink, adds graphical multi-domain simulation and model-based design for dynamic and embedded systems. As of 2020, MATLAB has more than 4 million users worldwide. They come from various backgrounds of engineering, science, and economics. History Origins MATLAB was invented by mathematician and computer programmer Cleve Moler. The idea for MATLAB was based on his 1960s PhD thesis. Moler became a math professor at the University of New Mexico a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nature (journal)
''Nature'' is a British weekly scientific journal founded and based in London, England. As a multidisciplinary publication, ''Nature'' features peer-reviewed research from a variety of academic disciplines, mainly in science and technology. It has core editorial offices across the United States, continental Europe, and Asia under the international scientific publishing company Springer Nature. ''Nature'' was one of the world's most cited scientific journals by the Science Edition of the 2019 '' Journal Citation Reports'' (with an ascribed impact factor of 42.778), making it one of the world's most-read and most prestigious academic journals. , it claimed an online readership of about three million unique readers per month. Founded in autumn 1869, ''Nature'' was first circulated by Norman Lockyer and Alexander Macmillan as a public forum for scientific innovations. The mid-20th century facilitated an editorial expansion for the journal; ''Nature'' redoubled its efforts in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transform Faults
A transform fault or transform boundary, is a fault along a plate boundary where the motion is predominantly horizontal. It ends abruptly where it connects to another plate boundary, either another transform, a spreading ridge, or a subduction zone. A transform fault is a special case of a ''strike-slip fault'' that also forms a plate boundary. Most such faults are found in oceanic crust, where they accommodate the lateral offset between segments of divergent boundaries, forming a zigzag pattern. This is a result of oblique seafloor spreading where the direction of motion is not perpendicular to the trend of the overall divergent boundary. A smaller number of such faults are found on land, although these are generally better-known, such as the San Andreas Fault and North Anatolian Fault. Nomenclature Transform boundaries are also known as conservative plate boundaries because they involve no addition or loss of lithosphere at the Earth's surface. Background Geophysicist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
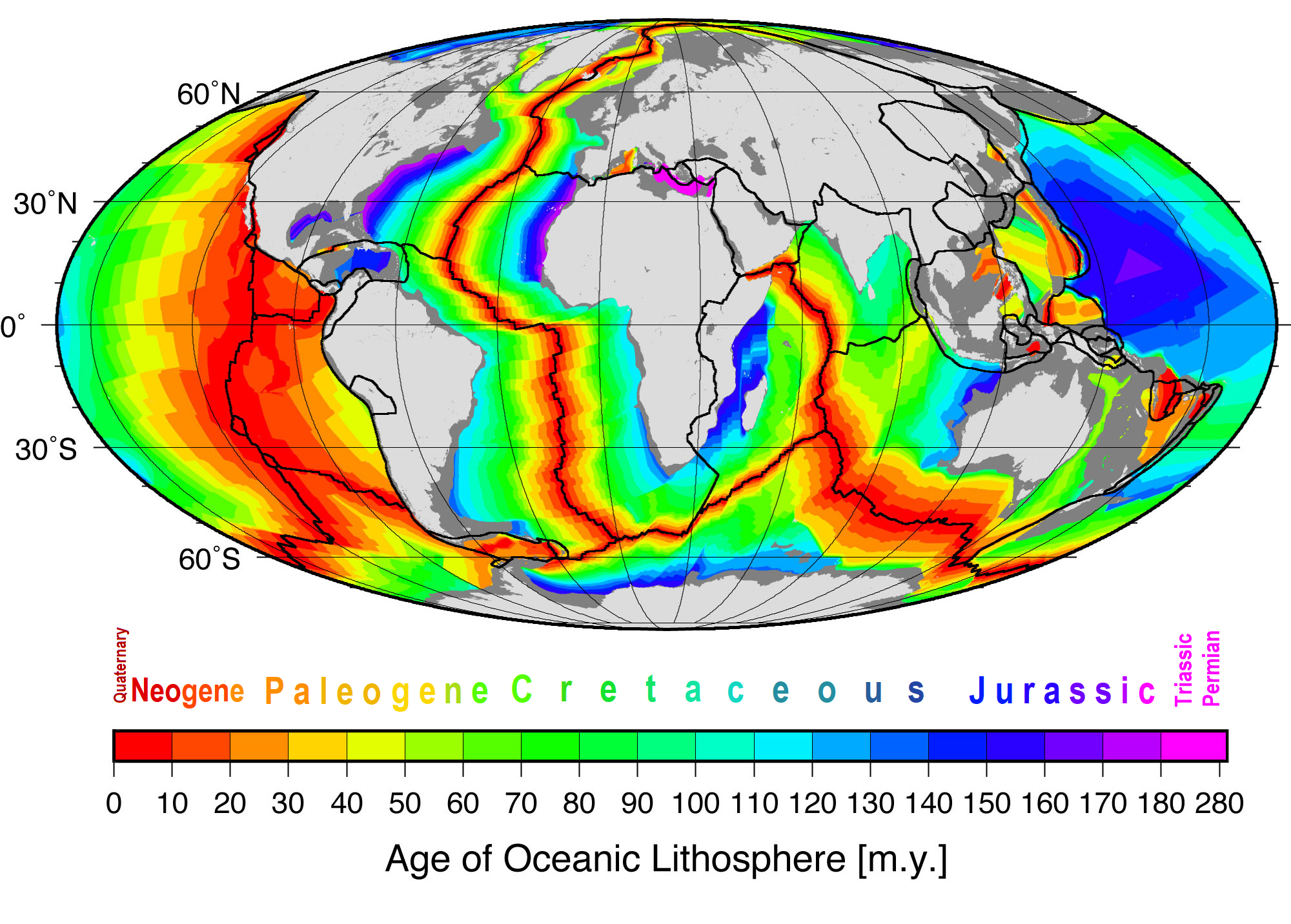
Sea Floor Spreading
Seafloor spreading or Seafloor spread is a process that occurs at mid-ocean ridges, where new oceanic crust is formed through volcanic activity and then gradually moves away from the ridge. History of study Earlier theories by Alfred Wegener and Alexander du Toit of continental drift postulated that continents in motion "plowed" through the fixed and immovable seafloor. The idea that the seafloor itself moves and also carries the continents with it as it spreads from a central rift axis was proposed by Harold Hammond Hess from Princeton University and Robert Dietz of the U.S. Naval Electronics Laboratory in San Diego in the 1960s. The phenomenon is known today as plate tectonics. In locations where two plates move apart, at mid-ocean ridges, new seafloor is continually formed during seafloor spreading. Significance Seafloor spreading helps explain continental drift in the theory of plate tectonics. When oceanic plates diverge, tensional stress causes fractures to occur in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subduction
Subduction is a geological process in which the oceanic lithosphere is recycled into the Earth's mantle at convergent boundaries. Where the oceanic lithosphere of a tectonic plate converges with the less dense lithosphere of a second plate, the heavier plate dives beneath the second plate and sinks into the mantle. A region where this process occurs is known as a subduction zone, and its surface expression is known as an arc-trench complex. The process of subduction has created most of the Earth's continental crust. Rates of subduction are typically measured in centimeters per year, with the average rate of convergence being approximately two to eight centimeters per year along most plate boundaries. Subduction is possible because the cold oceanic lithosphere is slightly denser than the underlying asthenosphere, the hot, ductile layer in the upper mantle underlying the cold, rigid lithosphere. Once initiated, stable subduction is driven mostly by the negative buoyancy of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
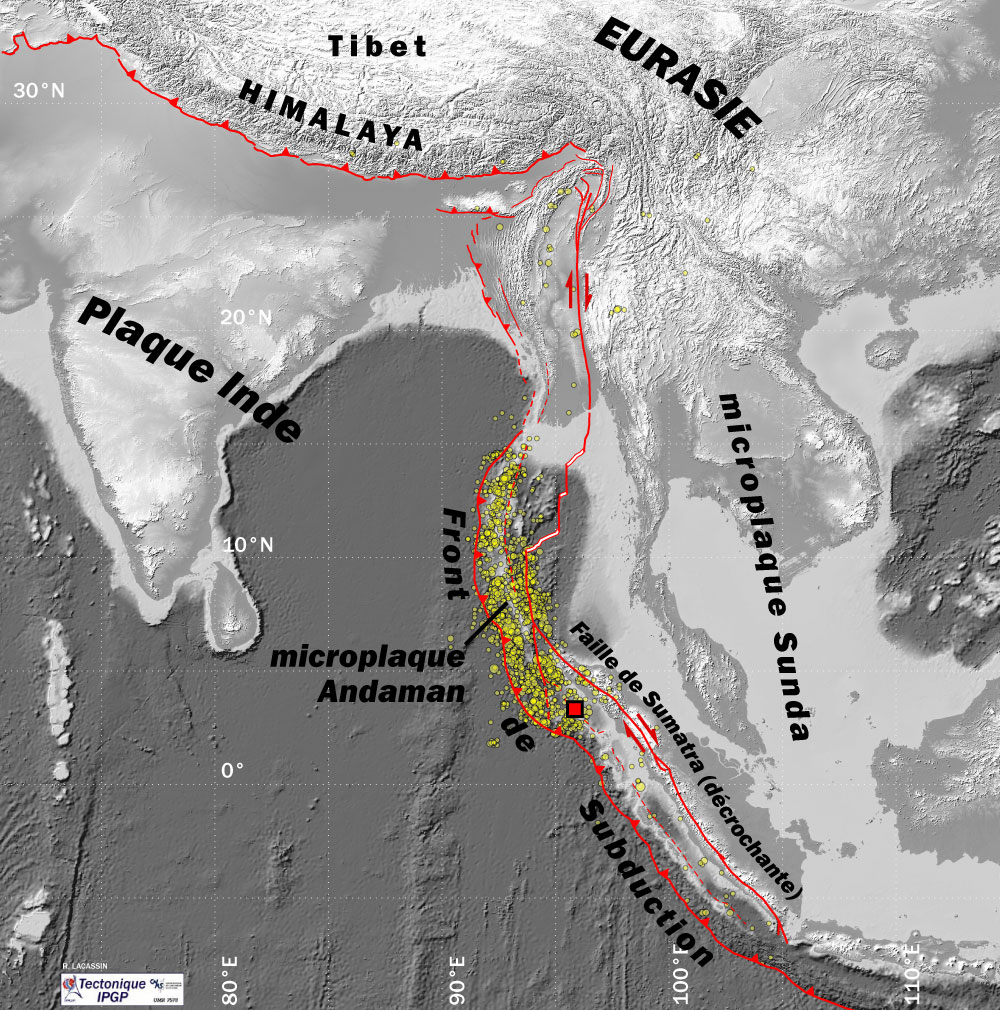
2004 Indian Ocean Earthquake
An earthquake and a tsunami, known as the Boxing Day Tsunami and, by the scientific community, the Sumatra–Andaman earthquake, occurred at 07:58:53 local time ( UTC+7) on 26 December 2004, with an epicentre off the west coast of northern Sumatra, Indonesia. It was an undersea megathrust earthquake that registered a magnitude of 9.1–9.3 , reaching a Mercalli intensity up to IX in certain areas. The earthquake was caused by a rupture along the fault between the Burma Plate and the Indian Plate. A series of massive tsunami waves grew up to high once heading inland, after being created by the underwater seismic activity offshore. Communities along the surrounding coasts of the Indian Ocean were devastated, and the tsunamis killed an estimated 227,898 people in 14 countries, making it one of the deadliest natural disasters in recorded history. The direct results caused major disruptions to living conditions and commerce in coastal provinces of surrounded countries, incl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sumatra 2004 Focal Mechanism
Sumatra is one of the Sunda Islands of western Indonesia. It is the largest island that is fully within Indonesian territory, as well as the sixth-largest island in the world at 473,481 km2 (182,812 mi.2), not including adjacent islands such as the Simeulue, Nias, Mentawai, Enggano, Riau Islands, Bangka Belitung and Krakatoa archipelago. Sumatra is an elongated landmass spanning a diagonal northwest–southeast axis. The Indian Ocean borders the northwest, west, and southwest coasts of Sumatra, with the island chain of Simeulue, Nias, Mentawai, and Enggano off the western coast. In the northeast, the narrow Strait of Malacca separates the island from the Malay Peninsula, which is an extension of the Eurasian continent. In the southeast, the narrow Sunda Strait, containing the Krakatoa Archipelago, separates Sumatra from Java. The northern tip of Sumatra is near the Andaman Islands, while off the southeastern coast lie the islands of Bangka and Belitung, Karimata S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Circle
In mathematics, a great circle or orthodrome is the circular intersection of a sphere and a plane passing through the sphere's center point. Any arc of a great circle is a geodesic of the sphere, so that great circles in spherical geometry are the natural analog of straight lines in Euclidean space. For any pair of distinct non- antipodal points on the sphere, there is a unique great circle passing through both. (Every great circle through any point also passes through its antipodal point, so there are infinitely many great circles through two antipodal points.) The shorter of the two great-circle arcs between two distinct points on the sphere is called the ''minor arc'', and is the shortest surface-path between them. Its arc length is the great-circle distance between the points (the intrinsic distance on a sphere), and is proportional to the measure of the central angle formed by the two points and the center of the sphere. A great circle is the largest circle that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |