|
Fritz Pleitgen
Fritz Ferdinand Pleitgen (21 March 1938 – 15 September 2022) was a German television journalist and author. He was correspondent in Moscow, East Berlin and Washington. Pleitgen was a supporter of Willy Brandt's Ostpolitik. In 1988, Pleitgen became editor-in-chief of television of Germany's then-largest public broadcaster, Westdeutscher Rundfunk (WDR), and was director of WDR from 1995 to 2007. He is regarded as one of the most influential German journalists and media makers. In 2010, he was the manager of Ruhr.2010, a project of European Capital of Culture. Life and career Pleitgen was born in Duisburg-Meiderich on 21 March 1938, the fifth child of a technical draftsman working at Krupp. He grew up in Bünde in East Westphalia and left high school without completing his programme, because he was already working for the Bünde local editorial office of Bielefeld's ' as a sports and court reporter. In 1961, he volunteered to become an editor. In 1963, Pleitgen began working as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duisburg
Duisburg () is a city in the Ruhr metropolitan area of the western German state of North Rhine-Westphalia. Lying on the confluence of the Rhine and the Ruhr rivers in the center of the Rhine-Ruhr Region, Duisburg is the 5th largest city in North Rhine-Westphalia and the 15th-largest city in Germany. In the Middle Ages, it was a city-state and a member of the Hanseatic League, and later became a major centre of iron, steel, and chemicals industries. For this reason, it was heavily bombed in World War II. Today it boasts the world's largest inland port, with 21 docks and 40 kilometres of wharf. Status Duisburg is a city in Germany's Rhineland, the fifth-largest (after Cologne, Düsseldorf, Dortmund and Essen) of the nation's most populous federal state of North Rhine-Westphalia. Its 500,000 inhabitants make it Germany's 15th-largest city. Located at the confluence of the Rhine river and its tributary the Ruhr river, it lies in the west of the Ruhr urban area, Germany's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
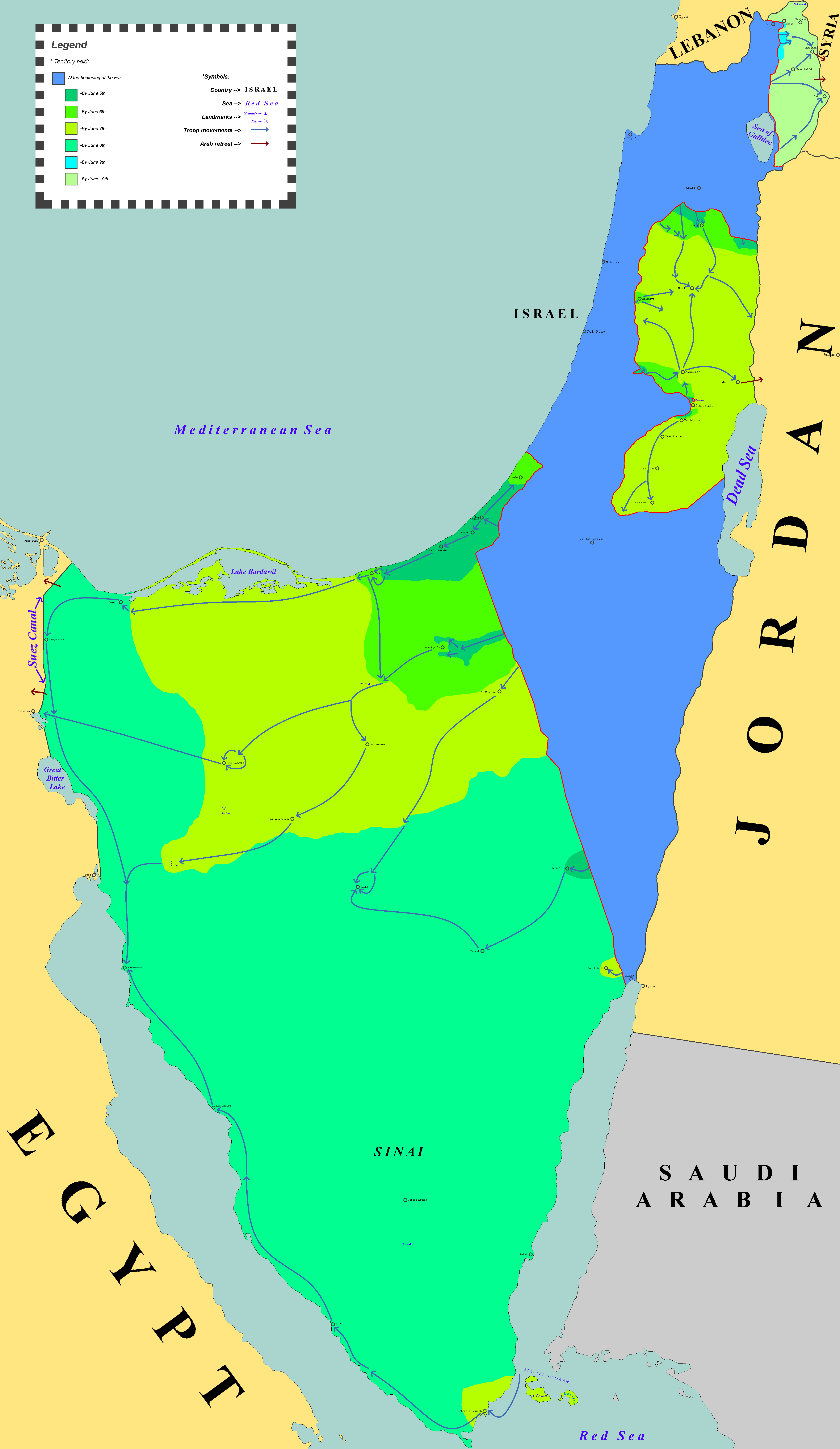
Six-Day War
The Six-Day War (, ; ar, النكسة, , or ) or June War, also known as the 1967 Arab–Israeli War or Third Arab–Israeli War, was fought between Israel and a coalition of Arab world, Arab states (primarily United Arab Republic, Egypt, Syria, and Jordan) from 5 to 10 June 1967. Escalated hostilities broke out amid poor relations between Israel and its Arab neighbours following the 1949 Armistice Agreements, which were signed at the end of the 1948 Arab–Israeli War, First Arab–Israeli War. Earlier, in 1956, regional tensions over the Straits of Tiran escalated in what became known as the Suez Crisis, when Israel invaded Egypt over the Israeli passage through the Suez Canal and Straits of Tiran, Egyptian closure of maritime passageways to Israeli shipping, ultimately resulting in the re-opening of the Straits of Tiran to Israel as well as the deployment of the United Nations Emergency Force (UNEF) along the Borders of Israel#Border with Egypt, Egypt–Israel border. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Havemann
Robert Havemann (; 11 March 1910 – 9 April 1982) was an East German chemist and dissident. Life and career He studied chemistry in Berlin and Munich from 1929 to 1933, and then later received a doctorate in physical chemistry from the Kaiser Wilhelm Institute. Havemann joined the Communist Party of Germany (KPD) in 1932 and was one of the founders of the resistance group, European Union. It was in connection with this group that he was arrested by the Gestapo in 1943. He received a death sentence, but his execution was continually postponed because of the intervention of former colleagues, who insisted that Havemann was as important due to his work on chemical weapons and that he was still needed to explain the research. His execution was postponed so many times, he was able to survive until the Brandenburg-Görden Prison was liberated by the Red Army.Bernd Florath. "Die Europäische Union," essay in Johannes Tuchel, ''Der vergessene Widerstand — zu Realgeschichte und Wahrn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stefan Heym
Helmut Flieg or Hellmuth Fliegel (10 April 1913 – 16 December 2001) was a German writer, known by his pseudonym Stefan Heym (). He lived in the United States and trained at Camp Ritchie, making him one of the Ritchie Boys of World War II. In 1952, he returned to his home to the part of his native Germany which was, from 1949 to 1990, the German Democratic Republic (GDR, "East Germany"). He published works in English and German at home and abroad, and despite longstanding criticism of the GDR remained a committed socialist. He was awarded the 1953 Heinrich Mann Prize, the 1959 National Prize of East Germany (2nd class), and the 1993 Jerusalem Prize. Biography Early years Flieg, born to a Jewish merchant family in Chemnitz, was an antifascist from an early age. In 1931, he was, at the instigation of local Nazis, expelled from the Gymnasium in his home town because of an anti-military poem. He completed school in Berlin, and began a degree in media studies there. Af ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Erich Honecker
Erich Ernst Paul Honecker (; 25 August 1912 – 29 May 1994) was a German communist politician who led the German Democratic Republic (East Germany) from 1971 until shortly before the fall of the Berlin Wall in November 1989. He held the posts of General Secretary of the Socialist Unity Party of Germany (SED) and Chairman of the National Defence Council; in 1976, he replaced Willi Stoph as Chairman of the State Council, the official head of state. As the leader of East Germany, Honecker had close ties to the Soviet Union, which maintained a large army in the country. Honecker's political career began in the 1930s when he became an official of the Communist Party of Germany, a position for which he was imprisoned by the Nazis. Following World War II, he was freed by the Soviet army and relaunched his political activities, founding the SED's youth organisation, the Free German Youth, in 1946 and serving as the group's chairman until 1955. As the Security Secretary of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stasi
The Ministry for State Security, commonly known as the (),An abbreviation of . was the state security service of the East Germany from 1950 to 1990. The Stasi's function was similar to the KGB, serving as a means of maintaining state authority, i.e., the "Sword and Shield of the Party" (). This was accomplished primarily through the use of a network of civilian informants. This organization contributed to the arrest of approximately 250,000 people in East Germany. The Stasi also conducted espionage and other clandestine operations abroad through its subordinate foreign intelligence service, the Office of Enlightenment, or Head Office A (german: Hauptverwaltung Aufklärung). They also maintained contacts and occasionally cooperated with West German terrorists. The Stasi was headquartered in East Berlin, with an extensive complex in Berlin-Lichtenberg and several smaller facilities throughout the city. Erich Mielke was the Stasi's longest-serving chief, in power for 32 of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andrei Amalrik
Andrei Alekseevich Amalrik (russian: Андре́й Алексе́евич Ама́льрик, 12 May 1938, Moscow – 12 November 1980, Guadalajara, Castile-La Mancha, Spain), alternatively spelled ''Andrei'' or ''Andrey'', was a Russian writer and dissident. Amalrik was best known in the Western world for his 1970 essay, ''Will the Soviet Union Survive Until 1984?''. Early life Amalrik was born in Moscow, during the time of Joseph Stalin's purges. When the Soviet revolution broke out, Andrei's father, then a young man, volunteered for the Red Army. After the war he went into the film industry. Andrei's father fought in World War II in the Northern Fleet and then the Red Army. He was overheard uttering negative views about Stalin's qualities as a military leader, which led to his arrest and imprisonment; he feared for his life, but shortly afterward was released to rejoin the army. In 1942 he was wounded at Stalingrad and invalided out of the service. Andrei's father's hardsh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yuri Orlov
Yuri Fyodorovich Orlov (russian: Ю́рий Фёдорович Орло́в, 13 August 1924 – 27 September 2020) was a particle accelerator physicist, human rights activist, Soviet dissident, founder of the Moscow Helsinki Group, a founding member of the Soviet Amnesty International group, and Professor of Physics at Cornell University. He was declared a prisoner of conscience while serving nine years in prison and internal exile for monitoring the Helsinki human rights accords as a founder of the human rights movement in the Soviet Union. Early career Yuri Orlov was born into a working-class family on 13 August 1924 and grew up in a village near Moscow. His parents were Klavdiya Petrovna Lebedeva and Fyodor Pavlovich Orlov. In March 1933, his father died. From 1944 to 1946, Orlov served as an officer in the Soviet army. In 1952, he graduated from the Moscow State University and began his postgraduate studies at the Institute for Theoretical and Experimental Physics wher ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lev Kopelev
Lev Zalmanovich (Zinovyevich) Kopelev (russian: Лев Залма́нович (Зино́вьевич) Ко́пелев, German: Lew Sinowjewitsch Kopelew, 9 April 1912, Kyiv – 18 June 1997, Cologne) was a Soviet author and dissident. Early life Kopelev was born in Kyiv, then Russian Empire, to a middle-class Jewish family. In 1926, his family moved to Kharkiv. While a student at Kharkiv State University's philosophy faculty, Kopelev began writing in Russian and Ukrainian languages; some of his articles were published in the ''Komsomolskaya Pravda'' newspaper. An idealist communist and active party member, he was first arrested in March 1929 for "consorting with the Bukharinist and Trotskyist opposition," and spent ten days in prison. Career Later, he worked as an editor of radio news broadcasts at a locomotive factory. In 1932, as a correspondent, Kopelev witnessed the NKVD's forced grain requisitioning and the dekulakization. Later, he described the Holodomor in his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hamburger Abendblatt
The ''Hamburger Abendblatt'' (English: ''Hamburg Evening Newspaper'') is a German daily newspaper in Hamburg. The paper focuses on news in Hamburg and area, and produces regional supplements with news from Norderstedt, Ahrensburg, Harburg, and Pinneberg. Politically the paper is mildly conservative, but usually pro-government, including during SPD administrations. History and profile Four previous Hamburg newspapers had the word ''Abendblatt'' ("Evening Newspaper") in their title, including one named the ''Hamburger Abendblatt'', founded on 2 May 1820. This incarnation of the ''Hamburger Abendblatt'', however, was first published after World War II beginning on 14 October 1948 with an initial edition of 60,000 copies. The paper received a publishing license from the Hamburg Senate and Mayor Max Brauer, making it the first daily paper of post-war Germany to receive a license from German rather than Allied occupation authorities. After about six months of operation, its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andrei Sakharov
Andrei Dmitrievich Sakharov ( rus, Андрей Дмитриевич Сахаров, p=ɐnˈdrʲej ˈdmʲitrʲɪjevʲɪtɕ ˈsaxərəf; 21 May 192114 December 1989) was a Soviet nuclear physicist, dissident, nobel laureate and activist for nuclear disarmament, peace, and human rights. He became renowned as the designer of the Soviet Union's RDS-37, a codename for Soviet development of thermonuclear weapons. Sakharov later became an advocate of civil liberties and civil reforms in the Soviet Union, for which he faced state persecution; these efforts earned him the Nobel Peace Prize in 1975. The Sakharov Prize, which is awarded annually by the European Parliament for people and organizations dedicated to human rights and freedoms, is named in his honor. Biography Early life Sakharov was born in Moscow on May 21, 1921. His father was Dmitri Ivanovich Sakharov, a physics professor and an amateur pianist. His father taught at the Second Moscow State University. Andrei's gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Augsburger Allgemeine
The ''Augsburger Allgemeine Zeitung'' is a major German regional daily newspaper published since 1945. History From 1807 to 1882, another paper named ''Allgemeine Zeitung'' was published in Augsburg but it is not connected to the later newspaper. Between 1933 and 1945, newspapers in Augsburg, as in the whole of Germany, were tightly controlled by the Nazi regime. With the fall of Nazi Germany, it became possible to publish anti-Nazi papers. However, in the early years the reviving free press had to contend with many restrictions placed by the Allied (specifically, American) Occupation authorities. The newspaper was first published on 30 October 1945 under the name of ''Schwäbische Landeszeitung'', under the initiative of Curt Frenzel. Originally, due to the restrictions in early post-war Germany, it was only published twice-weekly. Frenzel had received a licence to publish a newspaper from Colonel Bernhard MacMahon of the US military government in Bavaria. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |