|
Eumel
EUMEL (pronounced ''oimel'' for Extendable Multi User Microprocessor ELAN System and also known as L2 for Liedtke 2) is an operating system (OS) which began as a runtime system (environment) for the programming language ELAN. It was created in 1979 by Jochen Liedtke at the Bielefeld University. EUMEL initially ran on the 8-bit Zilog Z80 processor. It later was ported to many different computer architectures. More than 2000 Eumel systems shipped, mostly to schools and also to legal practices as a text processing platform. EUMEL is based on a virtual machine using a bitcode and achieves remarkable performance and function. Z80-based EUMEL systems provide full multi-user multi-tasking operation with virtual memory management and complete isolation of one process against all others. These systems usually execute ELAN programs faster than equivalent programs written in languages such as COBOL, BASIC, or Pascal, and compiled into Z80 machine code on other operating systems. One of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Jochen Liedtke
Jochen Liedtke (26 May 1953 – 10 June 2001) was a German computer scientist, noted for his work on microkernel operating systems, especially in creating the L4 microkernel family. Career Education In the mid-1970s Liedtke studied for a diploma degree in mathematics at the Bielefeld University. His thesis project was to build a compiler for the programming language ELAN, which had been launched for teaching programming in German schools. The compiler was written in ELAN. Post grad After his graduation in 1977, he remained at Bielefeld and worked on an Elan environment for the Zilog Z80 microprocessor. This required a runtime system (environment), which he named Eumel ("Extendable Multiuser Microprocessor ELAN-System", but also a colloquial north-German term for likeable fool). Eumel grew into a complete multi-tasking, multi-user operating system supporting orthogonal persistence, which started shipping (by whom? to whom?) in 1980 and was later ported to Zilog Z8000, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
L3 Microkernel
L4 is a family of second-generation microkernels, used to implement a variety of types of operating systems (OS), though mostly for Unix-like, ''Portable Operating System Interface'' (POSIX) compliant types. L4, like its predecessor microkernel L3, was created by German computer scientist Jochen Liedtke as a response to the poor performance of earlier microkernel-based OSes. Liedtke felt that a system designed from the start for high performance, rather than other goals, could produce a microkernel of practical use. His original implementation in hand-coded Intel i386-specific assembly language code in 1993 created attention by being 20 times faster than Mach. The follow-up publication two years later was considered so influential that it won the 2015 ACM SIGOPS Hall of Fame Award. Since its introduction, L4 has been developed to be cross-platform and to improve security, isolation, and robustness. There have been various re-implementations of the original L4 kernel application ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
ELAN (programming Language)
ELAN is an interpreted educational programming language for learning and teaching systematic programming. (Note: In May 2023 design commenced on a new programming language named 'Elan' also designed for teaching and learning programming in schools, but it has no historical connection to the 'ELAN' language described here.) It was developed in 1974 by C.H.A. Koster and a group at Technische Universität Berlin as an alternative to BASIC in teaching, and approved for use in secondary schools in Germany by the "Arbeitskreis Schulsprache". It was in use until the late 1980s in a number of schools in Germany, Belgium, the Netherlands, and Hungary for informatics teaching in secondary education, and used at the Radboud University Nijmegen in the Netherlands for teaching systematic programming to students from various disciplines and in teacher courses. The language design focuses strongly on structured programming, and has a special construction for stepwise refinement, allowing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Zilog Z80
The Zilog Z80 is an 8-bit computing, 8-bit microprocessor designed by Zilog that played an important role in the evolution of early personal computing. Launched in 1976, it was designed to be Backward compatibility, software-compatible with the Intel 8080, offering a compelling alternative due to its better Integrated circuit, integration and increased performance. Along with the 8080's seven Processor register, registers and flags register, the Z80 introduced an alternate register set, two 16-bit index registers, and additional instructions, including bit manipulation and block copy/search. Originally intended for use in embedded systems like the 8080, the Z80's combination of compatibility, affordability, and superior performance led to widespread adoption in video game systems and home computers throughout the late 1970s and early 1980s, helping to fuel the personal computing revolution. The Z80 was used in iconic products such as the Osborne 1, TRS-80, Radio Shack TRS-80, Col ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Text Processing
In computing, the term text processing refers to the theory and practice of automating the creation or manipulation of electronic text. ''Text'' usually refers to all the alphanumeric characters specified on the keyboard of the person engaging the practice, but in general ''text'' means the abstraction layer immediately above the standard character encoding of the target text. The term ''processing'' refers to automated (or mechanized) processing, as opposed to the same manipulation done manually. Text processing involves computer commands which invoke content, content changes, and cursor movement, for example to * search and replace * format * generate a processed report of the content of, or * filter a file or report of a text file. The text processing of a regular expression is a virtual editing machine, having a primitive programming language that has named registers (identifiers), and named positions in the sequence of characters comprising the text. Using these, the "text p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Orthogonal Persistence
In computer science, persistence refers to the characteristic of state of a system that outlives (persists for longer than) the process that created it. This is achieved in practice by storing the state as data in computer data storage. Programs have to transfer data to and from storage devices and have to provide mappings from the native programming-language data structures to the storage device data structures. Picture editing programs or word processors, for example, achieve state persistence by saving their documents to files. Orthogonal or transparent persistence Persistence is said to be "orthogonal" or "transparent" when it is implemented as an intrinsic property of the execution environment of a program. An orthogonal persistence environment does not require any specific actions by programs running in it to retrieve or save their state. Non-orthogonal persistence requires data to be written and read to and from storage using specific instructions in a program, resulti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
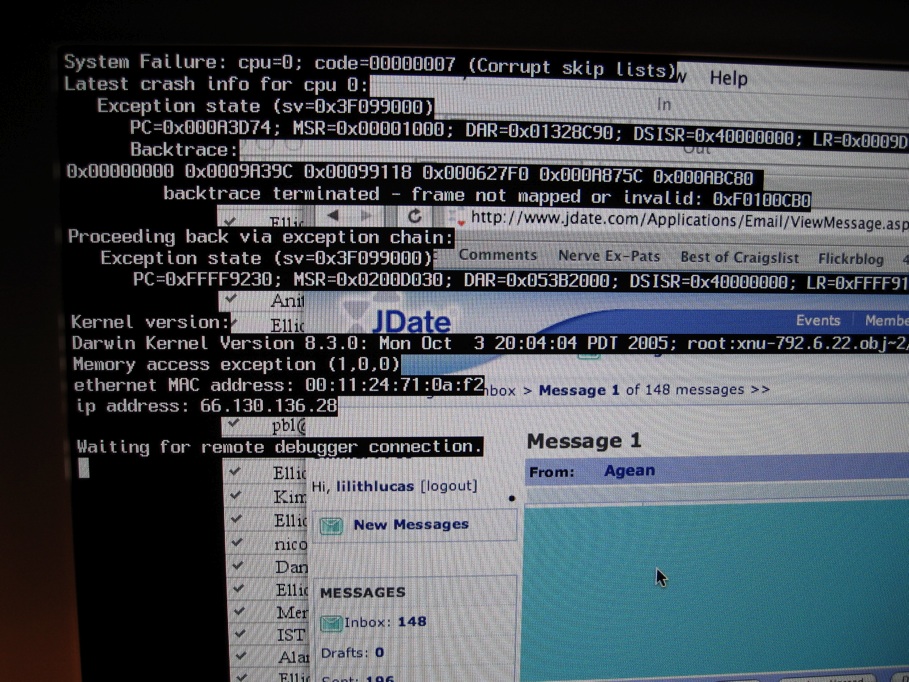
Crash (computing)
In computing, a crash, or system crash, occurs when a computer program such as a software application or an operating system stops functioning properly and exits. On some operating systems or individual applications, a crash reporting service will report the crash and any details relating to it (or give the user the option to do so), usually to the developer(s) of the application. If the program is a critical part of the operating system, the entire system may crash or hang, often resulting in a kernel panic or fatal system error. Most crashes are the result of a software bug. Typical causes include accessing invalid memory addresses, incorrect address values in the program counter, buffer overflow, overwriting a portion of the affected program code due to an earlier bug, executing invalid machine instructions (an illegal or unauthorized opcode), or triggering an unhandled exception. The original software bug that started this chain of events is typically considere ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Persistence (computer Science)
In computer science, persistence refers to the characteristic of State (computer science), state of a system that outlives (persists for longer than) the Process (computing), process that created it. This is achieved in practice by storing the state as data in computer data storage. Programs have to transfer data to and from storage devices and have to provide mappings from the native Programming language, programming-language Data structure, data structures to the storage device data structures. Picture editing programs or Word processor, word processors, for example, achieve State (computer science), state persistence by saving their documents to computer file, files. Orthogonal or transparent persistence Persistence is said to be "Orthogonality#Computer science, orthogonal" or "transparent" when it is implemented as an intrinsic property of the execution environment of a program. An orthogonal persistence environment does not require any specific actions by programs running i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Machine Code
In computer programming, machine code is computer code consisting of machine language instructions, which are used to control a computer's central processing unit (CPU). For conventional binary computers, machine code is the binaryOn nonbinary machines it is, e.g., a decimal representation. representation of a computer program that is actually read and interpreted by the computer. A program in machine code consists of a sequence of machine instructions (possibly interspersed with data). Each machine code instruction causes the CPU to perform a specific task. Examples of such tasks include: # Load a word from memory to a CPU register # Execute an arithmetic logic unit (ALU) operation on one or more registers or memory locations # Jump or skip to an instruction that is not the next one In general, each architecture family (e.g., x86, ARM) has its own instruction set architecture (ISA), and hence its own specific machine code language. There are exceptions, such as the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Pascal (programming Language)
Pascal is an imperative and procedural programming language, designed by Niklaus Wirth as a small, efficient language intended to encourage good programming practices using structured programming and data structuring. It is named after French mathematician, philosopher and physicist Blaise Pascal. Pascal was developed on the pattern of the ALGOL 60 language. Wirth was involved in the process to improve the language as part of the ALGOL X efforts and proposed a version named ALGOL W. This was not accepted, and the ALGOL X process bogged down. In 1968, Wirth decided to abandon the ALGOL X process and further improve ALGOL W, releasing this as Pascal in 1970. On top of ALGOL's scalars and arrays, Pascal enables defining complex datatypes and building dynamic and recursive data structures such as lists, trees and graphs. Pascal has strong typing on all objects, which means that one type of data cannot be converted to or interpreted as another without explicit conversions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
BASIC
Basic or BASIC may refer to: Science and technology * BASIC, a computer programming language * Basic (chemistry), having the properties of a base * Basic access authentication, in HTTP Entertainment * Basic (film), ''Basic'' (film), a 2003 film * Basic, one of the Galactic Basic, languages in ''Star Wars'' Music * Basic (Glen Campbell album), ''Basic'' (Glen Campbell album), 1978 * Basic (Robert Quine and Fred Maher album), ''Basic'' (Robert Quine and Fred Maher album), 1984 * B.A.S.I.C. (Alpinestars album), ''B.A.S.I.C.'' (Alpinestars album), 2000 * Basic (Brown Eyed Girls album), ''Basic'' (Brown Eyed Girls album), 2015 * B.A.S.I.C. (The Basics album), ''B.A.S.I.C.'' (The Basics album), 2019 Places * Basic, Mississippi, a community in the US * BASIC countries, Brazil, South Africa, India and China in climate change negotiations Organizations * BASIC Bank Limited, government owned bank in Bangladesh * Basic Books, an American publisher Other uses * Basic (cigarette), a brand ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |