|
Flat-sixteen Engine
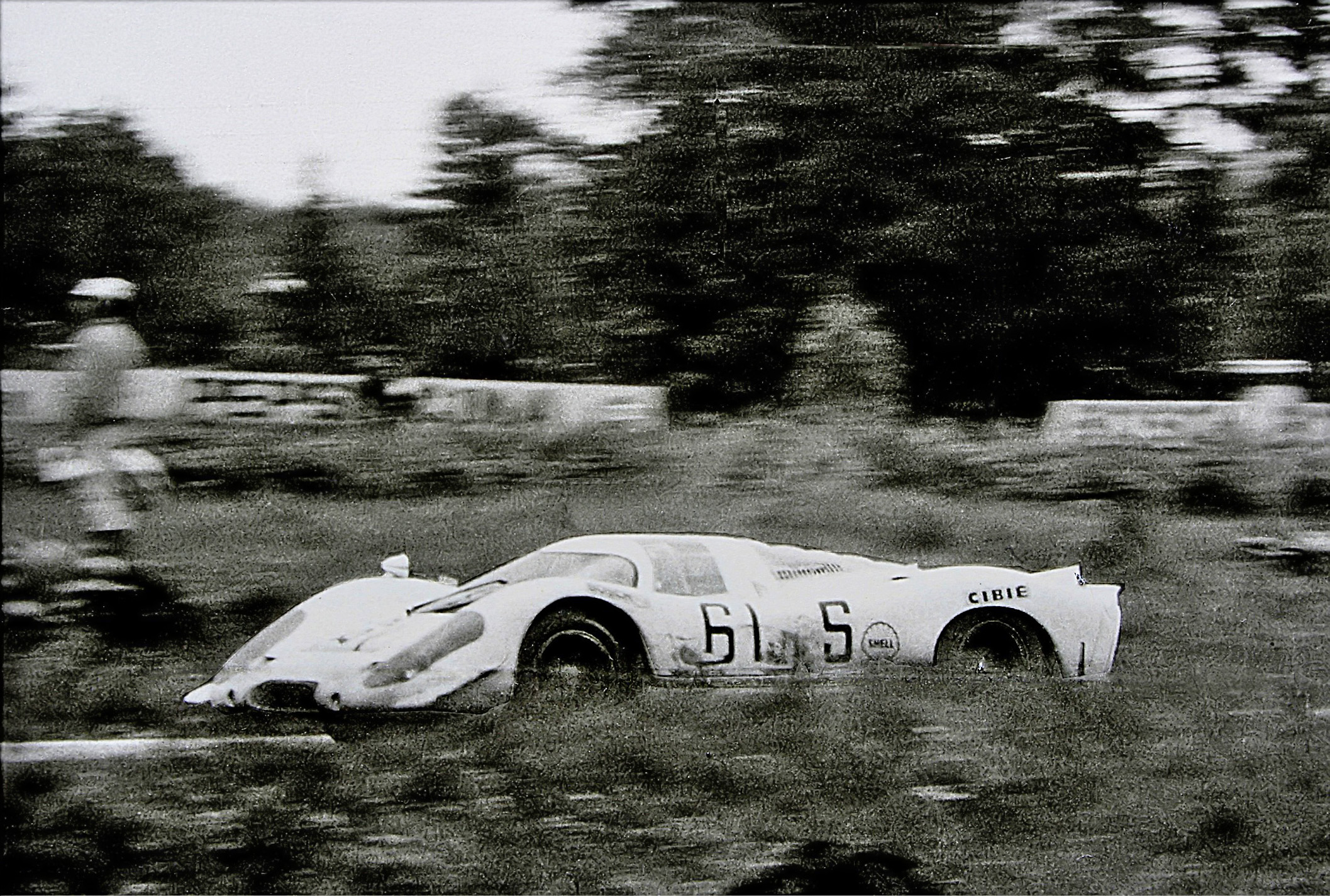
A flat-sixteen engine, also known as a horizontally opposed-sixteen, is a sixteen-cylinder piston engine with eight cylinders on each side of a central crankshaft. Flat-sixteen engines are less common than V16 engines, with only a couple of prototype racing engines using a flat-sixteen layout. Design These engines had two connecting rods per crankpin, so they could also be referred to as a 180 degree V16, rather than a boxer configuration as used by most flat engines with six cylinders or less. Coventry Climax FWMW The Coventry Climax FWMW was a prototype flat-sixteen engine designed between 1963 and 1965 that was intended for use in Formula One. The Brabham and Lotus teams designed cars for this engine but it was never raced. This was due to reliability problems in testing and a failure to generate the desired power output. Porsche 917 In 1971, Porsche developed a flat-sixteen prototype engine to use in the Porsche 917 that competed in the Can-Am championship. The pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Porsche 16cyl Engine
Dr. Ing. h.c. F. Porsche AG, usually shortened to Porsche (; see below), is a German automobile manufacturer specializing in luxury, high-performance sports cars, SUVs and sedans, headquartered in Stuttgart, Baden-Württemberg, Germany. The company is owned by Volkswagen AG, a controlling stake of which is owned by Porsche Automobil Holding SE, usually shortened to Porsche SE. Porsche's current lineup includes the 718, 911, Panamera, Macan, Cayenne and Taycan. The origins of the company date to the 1930s when German Bohemian automotive engineer Ferdinand Porsche founded Porsche with Adolf Rosenberger, a keystone figure in the creation of German automotive manufacturer and Audi precursor Auto Union, and Austrian businessman Anton Piëch, who was, at the time, also Ferdinand Porsche's son in law. In its early days, it was contracted by the German government to create a vehicle for the masses, which later became the Volkswagen Beetle. After World War II, when Ferdinand, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Piston Engine
A reciprocating engine, more often known as a piston engine, is a heat engine that uses one or more Reciprocating motion, reciprocating pistons to convert high temperature and high pressure into a Circular motion, rotating motion. This article describes the common features of all types. The main types are: the internal combustion engine, used extensively in motor vehicles; the steam engine, the mainstay of the Industrial Revolution; and the Stirling engine for niche applications. Internal combustion engines are further classified in two ways: either a spark-ignition engine, spark-ignition (SI) engine, where the spark plug initiates the combustion; or a compression-ignition engine, compression-ignition (CI) engine, where the air within the cylinder is compressed, Adiabatic process, thus heating it, so that the heated air ignites fuel that is injected diesel engine, then or hot-bulb engine, earlier.''Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach'' by Yunus A. Cengal and Michael A. Boles ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
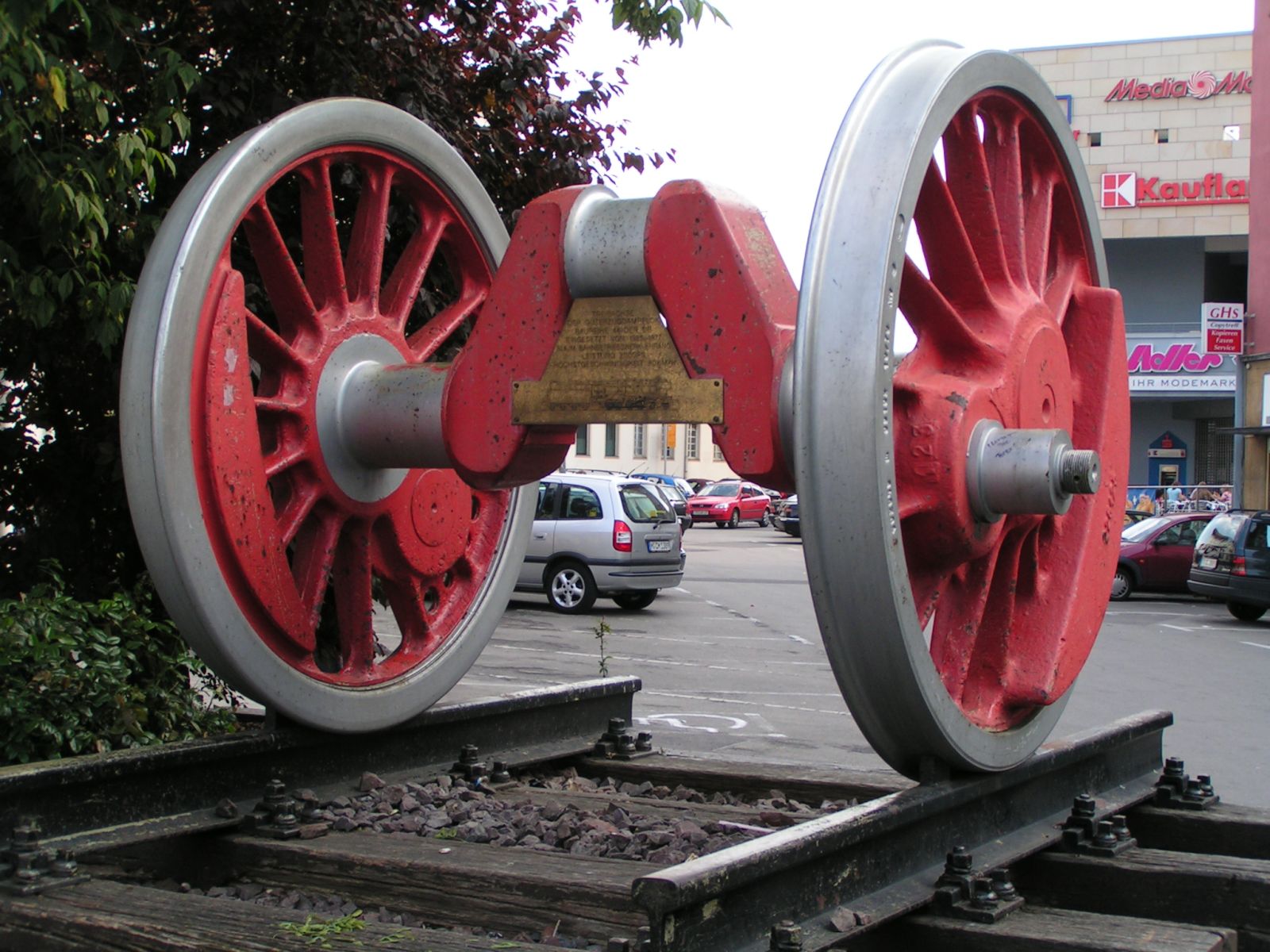
Crankshaft
A crankshaft is a mechanical component used in a reciprocating engine, piston engine to convert the reciprocating motion into rotational motion. The crankshaft is a rotating Shaft (mechanical engineering), shaft containing one or more crankpins, that are driven by the pistons via the connecting rods. The crankpins are also called ''rod bearing journals'', and they rotate within the "big end" of the connecting rods. Most modern crankshafts are located in the engine block. They are made from steel or cast iron, using either a forging, casting (metalworking), casting or machining process. Design The crankshaft is located within the engine block and held in place via main bearings which allow the crankshaft to rotate within the block. The up-down motion of each piston is transferred to the crankshaft via connecting rods. A flywheel is often attached to one end of the crankshaft, in order to smoothen the power delivery and reduce vibration. A crankshaft is subjected to enormou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
V16 Engine
A V16 engine is a sixteen-cylinder Internal combustion engine#Reciprocating engines, piston engine where two banks of eight cylinders are arranged in a V engine, V configuration around a common crankshaft. V16 engines are less common than engines with fewer cylinders, such as V8 and V12 engines. Each bank of a V16 engine can be thought of as a straight-eight engine, straight-eight, a design that can be inherently engine balance, balanced. Most V16 engines have a 45° bank angle. The first use of a V16 engine was in the 1910 Antoinette VII experimental aircraft, followed by several cars in the 1930s. Today, the most common applications for V16 engines are railroad locomotives, marine craft, and stationary power generators. Automotive applications Production cars The first production car to use a V16 engine was the Cadillac V-16, introduced in January 1930. The Cadillac V16 engine was initially produced with a displacement of , overhead valve engine, OHV and a V-angle of 45 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Connecting Rod
A connecting rod, also called a 'con rod', is the part of a reciprocating engine, piston engine which connects the piston to the crankshaft. Together with the crank (mechanism), crank, the connecting rod converts the reciprocating motion of the piston into the rotation of the crankshaft. The connecting rod is required to transmit the compressive and tensile forces from the piston. In its most common form, in an internal combustion engine, it allows pivoting on the piston end and rotation on the shaft end. The predecessor to the connecting rod is a mechanic linkage used by water mills to convert rotating motion of the water wheel into reciprocating motion. The most common usage of connecting rods is in internal combustion engines or on steam engines. __TOC__ Origins A connecting rod crank has been found in the Celtic Oppida at Paule in Brittany, dated to 69 BC. The predecessor to the connecting length is the Linkage (mechanical), mechanical linkage used by List of Roman wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crankpin
A crankpin or crank pin, also known as a rod bearing journal, is a mechanical device in an engine which connects the crankshaft to the connecting rod for each cylinder. It has a cylindrical surface, to allow the crankpin to rotate relative to the "big end" of the connecting rod. The most common configuration is for a crankpin to serve one cylinder. However, many V engines have each crankpin shared by each pair of cylinders. Design The crankpin connects to the larger end of the connecting rod for each cylinder. This end of the connecting rod is called the "big end", as opposed to the "small end" or "little end" (which connects to the wrist/gudgeon pin in the piston). The bearing which allows the crankpin to rotate around its shaft is called the "rod bearing". In automotive engines, the most common type of rod bearing is the plain bearing, however bushings or roller bearings are also used in some engines. Configurations In a single-cylinder engine, straight engine or fla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boxer Engine
A flat engine is a Internal combustion engine#Reciprocating engines, piston engine where the cylinders are located on either side of a central crankshaft. Flat engines are also known as horizontally opposed engines, however this is distinct from the less common opposed-piston engine design, whereby each cylinder has two pistons sharing a central combustion chamber. The most common configuration of flat engines is the #Boxer configuration, boxer engine configuration, in which the pistons of each opposed pair of cylinders move inwards and outwards at the same time. The other configuration is effectively a V engine with a 180-degree angle between the cylinder banks: in this configuration each pair of cylinders shares a single crankpin, so that as one piston moves inward, the other moves outward. The first flat engine (Benz Contramotor) was built in 1897 by Karl Benz. Flat engines have been used in aviation, motorcycle and automobile applications. They are now less common in car ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coventry Climax
Coventry Climax was a British manufacturer of forklift trucks, fire pumps, racing engines, and other speciality engines. History Pre WWI The company was started in 1903 as Lee Stroyer, a joint venture by Jens Stroyer and Pelham Lee. In 1905, following the departure of Stroyer, it was relocated to Paynes Lane, Coventry, and renamed as Coventry Simplex by Horace Pelham Lee, a former Daimler employee, who saw an opportunity in the nascent internal combustion engine market. An early user was GWK, who produced over 1,000 light cars with Coventry-Simplex two-cylinder engines between 1911 and 1915. Just before the First World War, a Coventry-Simplex engine was used by Lionel Martin to power the first Aston Martin car. Ernest Shackleton selected Coventry-Simplex to power the tractors that were to be used in his Imperial Trans-Antarctic Expedition of 1914. Hundreds of Coventry-Simplex engines were manufactured during the First World War to be used in generator sets for se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brabham
Motor Racing Developments Ltd., commonly known as Brabham ( ), was a British race car, racing car manufacturer and Formula One racing team. It was founded in 1960 by the Australian driver Jack Brabham and the British-Australian designer Ron Tauranac. The team had a successful thirty-year history, winning four Fédération Internationale de l'Automobile, FIA Formula One List of Formula One World Drivers' Champions, World Drivers' Championships and two List of Formula One World Constructors' Champions, World Constructors' Championships. Under Brabham and Tauranac, Brabham won double world championships in 1966 and 1967, with the 1966 drivers' title going to Jack Brabham and the 1967 title going to Denny Hulme. Jack Brabham is the only Formula One driver to win a Drivers' Championship in a car bearing his own name. Brabham was the first Formula One team to use a wind tunnel to design cars. It became the world's largest manufacturer of open wheel car, open-wheel racing cars sold to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Team Lotus
Team Lotus was the motorsport sister company of English sports car manufacturer Lotus Cars. The team ran cars in many motorsport categories including Formula One, Formula Two, Formula Ford, Formula Junior, American Championship Car Racing, IndyCar, and sports car racing. More than thirty years after its last race, Team Lotus remained one of the most successful racing teams of all time, winning seven Formula One List of Formula One World Constructors' Champions, Constructors' titles, six List of Formula One World Drivers' Champions, Drivers' Championships, and the Indianapolis 500 in the United States between 1962 and 1978. Under the direction of founder and chief designer Colin Chapman, Lotus was responsible for many innovative and experimental developments in critical motorsport, in both technical and commercial arenas. The Lotus name returned to Formula One in 2010 as Tony Fernandes's Team Lotus (2010–2011), Lotus Racing team. In 2011, Team Lotus's iconic black-and-gold liv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Porsche 917
The Porsche 917 is a sports prototype race car developed by German manufacturer Porsche to exploit the regulations regarding the construction of 5-litre sports cars. Powered by a Type 912 flat-12 engine which was progressively enlarged from 4.5 to 5.0 litres, the 917 was introduced in 1969 and initially proved unwieldy on the race track but continuous development improved the handling and it went on to dominate sports-car racing in 1970 and 1971. In 1970 it gave Porsche its first overall win at the 24 Hours of Le Mans, a feat it would repeat in 1971. It would be chiefly responsible for Porsche winning the World Sportscar Championship, International Championship for Makes in 1970 and 1971. Porsche went on to develop the 917 for Can-Am racing, culminating in the twin-turbocharged 917/30 which was even more dominant in the role. Porsche drivers would win the Can-Am championship in 1972 and 1973. 917 drivers also won the Interserie championship every year from 1969 to 1975. Origin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
W16 Engine
A W16 engine is a sixteen-cylinder piston engine with four banks of four cylinders in a W configuration. W16 engines are rarely produced, with the notable exception of the Volkswagen Group 8.0 WR16 engine, which has been used since 2005 in the Bugatti Veyron, Bugatti Chiron and their related models. __TOC__ Volkswagen Group The W16 engine that Volkswagen Group uses in its Bugatti Veyron and Chiron has a displacement of and four turbochargers. It is effectively two narrow-angle VR8 engines (based on the VR6 design) mated at an included angle of 90 degrees on a common crankshaft. The most powerful version of this engine, installed in the Bugatti Bolide, generates at 7,000 rpm. At the 1999 Geneva Auto Salon, Bentley presented Hunaudières, a concept two-seated mid-engined car with an 8-litre W16 engine. The engine was the basis for the Bugatti Veyron. Another concept car from Volkswagen Group to have the W16 engine is the Audi Rosemeyer, introduced in 2000 an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |