|
Francisco Serrão
Francisco Serrão (died 1521) was a Portuguese explorer and a possible cousin of Ferdinand Magellan. His 1512 voyage was the first known European sailing east past Malacca through modern Indonesia and the East Indies. He became a confidant of Sultan Bayan Sirrullah, the ruler of Ternate, becoming his personal advisor. He remained in Ternate where he died around the same time Magellan died. Voyage to the Indies Serrão served as captain of one of three vessels (and second in overall command under António de Abreu) sent from Malacca by Afonso de Albuquerque to find the Spice Islands of Banda in Maluku in 1511. Banda was the world's only source of nutmeg and mace, spices used as flavourings, medicines and preserving agents that were at the time highly valued in European markets. The Portuguese sought to dominate the source, rather than relying on Arab traders who sold it to the Venetians for exorbitant prices. Malay pilots guided the expedition east via Java and along the L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Mace (spice)
Nutmeg is the seed, or the ground spice derived from the seed, of several tree species of the genus '' Myristica''; fragrant nutmeg or true nutmeg ('' M. fragrans'') is a dark-leaved evergreen tree cultivated for two spices derived from its fruit: nutmeg, from its seed, and mace, from the seed covering. It is also a commercial source of nutmeg essential oil and nutmeg butter. Maluku's Banda Islands are the main producer of nutmeg and mace, and the true nutmeg tree is native to the islands. Nutmeg and mace, commonly used as food spices, have been traditionally employed for their psychoactive and aphrodisiac effects, though clinical evidence is lacking. High doses can cause serious toxic effects including acute psychosis, with risks heightened during pregnancy and with psychiatric conditions. Conifers of the genus ''Torreya'', commonly known as the nutmeg yews, have edible seeds of similar appearance, but are not closely related to ''M. fragrans'', and are not used as a spice. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Musket
A musket is a muzzle-loaded long gun that appeared as a smoothbore weapon in the early 16th century, at first as a heavier variant of the arquebus, capable of penetrating plate armour. By the mid-16th century, this type of musket gradually disappeared as the use of heavy armour declined, but ''musket'' continued as the generic term for smoothbore long guns until the mid-19th century. In turn, this style of musket was retired in the 19th century when rifled muskets (simply called rifles in modern terminology) using the Minié ball (invented by Claude-Étienne Minié in 1849) became common. The development of breech-loading firearms using self-contained Cartridge (firearms), cartridges, introduced by Casimir Lefaucheux in 1835, began to make muskets obsolete. The first reliable repeating rifles, the 1860 Henry rifle and its 1866 descendent the Winchester rifle, superseded muskets entirely. Repeating rifles quickly established themselves as the standard for rifle design, ending the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Mansel Longworth Dames
Mansel Longworth Dames (1850–1922) was a scholar of oriental and Portuguese languages. Longworth Dames was born in Bath, Somerset, Bath in 1850, the eldest son of George Longworth Dames and Caroline Amelia Brunswick. Longworth Dames passed the Indian Civil Service examination in 1868, and on his arrival in India in 1870 was posted to the Punjab, India, Punjab. He served continuously till his retirement in 1897, apart from in 1879 when he was on special duty with the troops during the Second Anglo-Afghan War. Much of his service was passed in the trans-Indus district of Dera Ghazi Khan, where he had opportunities for studying the Baluch people (Baloch) and became an authority on the various dialects of the Balochi language, Baluch and Pushtu languages. In 1891 he published a Baluchi grammar and textbook, which was used for many years by students. He contributed in 1904 to the monograph series of the Royal Asiatic Society an account of the Baluch, and in the following year the R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Junk (ship)
A junk () is a type of China, Chinese sailing ship characterized by a central rudder, an overhanging flat Transom (nautical), transom, watertight Bulkhead (partition), bulkheads, and a flat-bottomed design. They are also characteristically built using iron nails and clamps. The term applies to many types of small coastal or river ships, usually serving as cargo ships, pleasure boats, or houseboats, but also going up in size up to large ocean-going vessels. There can be significant regional variations in the type of rig and the layout of the vessel. Chinese junks were originally only fluvial and had square sails, but by the Song dynasty (), they adopted ocean-going technologies acquired from Southeast Asian ''k'un-lun po'' trade ships. Tanja sails and fully-battened junk rigs were introduced to Chinese junks by the 12th century CE. Similar designs to the Chinese junk were also adopted by other East Asian countries, most notably Japan, where junks were used as merchant ships to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Entrepôt
An entrepôt ( ; ) or transshipment port is a port, city, or trading post where merchandise may be imported, stored, or traded, usually to be exported again. Such cities often sprang up and such ports and trading posts often developed into commercial cities due to the growth and expansion of long-distance trade. These places played a critical role in trade during the days of wind-powered shipping. In modern times customs areas have largely made entrepôts obsolete, but the term is still used to refer to duty-free ports with a high volume of re-export trade. ''Entrepôt'' also means 'warehouse' in modern French, and is derived from the Latin roots 'between' + 'position', literally 'that which is placed between'. Entrepôts had an important role in the early modern period, when mercantile shipping flourished between Europe and its colonial empires in the Americas and Asia. For example, the spice trade to Europe, which necessitated long trade routes, featured a much higher m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Clove
Cloves are the aromatic flower buds of a tree in the family Myrtaceae, ''Syzygium aromaticum'' (). They are native to the Maluku Islands, or Moluccas, in Indonesia, and are commonly used as a spice, flavoring, or Aroma compound, fragrance in final good, consumer products, such as toothpaste, soaps, or cosmetics. Cloves are available throughout the year owing to different harvest seasons across various countries. Etymology The word ''clove'', first used in English in the 15th century, derives via Middle English , Anglo-French ''clowes de gilofre'' and Old French , from the Latin word ' "nail". The related English word ''gillyflower'', originally meaning "clove", derives via said Old French and Latin ', from the Greek "clove", literally "nut leaf". Description The clove tree is an evergreen that grows up to tall, with large leaves and crimson flowers grouped in terminal clusters. The flower buds initially have a pale hue, gradually turn green, then transition to a bright red ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Hitu
Hitu is an Austronesian language of the Central Malayo-Polynesian subgroup spoken on Ambon Island in eastern Indonesia Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania, between the Indian Ocean, Indian and Pacific Ocean, Pacific oceans. Comprising over List of islands of Indonesia, 17,000 islands, including Sumatra, ..., part of a dialect chain of Seram Island. ''Hitu'' is the name of a village; each of the villages, Wakal, Morela, Mamala, Hitu, and Hila, are said to have their own dialect. References Central Maluku languages Languages of Indonesia Seram Island {{au-lang-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Javanese People
The Javanese ( , ; ) are an Austronesian peoples, Austronesian ethnic group native to the central and eastern part of the Indonesian island of Java. With more than 100 million people, Javanese people are the largest ethnic group in both Indonesia and in Southeast Asia as a whole. Their native language is Javanese language, Javanese, it is the largest of the Austronesian languages in List of languages by number of native speakers, number of native speakers and also the largest regional language in Southeast Asia. As the largest ethnic group in the region, the Javanese have historically dominated the social, political, and cultural landscape of both Indonesia and Southeast Asia. There are significant numbers of Javanese diaspora outside of Central Java, central and East Java, eastern Java regions, including the other provinces of Indonesia, as well as other countries such as Suriname, Singapore, Malaysia, Egypt, Saudi Arabia, South Africa, Sri Lanka, Yemen and the Netherlands. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Gresik
Gresik Regency ( older spelling: Grissee, ) is a regency within East Java Province of Indonesia. As well as a large part of the northern and western suburbs of the city of Surabaya, it includes the offshore Bawean Island, some 125 km to the north of Java and Madura. Almost a third of the Gresik Regency's area is the coastal area; the Districts in this zone are Kebomas District, (part of) Gresik District, Manyar District, Bungah District, and Ujungpangkah District. The regency covers and an area of 1,191.26 km2, and it had a population of 1,177,042 at the 2010 CensusBiro Pusat Statistik, Jakarta, 2011. and 1,311,215 at the 2020 Census;Badan Pusat Statistik, Jakarta, 2021. the official estimate as at mid 2024 was 1,327,497 (comprising 667,540 males and 659,957 females).Badan Pusat Statistik, Jakarta, 28 February 2025, ''Kabupaten Gresik Dalam Angka 2025'' (Katalog-BPS 1102001.3525) The regency's administrative centre is the town of Gresik, about 25 km to the northwest of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
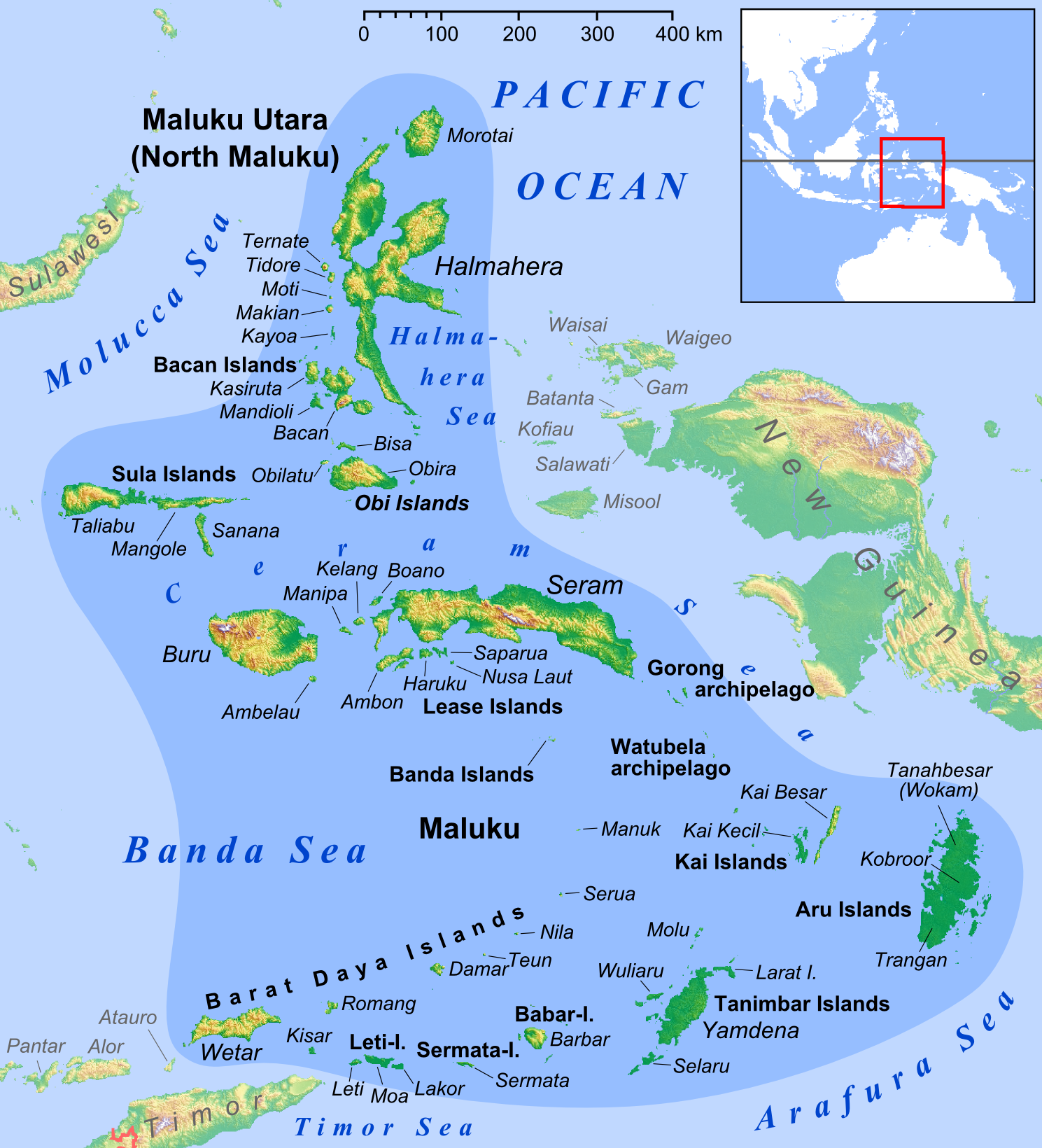
Ambon Island
Ambon Island is part of the Maluku Islands of Indonesia. The island has an area of and is mountainous, well watered, and fertile. Ambon Island consists of two territories: the city of Ambon, Maluku, Ambon to the south, and three districts (''kecamatan'') of the Central Maluku Regency to the north. The main city and seaport is Ambon, Maluku, Ambon (with a 2020 Census population of 347,288), which is also the capital of Maluku (province), Maluku Provinces of Indonesia, province, while those districts of Maluku Tengah Regency situated on Ambon Island had a 2020 Census population of 128,069. By mid 2023 those populations were estimated to have become 354,052 and 128,754 respectively, resulting in an all-island population of 482,806. Ambon has an Pattimura Airport, airport and is home to the Pattimura University and Open University (Universitas Terbuka), state universities, and a few private universities, which include Darussalam University (Universitas Darussalam, UNDAR) and Univer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Lesser Sunda Islands
The Lesser Sunda Islands (, , ), now known as Nusa Tenggara Islands (, or "Southeast Islands"), are an archipelago in the Indonesian archipelago. Most of the Lesser Sunda Islands are located within the Wallacea region, except for the Bali province which is west of the Wallace Line and is within the Sunda Shelf. Together with the Greater Sunda Islands to the west, they make up the Sunda Islands. The islands are part of a volcanic arc, the Sunda Arc, formed by subduction along the Sunda Trench in the Java Sea. In 1930 the population was 3,460,059; today over 17 million people live on the islands. Etymologically, Nusa Tenggara means "Southeast Islands" from the words of ''nusa'' which means 'island' from Old Javanese language and ''tenggara'' means 'southeast'. The main Lesser Sunda Islands are, from west to east: Bali, Lombok, Sumbawa, Flores, Sumba, Savu, Rote Island, Rote, Timor, Atauro, Alor archipelago, Barat Daya Islands, and Tanimbar Islands. Apart from the eastern half o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |