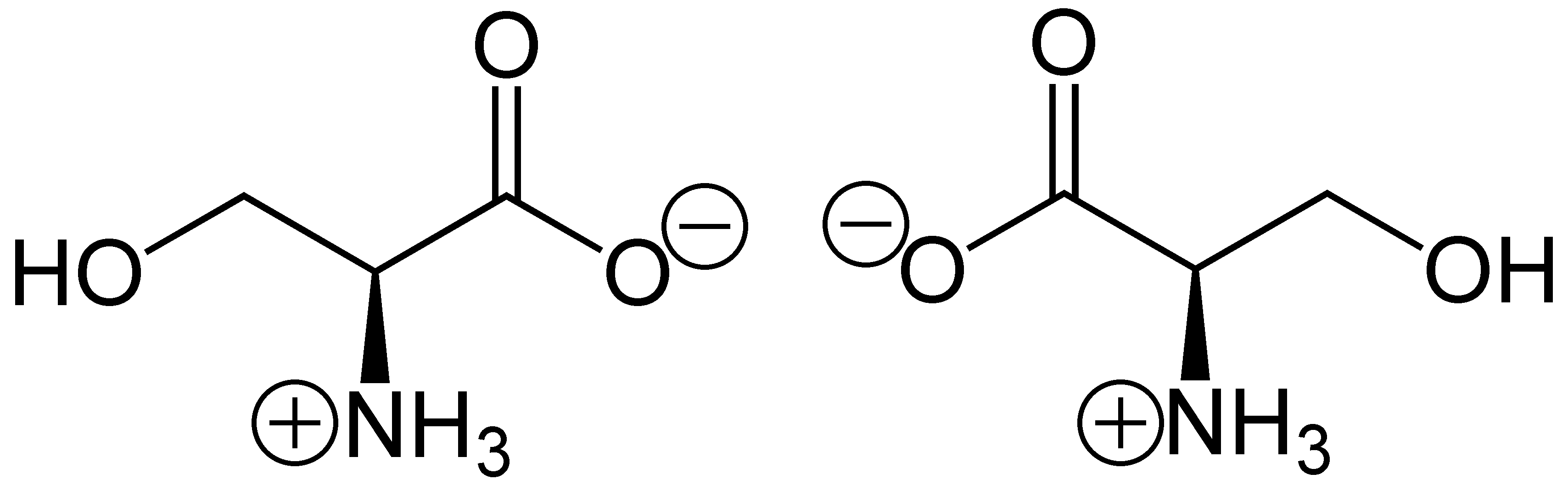|
Eudysmic Ratio
The eudysmic ratio (also spelled eudismic ratio) represents the difference in pharmacologic activity between the two enantiomers of a drug. In most cases where a chiral compound is biologically active, one enantiomer is more active than the other. The eudysmic ratio is the ratio of activity between the two. A eudysmic ratio significantly differing from 1 means that they are statistically different in activity. Eudisimic ratio (ER) reflects the degree of enantioselectivity of the biological systems. For example, (S)-propranolol (ER = 130) meaning that (S)-propranolol is 130 times more active as its (R)-enantiomer. Terminology The eutomer is the enantiomer having the desired pharmacological activity, e.g., as an active ingredient in a drug. The distomer, on the other hand, is the enantiomer of the eutomer which may have undesired bioactivity or may be bio-inert. A racemic mixture is an equal mixture of both enantiomers, which may be easier to manufacture than a single enantio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biological Activity
In pharmacology, biological activity or pharmacological activity describes the beneficial or adverse effects of a drug on living matter. When a drug is a complex chemical mixture, this activity is exerted by the substance's active ingredient or pharmacophore but can be modified by the other constituents. Among the various properties of chemical compounds, pharmacological/biological activity plays a crucial role since it suggests uses of the compounds in the medical applications. However, chemical compounds may show some adverse and toxic effects which may prevent their use in medical practice. Activity is generally dosage-dependent. Further, it is common to have effects ranging from beneficial to adverse for one substance when going from low to high doses. Activity depends critically on fulfillment of the ADME criteria. To be an effective drug, a compound not only must be active against a target, but also possess the appropriate ADME (Absorption, Distribution, Metabolism, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Levomethorphan
Levomethorphan (LVM) ( INN, BAN) is an opioid analgesic of the morphinan family that has never been marketed. It is the L-stereoisomer of racemethorphan (methorphan). The effects of the two isomers of the racemethorphan are quite different, with dextromethorphan (DXM) being an antitussive at low doses and a dissociative hallucinogen at much higher doses. Levomethorphan is about five times stronger than morphine. Levomethorphan is a prodrug to levorphanol, analogously to DXM acting as a prodrug to dextrorphan or codeine behaving as a prodrug to morphine. As such, levomethorphan has similar effects to levorphanol but is less potent as it must be demethylated to the active form by liver enzymes before being able to produce its effects. As a prodrug of levorphanol, levomethorphan functions as a potent agonist of all three of the opioid receptors, μ, κ (κ1 and κ3 but notably not κ2), and δ, as an NMDA receptor antagonist, and as a serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enantiopure Drug
An enantiopure drug is a pharmaceutical that is available in one specific enantiomeric form. Most biological molecules (proteins, sugars, etc.) are present in only one of many chiral forms, so different enantiomers of a chiral drug molecule bind differently (or not at all) to target receptors. Chirality can be observed when the geometric properties of an object is not superimposable with its mirror image. Two forms of a molecule are formed (both mirror images) from a chiral carbon, these two forms are called enantiomers. One enantiomer of a drug may have a desired beneficial effect while the other may cause serious and undesired side effects, or sometimes even beneficial but entirely different effects. The desired enantiomer is known as an eutomer while the undesired enantiomer is known as the distomer. When equal amounts of both enantiomers are found in a mixture, the mixture is known as a racemic mixture. If a mixture for a drug does not have a 1:1 ratio of its enantiomers it is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
D-amino Acid Oxidase
D-amino acid oxidase (DAAO; also OXDA, DAMOX) is an enzyme with the function on a molecular level to oxidize D-amino acids to the corresponding α-keto acids, producing ammonia and hydrogen peroxide. This results in a number of physiological effects in various systems, most notably the brain. The enzyme is most active toward neutral D-amino acids, and not active toward acidic D-amino acids. One of its most important targets in mammals is D-Serine in the central nervous system. By targeting this and other D-amino acids in vertebrates, DAAO is important in detoxification. The role in microorganisms is slightly different, breaking down D-amino acids to generate energy. DAAO is expressed in a wide range of species from yeasts to human. It is not present in plants or in bacteria which instead use D-amino acid dehydrogenase. DAAO in humans is a candidate susceptibility gene and together with G72 may play a role in the glutamatergic mechanisms of schizophrenia. DAAO also plays a r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DDO (gene)
D-aspartate oxidase is an enzyme that is encoded by the ''DDO'' gene. The protein encoded by this gene is a peroxisomal flavoprotein that catalyzes the oxidative deamination of D-aspartate and ''N''-methyl D-aspartate. Flavin adenine dinucleotide Flavin may refer to: Placename * Flavin, Aveyron, a commune in southern France Surname * Adrian Flavin (born 1979), a professional rugby player * Christopher Flavin, president of the Worldwatch Institute * Dan Flavin (1933–1996), a minimalis ... or 6-hydroxyflavin adenine dinucleotide can serve as the cofactor in this reaction. Two (or four, according to ) transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. References Further reading * * * * * * * * * {{gene-6-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transaminase
Transaminases or aminotransferases are enzymes that catalyze a transamination reaction between an amino acid and an α- keto acid. They are important in the synthesis of amino acids, which form proteins. Function and mechanism An amino acid contains an amine (NH2) group. A keto acid contains a keto (=O) group. In transamination, the NH2 group on one molecule is exchanged with the =O group on the other molecule. The amino acid becomes a keto acid, and the keto acid becomes an amino acid. Most transaminases are protein enzymes. However, some transamination activities of the ribosome have been found to be catalyzed by ribozymes (RNA enzymes). Examples being the hammerhead ribozyme, the VS ribozyme and the hairpin ribozyme. Transaminases require the coenzyme pyridoxal phosphate, which is converted into pyridoxamine in the first half-reaction, when an amino acid is converted into a keto acid. Enzyme-bound pyridoxamine in turn reacts with pyruvate, oxaloacetate, or alpha- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alpha-ketoacid
In organic chemistry, keto acids or ketoacids (also called oxo acids or oxoacids) are organic compounds that contain a carboxylic acid group () and a ketone group ().Franz Dietrich Klingler, Wolfgang Ebertz "Oxocarboxylic Acids" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry 2005, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. In several cases, the keto group is hydrated. The alpha-keto acids are especially important in biology as they are involved in the Krebs citric acid cycle and in glycolysis. Common types of keto acids include: *Alpha-keto acids, alpha-ketoacids, or 2-oxoacids have the keto group adjacent to the carboxylic acid. They often arise by oxidative deamination of amino acids, and reciprocally, they are precursors to the same. Alpha-keto acids possesses extensive chemistry as acylation agents. Furthermore, alpha-keto acids such as phenylpyruvic acid are endogenous sources for carbon monoxide (as a gasotransmitter) and pharmaceutical prodrug scaffold. Important representatives: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
D-serine
Serine (symbol Ser or S) is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated − form under biological conditions), a carboxyl group (which is in the deprotonated − form under biological conditions), and a side chain consisting of a hydroxymethyl group, classifying it as a polar amino acid. It can be synthesized in the human body under normal physiological circumstances, making it a nonessential amino acid. It is encoded by the codons UCU, UCC, UCA, UCG, AGU and AGC. Occurrence This compound is one of the naturally occurring proteinogenic amino acids. Only the L-stereoisomer appears naturally in proteins. It is not essential to the human diet, since it is synthesized in the body from other metabolites, including glycine. Serine was first obtained from silk protein, a particularly rich source, in 1865 by Emil Cramer. Its name is derived from the Latin for silk, ''sericum''. Serine's structure was esta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
D-aspartate
Aspartic acid (symbol Asp or D; the ionic form is known as aspartate), is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. Like all other amino acids, it contains an amino group and a carboxylic acid. Its α-amino group is in the protonated –NH form under physiological conditions, while its α-carboxylic acid group is deprotonated −COO− under physiological conditions. Aspartic acid has an acidic side chain (CH2COOH) which reacts with other amino acids, enzymes and proteins in the body. Under physiological conditions (pH 7.4) in proteins the side chain usually occurs as the negatively charged aspartate form, −COO−. It is a non-essential amino acid in humans, meaning the body can synthesize it as needed. It is encoded by the codons GAU and GAC. D-Aspartate is one of two D-amino acids commonly found in mammals. .html" ;"title="/sup>">/sup> In proteins aspartate sidechains are often hydrogen bonded to form asx turns or asx motifs, which frequently occur at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amino Acid
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although hundreds of amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the alpha-amino acids, which comprise proteins. Only 22 alpha amino acids appear in the genetic code. Amino acids can be classified according to the locations of the core structural functional groups, as Alpha and beta carbon, alpha- , beta- , gamma- or delta- amino acids; other categories relate to Chemical polarity, polarity, ionization, and side chain group type (aliphatic, Open-chain compound, acyclic, aromatic, containing hydroxyl or sulfur, etc.). In the form of proteins, amino acid '' residues'' form the second-largest component (water being the largest) of human muscles and other tissues. Beyond their role as residues in proteins, amino acids participate in a number of processes such as neurotransmitter transport and biosynthesis. It is thought that they played a key role in enabling l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
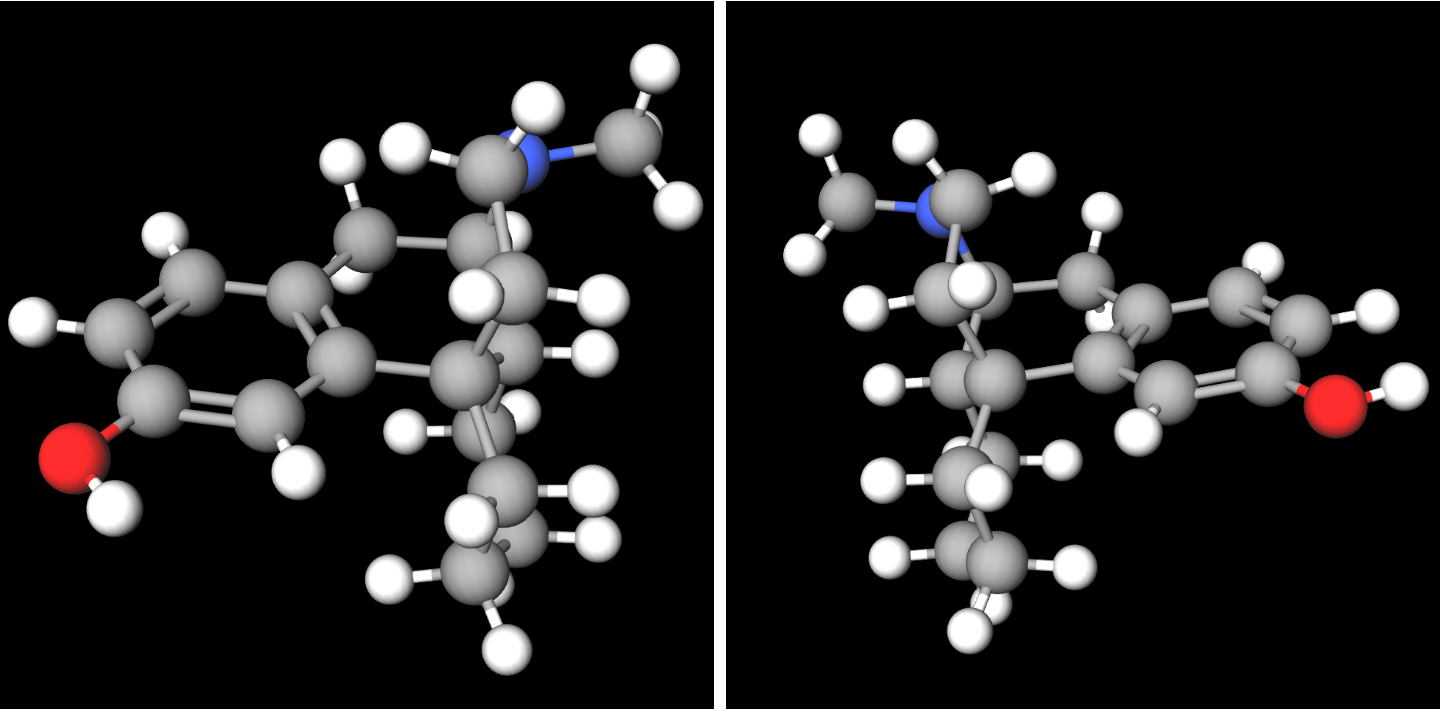
Levorphanol
Levorphanol (brand name Levo-Dromoran) is an opioid medication used to treat moderate to severe pain. It is the levorotatory enantiomer of the compound racemorphan. Its dextrorotatory counterpart is dextrorphan. It was first described in Germany in 1946. The drug has been in medical use in the United States since 1953. Pharmacology Levorphanol acts predominantly as an agonist of the μ-opioid receptor (MOR), but is also an agonist of the δ-opioid receptor (DOR), κ-opioid receptor (KOR), and the nociceptin receptor (NOP), as well as an NMDA receptor antagonist and a serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor (SNRI). Levorphanol, similarly to certain other opioids, also acts as a glycine receptor antagonist and GABA receptor antagonist at very high concentrations. Levorphanol is 6 to 8 times as potent as morphine at the MOR. Relative to morphine, levorphanol lacks complete cross-tolerance and possesses greater intrinsic activity at the MOR. The duration of action is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dextrorphan
Dextrorphan (DXO) is a psychoactive drug of the morphinan class which acts as an antitussive or cough suppressant and dissociative hallucinogen. It is the dextrorotatory enantiomer of racemorphan; the levorotatory enantiomer is levorphanol. Dextrorphan is produced by O-demethylation of dextromethorphan by CYP2D6. Dextrorphan is an NMDA antagonist and contributes to the psychoactive effects of dextromethorphan. Pharmacology Pharmacodynamics The pharmacology of dextrorphan is similar to that of dextromethorphan (DXM). However, dextrorphan is much more potent as an NMDA receptor antagonist as well much less active as a serotonin reuptake inhibitor, but retains DXM's activity as a norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor. It also has more affinity for the opiod receptors than dextromethorphan, significantly so at high doses. Pharmacokinetics Dextrorphan has a notably longer elimination half-life than its parent compound, and therefore has a tendency to accumulate in the blood after ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |