|
Fever Of Unknown Origin
Fever of unknown origin (FUO) refers to a condition in which the patient has an elevated temperature (fever) but, despite investigations by a physician, no explanation has been found.Mandell's Principles and Practices of Infection Diseases 6th Edition (2004) by Gerald L. Mandell MD, MACP, John E. Bennett MD, Raphael Dolin MD, · Hardback · 4016 Pages Churchill LivingstoneHarrison's Principles of Internal Medicine 16th Edition, The Companies, [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fever
Fever, also referred to as pyrexia, is defined as having a temperature above the normal range due to an increase in the body's temperature set point. There is not a single agreed-upon upper limit for normal temperature with sources using values between in humans. The increase in set point triggers increased muscle contractions and causes a feeling of cold or chills. This results in greater heat production and efforts to conserve heat. When the set point temperature returns to normal, a person feels hot, becomes flushed, and may begin to sweat. Rarely a fever may trigger a febrile seizure, with this being more common in young children. Fevers do not typically go higher than . A fever can be caused by many medical conditions ranging from non-serious to life-threatening. This includes viral, bacterial, and parasitic infections—such as influenza, the common cold, meningitis, urinary tract infections, appendicitis, Lassa, COVID-19, and malaria. Non-infectious cau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HHV-6
Human herpesvirus 6 (HHV-6) is the common collective name for ''human betaherpesvirus 6A'' (HHV-6A) and ''human betaherpesvirus 6B'' (HHV-6B). These closely related viruses are two of the nine known herpesviruses that have humans as their primary host. HHV-6A and HHV-6B are double-stranded DNA viruses within the ''Betaherpesvirinae'' subfamily and of the genus '' Roseolovirus''. HHV-6A and HHV-6B infect almost all of the human populations that have been tested. HHV-6A has been described as more neurovirulent, and as such is more frequently found in patients with neuroinflammatory diseases such as multiple sclerosis. HHV-6 (and HHV-7) levels in the brain are also elevated in people with Alzheimer's disease. HHV-6B primary infection is the cause of the common childhood illness exanthema subitum (also known as roseola infantum or sixth disease). It is passed on from child to child. It is uncommon for adults to contract this disease as most people have had it by kindergarten, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
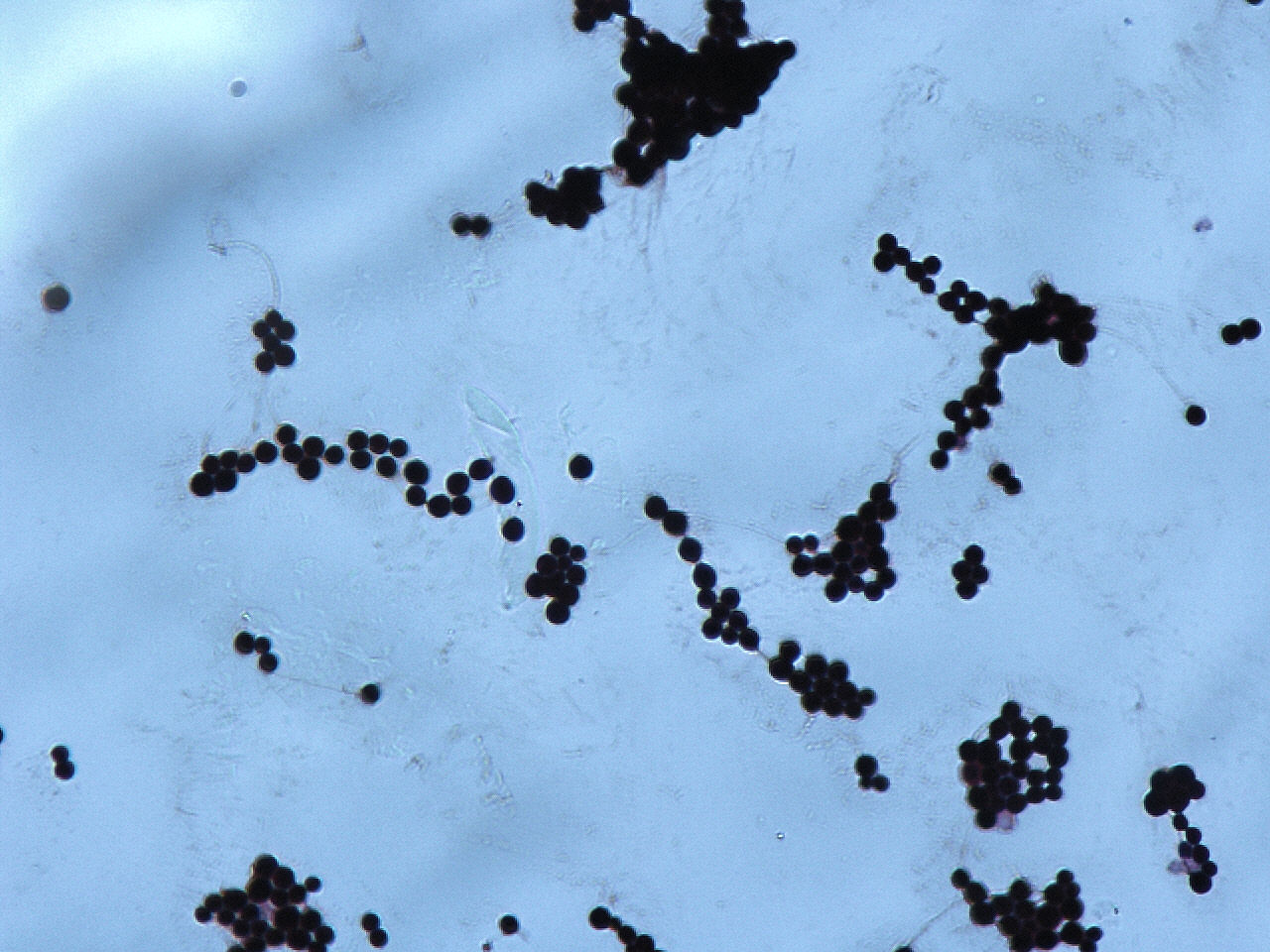
Cryptococcus Neoformans
''Cryptococcus neoformans'' is an encapsulated yeast belonging to the class Tremellomycetes and an obligate aerobe that can live in both plants and animals. Its teleomorph is a filamentous fungus, formerly referred to ''Filobasidiella neoformans''. In its yeast state, it is often found in bird excrement. ''Cryptococcus neoformans'' can cause disease in apparently immunocompetent, as well as immunocompromised, hosts. Classification ''Cryptococcus neoformans'' has undergone numerous nomenclature revisions since its first description in 1895. It formerly contained two varieties: ''C. neoformans ''var.'' neoformans'' and ''C. neoformans '' var.'' grubii''. A third variety, ''C. neoformans ''var.'' gattii'', was later defined as a distinct species, ''Cryptococcus gattii''. The most recent classification system divides these varieties into seven species. ''C. neoformans'' refers to ''C. neoformans '' var.'' grubii''. A new species name, ''Cryptococcus deneoformans'', is used for th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mucormycosis
Mucormycosis, also known as black fungus, is a serious fungal infection that comes under fulminant fungal sinusitis, usually in people who are immunocompromised. It is curable only when diagnosed early. Symptoms depend on where in the body the infection occurs. It most commonly infects the nose, sinuses, eye, and brain resulting in a runny nose, one-sided facial swelling and pain, headache, fever, blurred vision, bulging or displacement of the eye (proptosis), and tissue death. Other forms of disease may infect the lungs, stomach and intestines, and skin. It is spread by spores of molds of the order Mucorales, most often through inhalation, contaminated food, or contamination of open wounds. These fungi are common in soils, decomposing organic matter (such as rotting fruit and vegetables), and animal manure, but usually do not affect people. It is not transmitted between people. Risk factors include diabetes with persistently high blood sugar levels or diabetic ketoacidos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
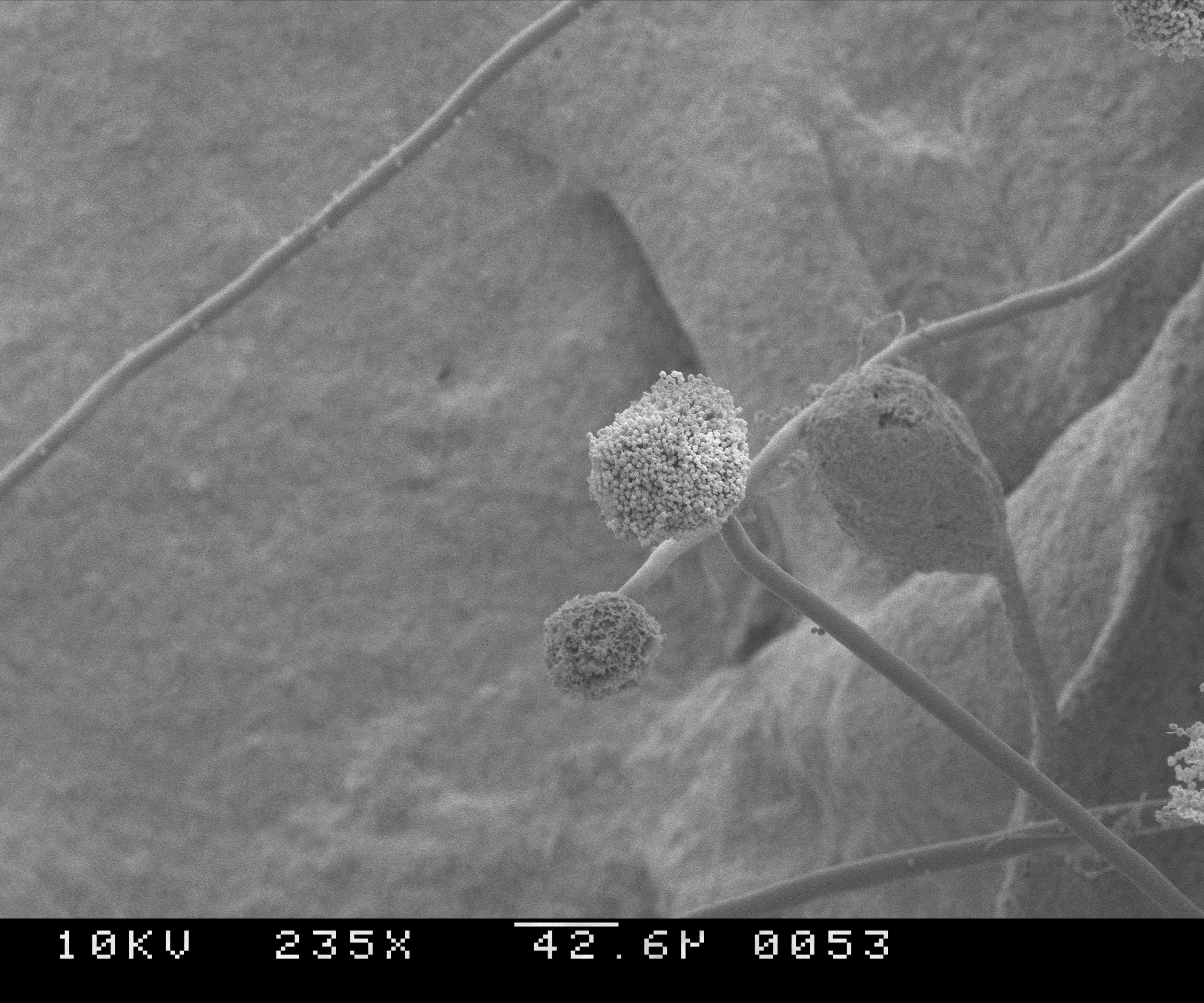
Aspergillosis
Aspergillosis is a fungal infection of usually the lungs, caused by the genus ''Aspergillus'', a common mould that is breathed in frequently from the air around, but does not usually affect most people. It generally occurs in people with lung diseases such as asthma, cystic fibrosis or tuberculosis, or those who have had a stem cell or organ transplant, and those who cannot fight infection because of medications they take such as steroids and some cancer treatments. Rarely, it can affect skin. Aspergillosis occurs in humans, birds and other animals. Aspergillosis occurs in chronic or acute forms which are clinically very distinct. Most cases of acute aspergillosis occur in people with severely compromised immune systems, e.g. those undergoing bone marrow transplantation. Chronic colonization or infection can cause complications in people with underlying respiratory illnesses, such as asthma, cystic fibrosis, sarcoidosis, tuberculosis, or chronic obstructive pulmonary diseas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Talaromycosis
Talaromycosis is a fungal infection that presents with painless skin lesions of face and neck, fever, anaemia, large lymph glands and liver. It is caused by the fungus''Talaromyces marneffei'', which is found in soil and decomposing organic matter. The infection is thought to be acquired by breathing in the fungus from the environment, however, the environmental source of the organism is not known. It typically occurs in people who are already sick and unable to fight infection such as HIV/AIDS, cancer, organ transplant, long-term steroid use, old age, malnutrition or autoimmune disease. It generally does not affect healthy people and does not spread from person to person. Diagnosis is usually made by identification of the fungus from clinical specimens, either by microscopy or culture. Biopsies of skin lesions, lymph nodes, and bone marrow demonstrate the presence of organisms on histopathology. Medical imaging may reveal shadows in the lungs. The disease can look sim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
B Symptoms
B symptoms are a set of symptoms, namely fever, night sweats, and unintentional weight loss, that can be associated with both Hodgkin lymphoma and non-Hodgkin lymphoma. These symptoms are not specific to lymphomas, especially each one considered individually, and even as a trio they are not pathognomonic for lymphomas, but the presence of the trio is sensitive enough for lymphomas to warrant diagnostic investigation and differential diagnosis. The presence or absence of B symptoms has prognostic significance in lymphomas and is reflected in their staging. Description and nomenclature B symptoms are so called because Ann Arbor staging of lymphomas includes both a number (I–IV) and a letter (A or B). "A" indicates the absence of systemic symptoms, while "B" indicates their presence. B symptoms include: * Fever greater than 38 °C. Pel–Ebstein fever, the classic intermittent fever associated with Hodgkin disease, occurs at variable intervals of days to weeks and lasts f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paracoccidioidomycosis
Paracoccidioidomycosis (PCM), also known as South American blastomycosis, is a fungal infection that can occur as a mouth and skin type, lymphangitic type, multi-organ involvement type (particularly lungs), or mixed type. If there are mouth ulcers or skin lesions, the disease is likely to be widespread. There may be no symptoms, or it may present with fever, sepsis, weight loss, large glands, or a large liver and spleen. The cause is fungi in the genus ''Paracoccidioides'', including ''Paracoccidioides brasiliensis'' and ''Paracoccidioides lutzii'', acquired by breathing in fungal spores. Diagnosis is by sampling of blood, sputum, or skin. The disease can appear similar to tuberculosis, leukaemia, and lymphoma Treatment is with antifungals; itraconazole. For severe disease, treatment is with amphotericin B followed by itraconazole, or trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole as an alternative. It is endemic to Central and South America, and is considered a type of neglected tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coccidiomycosis
Coccidioidomycosis (, ), commonly known as cocci, Valley fever, as well as California fever, desert rheumatism, or San Joaquin Valley fever, is a mammalian fungal disease caused by ''Coccidioides immitis'' or ''Coccidioides posadasii''. Coccidioidomycosis is endemic in certain parts of the United States in Arizona, California, Nevada, New Mexico, Texas, Utah, and northern Mexico. ''C. immitis'' is a dimorphic saprophytic fungus that grows as a mycelium in the soil and produces a spherule form in the host organism. It resides in the soil in certain parts of the southwestern United States, most notably in California and Arizona. It is also commonly found in northern Mexico, and parts of Central and South America. ''C. immitis'' is dormant during long dry spells, then develops as a mold with long filaments that break off into airborne spores when it rains. The spores, known as arthroconidia, are swept into the air by disruption of the soil, such as during construction, farming, l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lymphadenopathy
Lymphadenopathy or adenopathy is a disease of the lymph nodes, in which they are abnormal in size or consistency. Lymphadenopathy of an inflammatory type (the most common type) is lymphadenitis, producing swollen or enlarged lymph nodes. In clinical practice, the distinction between lymphadenopathy and lymphadenitis is rarely made and the words are usually treated as synonymous. Inflammation of the lymphatic vessels is known as lymphangitis. Infectious lymphadenitis affecting lymph nodes in the neck is often called scrofula. Lymphadenopathy is a common and nonspecific sign. Common causes include infections (from minor causes such as the common cold and post-vaccination swelling to serious ones such as HIV/AIDS), autoimmune diseases, and cancer. Lymphadenopathy is frequently idiopathic and self-limiting. Causes Lymph node enlargement is recognized as a common sign of infectious, autoimmune, or malignant disease. Examples may include: * Reactive: acute infection (''e.g.,'' b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pharyngitis
Pharyngitis is inflammation of the back of the throat, known as the pharynx. It typically results in a sore throat and fever. Other symptoms may include a runny nose, cough, headache, difficulty swallowing, swollen lymph nodes, and a hoarse voice. Symptoms usually last 3–5 days, but can be longer depending on cause. Complications can include sinusitis and acute otitis media. Pharyngitis is a type of upper respiratory tract infection. Most cases are caused by a viral infection. Strep throat, a bacterial infection, is the cause in about 25% of children and 10% of adults. Uncommon causes include other bacteria such as ''gonococcus'', fungi, irritants such as smoke, allergies, and gastroesophageal reflux disease. Specific testing is not recommended in people who have clear symptoms of a viral infection, such as a cold. Otherwise, a rapid antigen detection test or throat swab is recommended. PCR testing is becoming commonly used as it is as good as taking a thro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Splenomegaly
Splenomegaly is an enlargement of the spleen. The spleen usually lies in the left upper quadrant (LUQ) of the human abdomen. Splenomegaly is one of the four cardinal signs of ''hypersplenism'' which include: some reduction in number of circulating blood cells affecting granulocytes, erythrocytes or platelets in any combination; a compensatory proliferative response in the bone marrow; and the potential for correction of these abnormalities by splenectomy. Splenomegaly is usually associated with increased workload (such as in hemolytic anemias), which suggests that it is a response to hyperfunction. It is therefore not surprising that splenomegaly is associated with any disease process that involves abnormal red blood cells being destroyed in the spleen. Other common causes include congestion due to portal hypertension and infiltration by leukemias and lymphomas. Thus, the finding of an enlarged spleen, along with caput medusae, is an important sign of portal hypertension. D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |






.jpg)
