|
Extensor Pollicis Brevis Muscle
In human anatomy, the extensor pollicis brevis is a skeletal muscle on the dorsal side of the forearm. It lies on the medial side of, and is closely connected with, the abductor pollicis longus. The extensor pollicis brevis (EPB) belongs to the deep group of the posterior fascial compartment of the forearm. It is a part of the lateral border of the anatomical snuffbox. Structure The extensor pollicis brevis arises from the ulna distal to the abductor pollicis longus, from the interosseous membrane, and from the dorsal surface of the radius. Its direction is similar to that of the abductor pollicis longus, its tendon passing the same groove on the lateral side of the lower end of the radius, to be inserted into the base of the first phalanx of the thumb. Variation Absence; fusion of tendon with that of the extensor pollicis longus or abductor pollicis longus muscle. Function In a close relationship to the abductor pollicis longus, the extensor pollicis brevis both exten ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
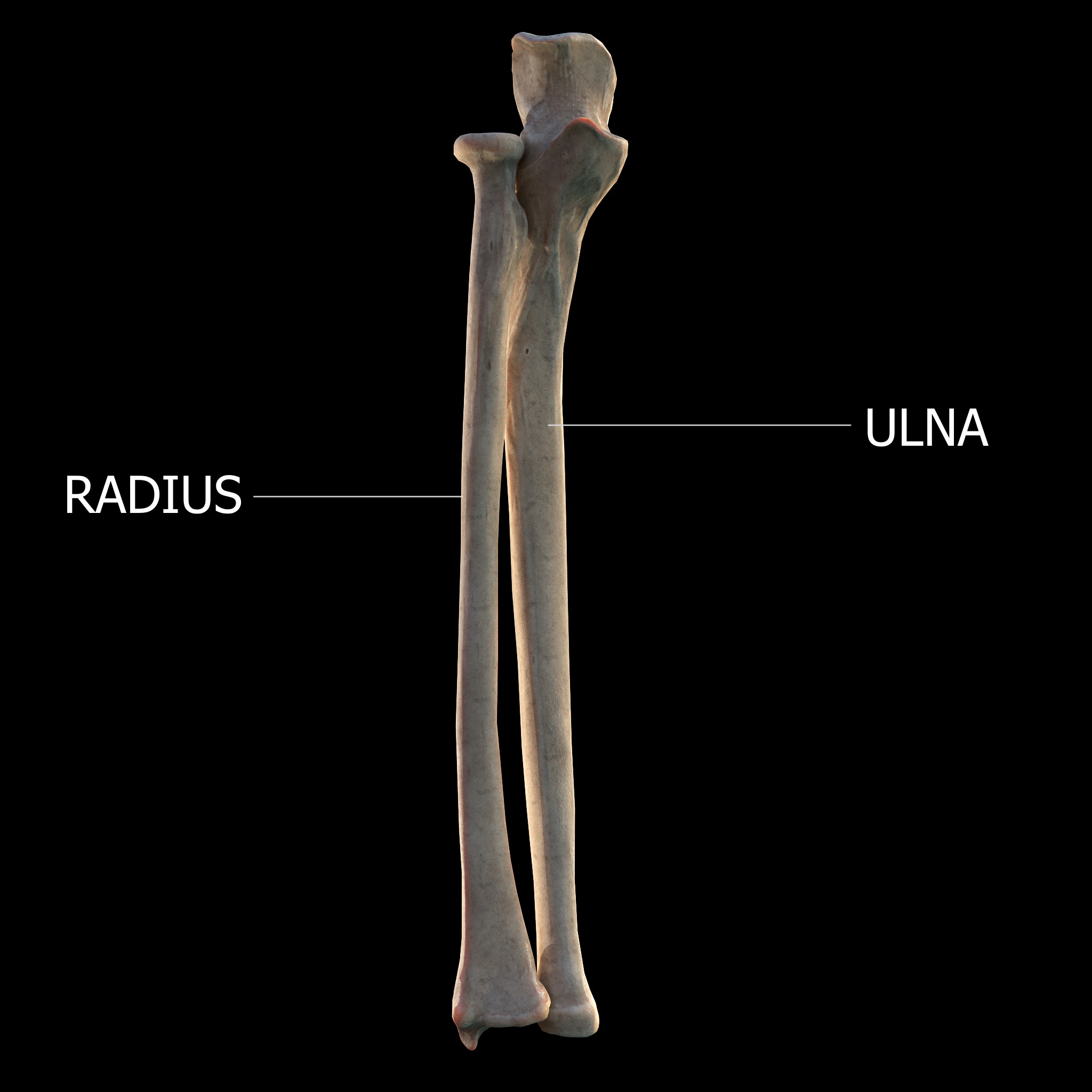
Radius (bone)
The radius or radial bone is one of the two large bones of the forearm, the other being the ulna. It extends from the lateral side of the elbow to the thumb side of the wrist and runs parallel to the ulna. The ulna is usually slightly longer than the radius, but the radius is thicker. Therefore the radius is considered to be the larger of the two. It is a long bone, prism-shaped and slightly curved longitudinally. The radius is part of two joints: the elbow and the wrist. At the elbow, it joins with the capitulum of the humerus, and in a separate region, with the ulna at the radial notch. At the wrist, the radius forms a joint with the ulna bone. The corresponding bone in the lower leg is the fibula. Structure The long narrow medullary cavity is enclosed in a strong wall of compact bone. It is thickest along the interosseous border and thinnest at the extremities, same over the cup-shaped articular surface (fovea) of the head. The trabeculae of the spongy ti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Anatomy
The human body is the structure of a human being. It is composed of many different types of cells that together create tissues and subsequently organ systems. They ensure homeostasis and the viability of the human body. It comprises a head, hair, neck, trunk (which includes the thorax and abdomen), arms and hands, legs and feet. The study of the human body involves anatomy, physiology, histology and embryology. The body varies anatomically in known ways. Physiology focuses on the systems and organs of the human body and their functions. Many systems and mechanisms interact in order to maintain homeostasis, with safe levels of substances such as sugar and oxygen in the blood. The body is studied by health professionals, physiologists, anatomists, and by artists to assist them in their work. Composition The human body is composed of elements including hydrogen, oxygen, carbon, calcium and phosphorus. These elements reside in trillions of cells and non-cellular c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anatomical Snuff Box
The anatomical snuff box or snuffbox or foveola radialis is a triangular deepening on the radial, dorsal aspect of the hand—at the level of the carpal bones, specifically, the scaphoid and trapezium bones forming the floor. The name originates from the use of this surface for placing and then sniffing powdered tobacco, or " snuff." It is sometimes referred to by its French name ''tabatière''. Structure Boundaries * The medial border (ulnar side) of the snuffbox is the tendon of the extensor pollicis longus. * The lateral border (radial side) is a pair of parallel and intimate tendons, of the extensor pollicis brevis and the abductor pollicis longus. (Accordingly, the anatomical snuffbox is most visible, having a more pronounced concavity, during thumb extension.) * The proximal border is formed by the styloid process of the radius * The distal border is formed by the approximate apex of the schematic snuffbox isosceles triangle. * The floor of the snuffbox varies depending on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carpometacarpal Joint
The carpometacarpal (CMC) joints are five joints in the wrist that articulate the distal row of carpal bones and the proximal bases of the five metacarpal bones. The CMC joint of the thumb or the first CMC joint, also known as the trapeziometacarpal (TMC) joint, differs significantly from the other four CMC joints and is therefore described separately. Thumb The carpometacarpal joint of the thumb (''pollex''), also known as the first carpometacarpal joint, or the trapeziometacarpal joint (TMC) because it connects the trapezium to the first metacarpal bone, plays an irreplaceable role in the normal functioning of the thumb. The most important joint connecting the wrist to the metacarpus, osteoarthritis of the TMC is a severely disabling condition; up to twenty times more common among elderly women than in average. Pronation-supination of the first metacarpal is especially important for the action of opposition. The movements of the first CMC are limited by the shape of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interosseous Membrane Of The Forearm
The interosseous membrane of the forearm (rarely middle or intermediate radioulnar joint) is a fibrous sheet that connects the interosseous margins of the radius and the ulna. It is the main part of the radio-ulnar syndesmosis, a fibrous joint between the two bones. Function The interosseous membrane divides the forearm into anterior and posterior compartments, serves as a site of attachment for muscles of the forearm, and transfers loads placed on the forearm. The interosseous membrane is designed to shift compressive loads (as in doing a hand-stand) from the distal radius to the proximal ulna. The fibers within the interosseous membrane are oriented obliquely so that when force is applied the fibers are drawn taut, shifting more of the load to the ulna. This reduces the wear and tear of placing the whole load on a single joint. The role of the membrane in load shifting is illustrated when the interosseous membrane is cut; the forces on each bone equalize from their natural pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ulna
The ulna (''pl''. ulnae or ulnas) is a long bone found in the forearm that stretches from the elbow to the smallest finger, and when in anatomical position, is found on the medial side of the forearm. That is, the ulna is on the same side of the forearm as the little finger. It runs parallel to the radius, the other long bone in the forearm. The ulna is usually slightly longer than the radius, but the radius is thicker. Therefore, the radius is considered to be the larger of the two. Structure The ulna is a long bone found in the forearm that stretches from the elbow to the smallest finger, and when in anatomical position, is found on the medial side of the forearm. It is broader close to the elbow, and narrows as it approaches the wrist. Close to the elbow, the ulna has a bony process, the olecranon process, a hook-like structure that fits into the olecranon fossa of the humerus. This prevents hyperextension and forms a hinge joint with the trochlea of the humerus. Ther ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abductor Pollicis Longus Muscle
In human anatomy, the abductor pollicis longus (APL) is one of the extrinsic muscles of the hand. Its major function is to abduct the thumb at the wrist. Its tendon forms the anterior border of the anatomical snuffbox. Structure The abductor pollicis longus lies immediately below the supinator and is sometimes united with it. It arises from the lateral part of the dorsal surface of the body of the ulna, below the insertion of the anconeus, from the interosseous membrane, and from the middle third of the dorsal surface of the body of the radius.''Gray's Anatomy'' (1918), see infobox Passing obliquely downward and lateralward, it ends in a tendon, which runs through a groove on the lateral side of the lower end of the radius, accompanied by the tendon of the extensor pollicis brevis. The insertion is divided into a distal, superficial part and a proximal, deep part. The superficial part is inserted with one or more tendons into the radial side of the base of the first meta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Forearm
The forearm is the region of the upper limb between the elbow and the wrist. The term forearm is used in anatomy to distinguish it from the arm, a word which is most often used to describe the entire appendage of the upper limb, but which in anatomy, technically, means only the region of the upper arm, whereas the lower "arm" is called the forearm. It is homologous to the region of the leg that lies between the knee and the ankle joints, the crus. The forearm contains two long bones, the radius and the ulna, forming the two radioulnar joints. The interosseous membrane connects these bones. Ultimately, the forearm is covered by skin, the anterior surface usually being less hairy than the posterior surface. The forearm contains many muscles, including the flexors and extensors of the wrist, flexors and extensors of the digits, a flexor of the elbow (brachioradialis), and pronators and supinators that turn the hand to face down or upwards, respectively. In cross-section, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skeletal Muscle
Skeletal muscles (commonly referred to as muscles) are organs of the vertebrate muscular system and typically are attached by tendons to bones of a skeleton. The muscle cells of skeletal muscles are much longer than in the other types of muscle tissue, and are often known as muscle fibers. The muscle tissue of a skeletal muscle is striated – having a striped appearance due to the arrangement of the sarcomeres. Skeletal muscles are voluntary muscles under the control of the somatic nervous system. The other types of muscle are cardiac muscle which is also striated and smooth muscle which is non-striated; both of these types of muscle tissue are classified as involuntary, or, under the control of the autonomic nervous system. A skeletal muscle contains multiple fascicles – bundles of muscle fibers. Each individual fiber, and each muscle is surrounded by a type of connective tissue layer of fascia. Muscle fibers are formed from the fusion of developmental myobla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Posterior Interosseous Nerve
The posterior interosseous nerve (or dorsal interosseous nerve) is a nerve in the forearm. It is the continuation of the deep branch of the radial nerve, after this has crossed the supinator muscle. It is considerably diminished in size compared to the deep branch of the radial nerve. The nerve fibers originate from cervical segments C7 and C8 in the spinal column. Structure Course It descends along the interosseous membrane, anterior to the extensor pollicis longus muscle, to the back of the carpus, where it presents a gangliform enlargement from which filaments are distributed to the ligaments and articulations of the carpus. Supply The posterior interosseous nerve supplies all the muscles of the posterior compartment of the forearm, except anconeus muscle, brachioradialis muscle, and extensor carpi radialis longus muscle. In other words, it supplies the following muscles: * Extensor carpi radialis brevis muscle — deep branch of radial nerve * Extensor digitorum muscle * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interosseous Membrane
An interosseous membrane is a thick dense fibrous sheet of connective tissue that spans the space between two bones, forming a type of syndesmosis joint. Interosseous membranes in the human body: * Interosseous membrane of forearm * Interosseous membrane of leg The interosseous membrane of the leg (middle tibiofibular ligament) extends between the interosseous crests of the tibia and fibula, helps stabilize the Tib-Fib relationship and separates the muscles on the front from those on the back of the leg. ... Gallery File:5 ligaments of interosseous membrane of forearm.png, Five ligaments of interosseous membrane of forearm:* Central band (key portion to be reconstructed in case of injury)* Accessory band * Distal oblique bundle * Proximal oblique cord* Dorsal oblique accessory cord Notes External links * * {{Authority control Skeletal system ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Posterior Interosseous Artery
The posterior interosseous artery (dorsal interosseous artery) is an artery of the forearm. It is a branch of the common interosseous artery, which is a branch of the ulnar artery. Structure The posterior interosseous artery passes backward between the oblique cord and the upper border of the interosseous membrane. It appears between the contiguous borders of supinator muscle and the abductor pollicis longus muscle, and runs down the back of the forearm between the superficial and deep layers of muscles, to both of which it distributes branches. Where it lies on abductor pollicis longus muscle and the extensor pollicis brevis muscle, it is accompanied by the dorsal interosseous nerve. At the lower part of the forearm it anastomoses with the termination of the volar interosseous artery, and with the dorsal carpal network. Branches Near its origin, it gives off the interosseous recurrent artery. This ascends to the interval between the lateral epicondyle and olecranon, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |