|
Fiscal Policy Debate
The monetary/fiscal policy debate,McCallum (1985) otherwise known as the Ando–Modigliani/Friedman–Meiselman debateEisner (1988) (or AM/FM debate from the main instigators' initials, and for this reason sometimes jokingly called the "radio stations debate"See AM Broadcasting and FM BroadcastingGramlich (2004)), was the exchange of viewpoints about the comparative efficiency of monetary policies and fiscal policies that originated with a workFriedman/Meiselman (1963) co-authored by Milton Friedman and David I. Meiselman and first published in 1963, as part of studies submitted to the Commission on Money and Credit. Surveys of American Economic Association (AEA) members since the 1970s have shown that professional economists generally agree with the statement: "Fiscal policy has a significant stimulative impact on a less than fully employed economy." Conversely, while a 2000 survey of AEA members found that while 72 percent generally agreed with the statement that "Management ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Initials
In a written or published work, an initial is a letter at the beginning of a word, a chapter, or a paragraph that is larger than the rest of the text. The word is ultimately derived from the Latin ''initiālis'', which means ''of the beginning''. An initial is often several lines in height, and, in older books or manuscripts, may take the form of an inhabited or historiated initial. There are certain important initials, such as the Beatus initial, or B, of ''Beatus vir...'' at the opening of Psalm 1 at the start of a vulgate Latin. These specific initials in an illuminated manuscript were also called initia (singular: initium). History The classical tradition was slow to use capital letters for initials at all; in surviving Roman texts it often is difficult even to separate the words as spacing was not used either. In late antiquity (–6th century) both came into common use in Italy, the initials usually were set in the left margin (as in the second example below), as thou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Federal Reserve
The Federal Reserve System (often shortened to the Federal Reserve, or simply the Fed) is the central banking system of the United States. It was created on December 23, 1913, with the enactment of the Federal Reserve Act, after a series of financial panics (particularly the panic of 1907) led to the desire for central control of the monetary system in order to alleviate financial crises. Although an instrument of the U.S. government, the Federal Reserve System considers itself "an independent central bank because its monetary policy decisions do not have to be approved by the president or by anyone else in the executive or legislative branches of government, it does not receive funding appropriated by Congress, and the terms of the members of the board of governors span multiple presidential and congressional terms." Over the years, events such as the Great Depression in the 1930s and the Great Recession during the 2000s have led to the expansion of the roles and responsibi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
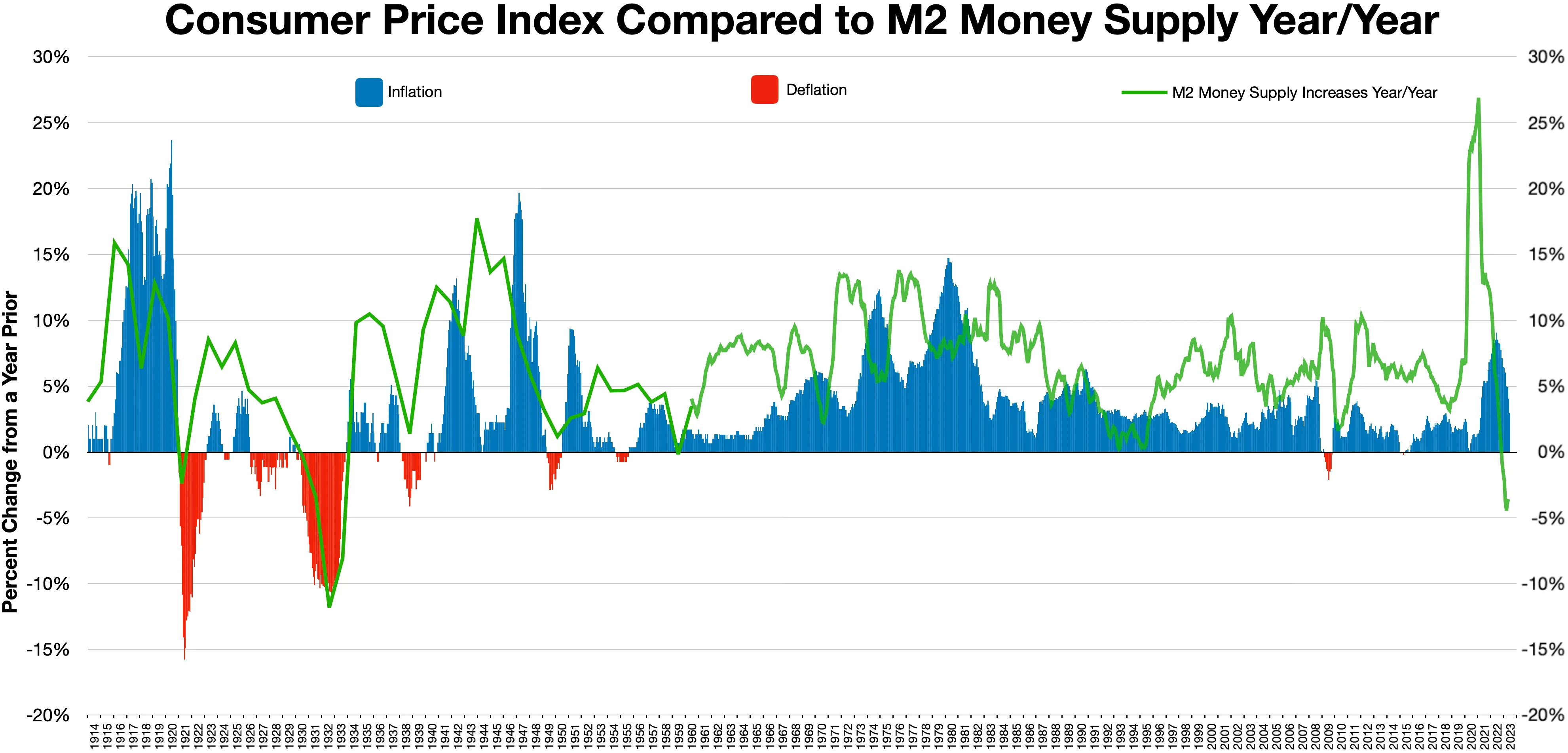
M2 (economics)
In macroeconomics, money supply (or money stock) refers to the total volume of money held by the public at a particular point in time. There are several ways to define "money", but standard measures usually include currency in circulation (i.e. physical cash) and demand deposits (depositors' easily accessed assets on the books of financial institutions). Money supply data is recorded and published, usually by the national statistical agency or the central bank of the country. Empirical money supply measures are usually named M1, M2, M3, etc., according to how wide a definition of money they embrace. The precise definitions vary from country to country, in part depending on national financial institutional traditions. Even for narrow aggregates like M1, by far the largest part of the money supply consists of deposits in commercial banks, whereas currency (banknotes and coins) issued by central banks only makes up a small part of the total money supply in modern economies. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Money Velocity
image:M3 Velocity in the US.png, 300px, Similar chart showing the logged velocity (green) of a broader measure of money M3 that covers M2 plus large institutional deposits. The US no longer publishes official M3 measures, so the chart only runs through 2005. Employment again shown in blue, recessions as grey bars. The velocity of money measures the number of times that one unit of currency is used to purchase goods and services within a given time period. In other words, it represents how many times per period money is changing hands, or is circulating to other owners in return for valuable goods and services. The concept relates the size of economic activity to a given money supply. The speed of money exchange is one of the variables that determine inflation. The measure of the velocity of money is usually the ratio of a country's or an economy's nominal gross national product (GNP) to its money supply. If the velocity of money is increasing, then transactions are occurring b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constant (mathematics)
In mathematics, the word constant conveys multiple meanings. As an adjective, it refers to non-variance (i.e. unchanging with respect to some other value); as a noun, it has two different meanings: * A fixed and well-defined number or other non-changing mathematical object, or the symbol denoting it. The terms '' mathematical constant'' or '' physical constant'' are sometimes used to distinguish this meaning. * A function whose value remains unchanged (i.e., a '' constant function''). Such a constant is commonly represented by a variable which does not depend on the main variable(s) in question. For example, a general quadratic function is commonly written as: :a x^2 + b x + c\, , where , and are constants ( coefficients or parameters), and a variable—a placeholder for the argument of the function being studied. A more explicit way to denote this function is :x\mapsto a x^2 + b x + c \, , which makes the function-argument status of (and by extension the constancy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monetarist
Monetarism is a school of thought in monetary economics that emphasizes the role of policy-makers in controlling the amount of money in circulation. It gained prominence in the 1970s, but was mostly abandoned as a direct guidance to monetary policy during the following decade because of the rise of inflation targeting through movements of the official interest rate. The monetarist theory states that variations in the money supply have major influences on national output in the short run and on price levels over longer periods. Monetarists assert that the objectives of monetary policy are best met by targeting the growth rate of the money supply rather than by engaging in discretionary monetary policy.Phillip Cagan, 1987. "Monetarism", '' The New Palgrave: A Dictionary of Economics'', v. 3, Reprinted in John Eatwell et al. (1989), ''Money: The New Palgrave'', pp. 195–205, 492–97. Monetarism is commonly associated with neoliberalism. Monetarism is mainly associated with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Keynesian Economics
Keynesian economics ( ; sometimes Keynesianism, named after British economist John Maynard Keynes) are the various macroeconomics, macroeconomic theories and Economic model, models of how aggregate demand (total spending in the economy) strongly influences Output (economics), economic output and inflation. In the Keynesian view, aggregate demand does not necessarily equal the aggregate supply, productive capacity of the economy. It is influenced by a host of factors that sometimes behave erratically and impact production, employment, and inflation. Keynesian economists generally argue that aggregate demand is volatile and unstable and that, consequently, a market economy often experiences inefficient macroeconomic outcomes, including economic recession, recessions when demand is too low and inflation when demand is too high. Further, they argue that these economic fluctuations can be mitigated by economic policy responses coordinated between a government and their central bank. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Least Squares
The method of least squares is a mathematical optimization technique that aims to determine the best fit function by minimizing the sum of the squares of the differences between the observed values and the predicted values of the model. The method is widely used in areas such as regression analysis, curve fitting and data modeling. The least squares method can be categorized into linear and nonlinear forms, depending on the relationship between the model parameters and the observed data. The method was first proposed by Adrien-Marie Legendre in 1805 and further developed by Carl Friedrich Gauss. History Founding The method of least squares grew out of the fields of astronomy and geodesy, as scientists and mathematicians sought to provide solutions to the challenges of navigating the Earth's oceans during the Age of Discovery. The accurate description of the behavior of celestial bodies was the key to enabling ships to sail in open seas, where sailors could no longer rely on la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reduced Form
In statistics, and particularly in econometrics, the reduced form of a simultaneous equations model, system of equations is the result of solving the system for the endogenous variables. This gives the latter as functions of the exogenous variables, if any. In econometrics, the equations of a structural model (econometrics), structural form model are estimation theory, estimated in their theoretically given form, while an alternative approach to estimation is to first solve the theoretical equations for the endogenous variables to obtain reduced form equations, and then to estimate the reduced form equations. Let ''Y'' be the vector of the variables to be explained (endogeneous variables) by a statistical model and ''X'' be the vector of explanatory (exogeneous) variables. In addition let \varepsilon be a vector of error terms. Then the general expression of a structural form is f(Y, X, \varepsilon) = 0 , where ''f'' is a function, possibly from vectors to vectors in the case of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Consumption (economics)
Consumption refers to the use of resources to fulfill present needs and desires. It is seen in contrast to investing, which is spending for acquisition of ''future'' income. Consumption is a major concept in economics and is also studied in many other social sciences. Different schools of economists define consumption differently. According to mainstream economics, mainstream economists, only the final purchase of newly produced Good (economics), goods and Service (economics), services by individuals for immediate use constitutes consumption, while other types of expenditure — in particular, fixed investment, intermediate consumption, and government spending — are placed in separate categories (see consumer choice). Other economists define consumption much more broadly, as the aggregate of all economic activity that does not entail the design, production and marketing of goods and services (e.g., the selection, adoption, use, disposal and recycling of goods and services). E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Money Supply
In macroeconomics, money supply (or money stock) refers to the total volume of money held by the public at a particular point in time. There are several ways to define "money", but standard measures usually include currency in circulation (i.e. physical cash) and demand deposits (depositors' easily accessed assets on the books of financial institutions). Money supply data is recorded and published, usually by the national statistical agency or the central bank of the country. Empirical money supply measures are usually named M1, M2, M3, etc., according to how wide a definition of money they embrace. The precise definitions vary from country to country, in part depending on national financial institutional traditions. Even for narrow aggregates like M1, by far the largest part of the money supply consists of deposits in commercial banks, whereas currency (banknotes and coins) issued by central banks only makes up a small part of the total money supply in modern economies. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |