|
Euan MacDonald Centre
The Euan MacDonald Centre is a research centre which is part of the University of Edinburgh. The centre was established in 2007 and seeks to improve the lives of patients with motor neurone disease (MND). The centre was part funded by a donation by Euan MacDonald, who was diagnosed with MND in 2003, and his father Donald MacDonald. In addition to conducting research, the centre also offers clinical treatments. Around 130 are diagnosed with MND each year in Scotland alone. In 2013, the centre announced a new partnership with the J9 Foundation which provides support for people with MND in South Africa. Discoveries by the centre include the finding that Zebrafish are able to produce motor neurones when they repair their spinal cords from injury and abnormalities in the protein TDP-43 result in the death of motor neurone cells. The Euan MacDonald Centre is currently leading a new UK-wide clinical trial, MND-SMART which aims to find treatments for MND. In 2021, The Euan MacDonald Ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Edinburgh
The University of Edinburgh (, ; abbreviated as ''Edin.'' in Post-nominal letters, post-nominals) is a Public university, public research university based in Edinburgh, Scotland. Founded by the City of Edinburgh Council, town council under the authority of a royal charter from King James VI and I, James VI in 1582 and officially opened in 1583, it is one of Scotland's Ancient universities of Scotland, four ancient universities and the List of oldest universities in continuous operation, sixth-oldest university in continuous operation in the English-speaking world. The university played a crucial role in Edinburgh becoming a leading intellectual centre during the Scottish Enlightenment and contributed to the city being nicknamed the "Etymology of Edinburgh#Athens of the North, Athens of the North". The three main global university rankings (Academic Ranking of World Universities, ARWU, Times Higher Education World University Rankings, THE, and QS World University Rankings, QS) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Motor Neurone Disease
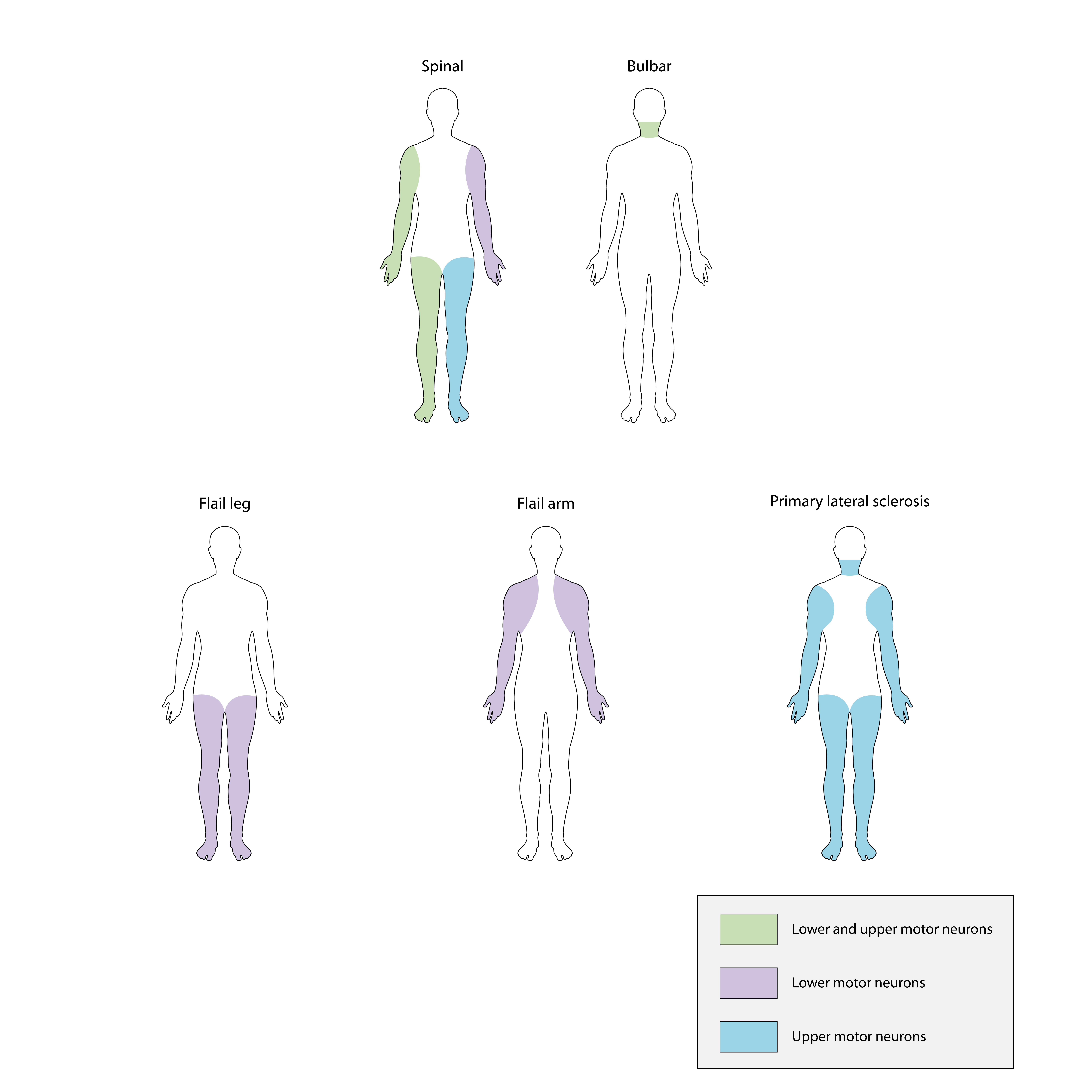
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), also known as motor neuron disease (MND) or—in the United States—Lou Gehrig's disease (LGD), is a rare, terminal neurodegenerative disorder that results in the progressive loss of both upper and lower motor neurons that normally control voluntary muscle contraction. ALS is the most common form of the motor neuron diseases. ALS often presents in its early stages with gradual muscle stiffness, twitches, weakness, and wasting. Motor neuron loss typically continues until the abilities to eat, speak, move, and, lastly, breathe are all lost. While only 15% of people with ALS also fully develop frontotemporal dementia, an estimated 50% face at least some minor difficulties with thinking and behavior. Depending on which of the aforementioned symptoms develops first, ALS is classified as ''limb-onset'' (begins with weakness in the arms or legs) or ''bulbar-onset'' (begins with difficulty in speaking or swallowing). Most cases of ALS (abou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Euan MacDonald
Euan James Stuart MacDonald MBE (14 August 1974 – 21 August 2024) was a Scottish businessman. He studied at the University of St Andrews and the University of Edinburgh. MacDonald was diagnosed with Motor Neurone Disease (MND) in October 2003. Biography MacDonald was born in Sheffield in 1974. He moved to Edinburgh with his parents and siblings at a young age and went to school at George Watson's College before moving to Glenalmond College in Perthshire. Following this he studied at St Andrews, where he met his wife, and Edinburgh University. MacDonald established The Euan MacDonald Centre for Motor Neurone Disease Research in 2007 in partnership with the University of Edinburgh. With the Informatics Department at the University of Edinburgh, MacDonald also helped establish The Voicebank Study which enables people who are at risk of losing their voice through illness to preserve it. He was appointed a Member of the Order of the British Empire The Most Excellent Order ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zebrafish
The zebrafish (''Danio rerio'') is a species of freshwater ray-finned fish belonging to the family Danionidae of the order Cypriniformes. Native to South Asia, it is a popular aquarium fish, frequently sold under the trade name zebra danio (and thus often called a " tropical fish" although it is both tropical and subtropical). The zebrafish is an important and widely used vertebrate model organism in scientific research, particularly developmental biology, but also gene function, oncology, teratology, and drug development, in particular pre-clinical development. It is also notable for its regenerative abilities, and has been modified by researchers to produce many transgenic strains. Taxonomy The zebrafish is a derived member of the genus '' Brachydanio'', of the family Cyprinidae. It has a sister-group relationship with '' Danio aesculapii''. Zebrafish are also closely related to the genus '' Devario'', as demonstrated by a phylogenetic tree of close species. Distri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TDP-43
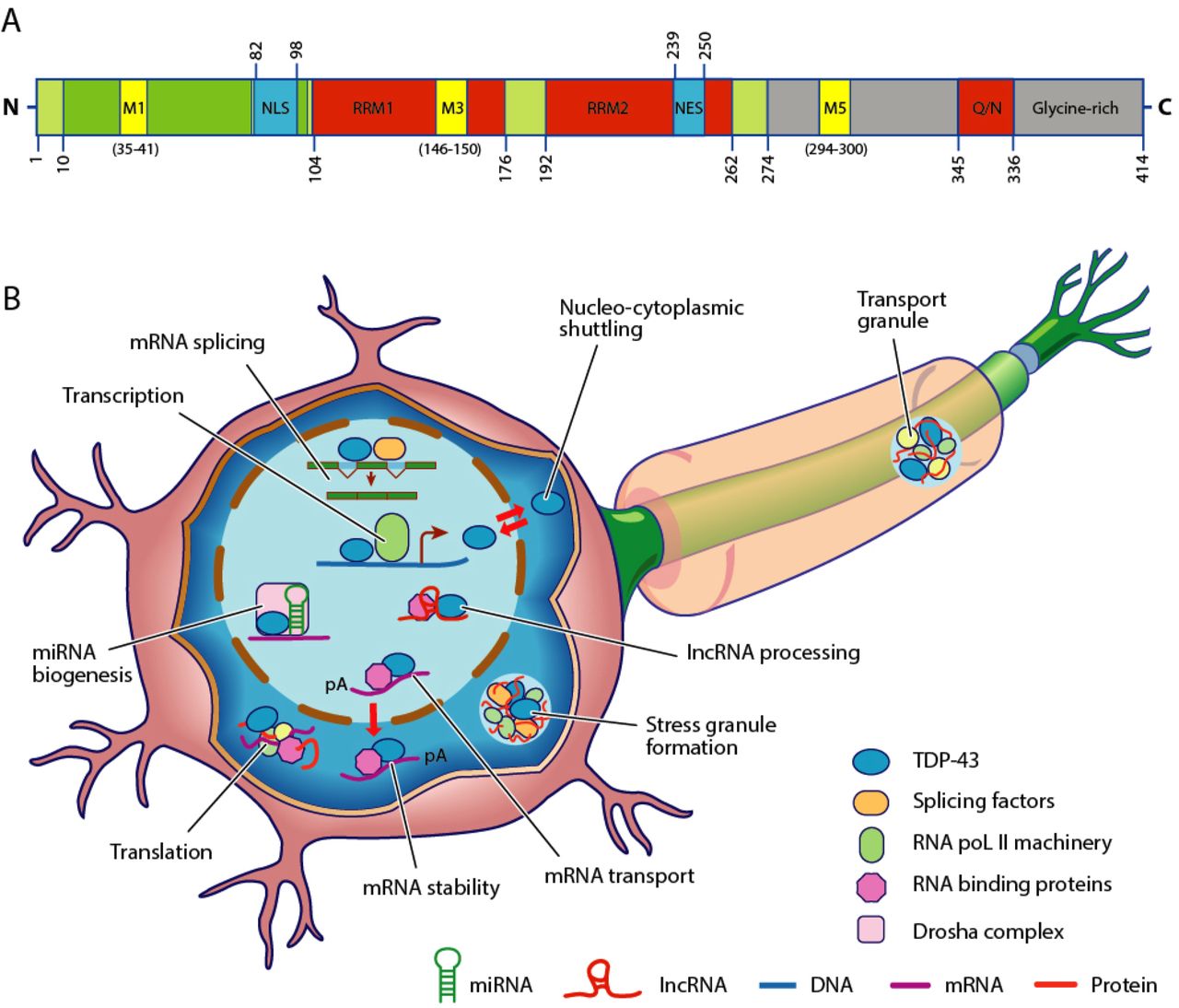
Transactive response DNA binding protein 43 kDa (TAR DNA-binding protein 43 or TDP-43) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''TARDBP'' gene. Structure TDP-43 is 414 amino acid residues long. It consists of four domains: an N-terminal domain spanning residues 1–76 (NTD) with a well-defined fold that has been shown to form a dimer or oligomer; two highly conserved folded RNA recognition motifs spanning residues 106–176 (RRM1) and 191–259 (RRM2), respectively, required to bind target RNA and DNA; an unstructured C-terminal domain encompassing residues 274–414 (CTD), which contains a glycine-rich region, is involved in protein-protein interactions, and harbors most of the mutations associated with familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. The entire protein devoid of large solubilising tags has been purified. The full-length protein is a dimer. The dimer is formed due to a self-interaction between two NTD domains, where the dimerisation can be propagated to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University College London
University College London (Trade name, branded as UCL) is a Public university, public research university in London, England. It is a Member institutions of the University of London, member institution of the Federal university, federal University of London, and is the second-largest list of universities in the United Kingdom by enrolment, university in the United Kingdom by total enrolment and the largest by postgraduate enrolment. Established in 1826 as London University (though without university degree-awarding powers) by founders who were inspired by the radical ideas of Jeremy Bentham, UCL was the first university institution to be established in London, and the first in England to be entirely secular and to admit students regardless of their religion. It was also, in 1878, among the first university colleges to admit women alongside men, two years after University College, Bristol, had done so. Intended by its founders to be Third-oldest university in England debate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Warwick
The University of Warwick ( ; abbreviated as ''Warw.'' in post-nominal letters) is a public research university on the outskirts of Coventry between the West Midlands and Warwickshire, England. The university was founded in 1965 as part of a government initiative to expand higher education. The Warwick Business School was established in 1967, the Warwick Law School in 1968, Warwick Manufacturing Group (WMG) in 1980, and Warwick Medical School in 2000. Warwick incorporated Coventry College of Education in 1979 and Horticulture Research International in 2004. Warwick is primarily based on a campus on the outskirts of Coventry, with a satellite campus in Wellesbourne and a central London base at the Shard. It is organised into three faculties—Arts; Science, Engineering and Medicine, and Social Sciences—within which there are thirty-two departments. Warwick has around 29,534 full-time students and 2,691 academic and research staff, with an average intake of 4,950 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Research Institutes Of The University Of Edinburgh
Research is creative and systematic work undertaken to increase the stock of knowledge. It involves the collection, organization, and analysis of evidence to increase understanding of a topic, characterized by a particular attentiveness to controlling sources of bias and error. These activities are characterized by accounting and controlling for biases. A research project may be an expansion of past work in the field. To test the validity of instruments, procedures, or experiments, research may replicate elements of prior projects or the project as a whole. The primary purposes of basic research (as opposed to applied research) are documentation, discovery, interpretation, and the research and development (R&D) of methods and systems for the advancement of human knowledge. Approaches to research depend on epistemologies, which vary considerably both within and between humanities and sciences. There are several forms of research: scientific, humanities, artistic, economic, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |