|
Ethics Of Nanotechnologies
Ethics of nanotechnology is the study of the ethical issues emerging from advances in nanotechnology and its impacts. According to Andrew Chen, ethical concerns about nanotechnologies should include the possibility of their military applications, the dangers posed by self-replicant nanomachines, and their use for surveillance monitoring and tracking. Risks to environment to public health are treated in a report from the Dutch National Institute for Public Health and the Environment as well as is a report of the European Environment Agency. Academic works on ethics of nanotechnology can be found in the journal Nanoethics. Guidelines According to the Markkula Center for Applied Ethics possible guidelines for an Ethics of nanotechnology could include: *Nanomachines should only be specialized, not for general purpose *Nanomachines should not be self replicating *Nanomachines should not be made to use an abundant natural compound as fuel *Nanomachines should be tagged so that they c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethics
Ethics or moral philosophy is a branch of philosophy that "involves systematizing, defending, and recommending concepts of right and wrong behavior".''Internet Encyclopedia of Philosophy'' The field of ethics, along with aesthetics, concerns matters of value; these fields comprise the branch of philosophy called axiology. Ethics seeks to resolve questions of human morality by defining concepts such as good and evil, right and wrong, virtue and vice, justice and crime. As a field of intellectual inquiry, moral philosophy is related to the fields of moral psychology, descriptive ethics, and value theory. Three major areas of study within ethics recognized today are: # Meta-ethics, concerning the theoretical meaning and reference of moral propositions, and how their truth values (if any) can be determined; # Normative ethics, concerning the practical means of determining a moral course of action; # Applied ethics, concerning what a person is obligated (or per ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Richard Feynman
Richard Phillips Feynman (; May 11, 1918 – February 15, 1988) was an American theoretical physicist, known for his work in the path integral formulation of quantum mechanics, the theory of quantum electrodynamics, the physics of the superfluidity of supercooled liquid helium, as well as his work in particle physics for which he proposed the parton model. For contributions to the development of quantum electrodynamics, Feynman received the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1965 jointly with Julian Schwinger and Shin'ichirō Tomonaga. Feynman developed a widely used pictorial representation scheme for the mathematical expressions describing the behavior of subatomic particles, which later became known as Feynman diagrams. During his lifetime, Feynman became one of the best-known scientists in the world. In a 1999 poll of 130 leading physicists worldwide by the British journal '' Physics World'', he was ranked the seventh-greatest physicist of all time. He assisted in the develop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
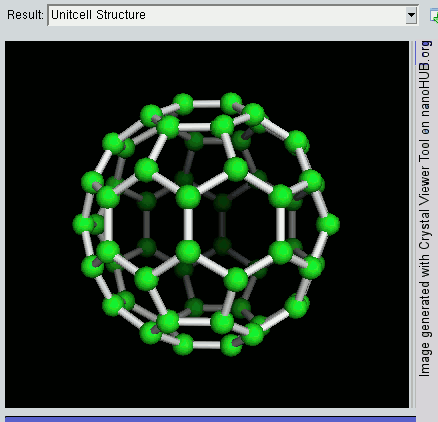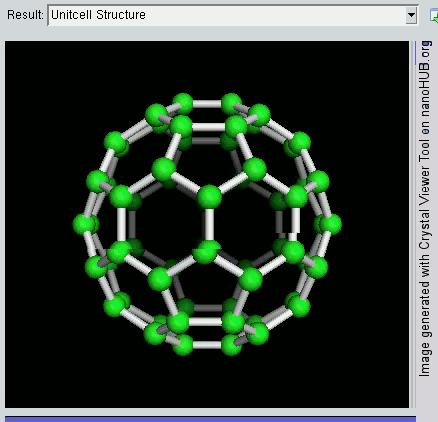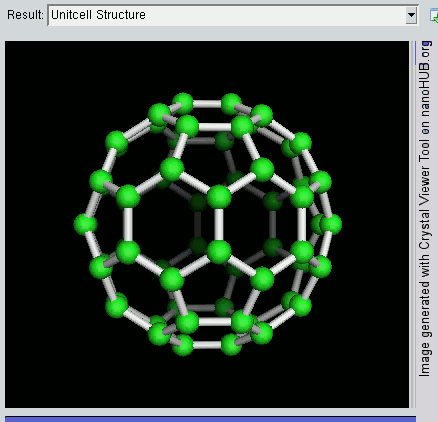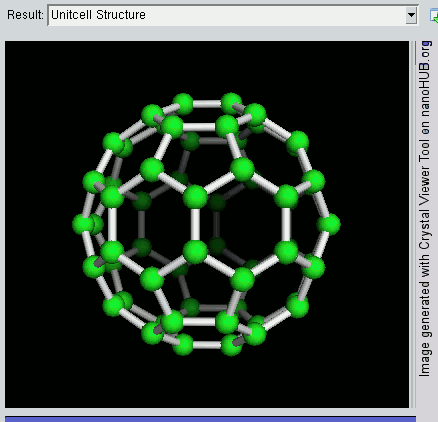
Nanomaterials
* Nanomaterials describe, in principle, materials of which a single unit is sized (in at least one dimension) between 1 and 100 nm (the usual definition of nanoscale). Nanomaterials research takes a materials science-based approach to nanotechnology, leveraging advances in materials metrology and synthesis which have been developed in support of microfabrication research. Materials with structure at the nanoscale often have unique optical, electronic, thermo-physical or mechanical properties. Nanomaterials are slowly becoming commercialized and beginning to emerge as commodities. Definition In ISO/TS 80004, ''nanomaterial'' is defined as the "material with any external dimension in the nanoscale or having internal structure or surface structure in the nanoscale", with ''nanoscale'' defined as the "length range approximately from 1 nm to 100 nm". This includes both ''nano-objects'', which are discrete pieces of material, and ''nanostructured materials'', which have i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nanotoxicity
Nanotoxicology is the study of the toxicity of nanomaterials. Because of quantum size effects and large surface area to volume ratio, nanomaterials have unique properties compared with their larger counterparts that affect their toxicity. Of the possible hazards, inhalation exposure appears to present the most concern, with animal studies showing pulmonary effects such as inflammation, fibrosis, and carcinogenicity for some nanomaterials. Skin contact and ingestion exposure are also a concern. Background Nanomaterials have at least one primary dimension of less than 100 nanometers, and often have properties different from those of their bulk components that are technologically useful. Because nanotechnology is a recent development, the health and safety effects of exposures to nanomaterials, and what levels of exposure may be acceptable, is not yet fully understood. Nanoparticles can be divided into combustion-derived nanoparticles (like diesel soot), manufactured nanopartic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atomically Precise Manufacturing
Atomically precise manufacturing (APM) is an application of nanotechnology where single molecules can be used to manufacture products at an atomic level. The technology currently has potential in highly technical fields like quantum computing, but if commercialized, would likely have a major impact across all fields of manufacturing. APM is classified as a disruptive technology, or a technology that creates large amounts of change in an existing industry. APM is currently under development, and no easy method to manipulate individual atoms has been discovered. If advancements are made that make the technology cheap and efficient, APM could be commercialized for large-scale usage. As a disruptive technology, APM could first be marketed in niche fields such as nanomedicine and quantum computing before seeing widespread use. Advantages of atomically precise manufacturing Traditional manufacturing processes are mainly based on the concepts of discrete manufacturing and process ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molecular Manufacturing
A molecular assembler, as defined by K. Eric Drexler, is a "proposed device able to guide chemical reactions by positioning reactive molecules with atomic precision". A molecular assembler is a kind of molecular machine. Some biological molecules such as ribosomes fit this definition. This is because they receive instructions from messenger RNA and then assemble specific sequences of amino acids to construct protein molecules. However, the term "molecular assembler" usually refers to theoretical human-made devices. Beginning in 2007, the British Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council has funded development of ribosome-like molecular assemblers. Clearly, molecular assemblers are possible in this limited sense. A technology roadmap project, led by the Battelle Memorial Institute and hosted by several U.S. National Laboratories has explored a range of atomically precise fabrication technologies, including both early-generation and longer-term prospects for pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nanotechnology
Nanotechnology, also shortened to nanotech, is the use of matter on an atomic, molecular, and supramolecular scale for industrial purposes. The earliest, widespread description of nanotechnology referred to the particular technological goal of precisely manipulating atoms and molecules for fabrication of macroscale products, also now referred to as molecular nanotechnology. A more generalized description of nanotechnology was subsequently established by the National Nanotechnology Initiative, which defined nanotechnology as the manipulation of matter with at least one dimension sized from 1 to 100 nanometers (nm). This definition reflects the fact that quantum mechanical effects are important at this quantum-realm scale, and so the definition shifted from a particular technological goal to a research category inclusive of all types of research and technologies that deal with the special properties of matter which occur below the given size threshold. It is therefore commo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seth Baum
Seth Baum is an American researcher involved in the field of risk research. He is the executive director of the Global Catastrophic Risk Institute (GCRI), a think tank focused on existential risk. He is also affiliated with the Blue Marble Space Institute of Science and the Columbia University Center for Research on Environmental Decisions. Academic career Baum obtained his BS in optics and mathematics in 2003 at the University of Rochester, followed by an MS in Electrical Engineering, Northeastern University in 2006. In 2012, he obtained his PhD in Geography with his dissertation on climate change policy: "Discounting Across Space and Time in Climate Change Assessment" from Pennsylvania State University. Later, he completed a post-doctoral fellowship with the Columbia University Center for Research on Environmental Decisions. Baum then steered his research interests into astrophysics and global risks, including global warming and nuclear war, and the development of effective ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Steven Umbrello
Stephen or Steven is a common English first name. It is particularly significant to Christians, as it belonged to Saint Stephen ( grc-gre, Στέφανος ), an early disciple and deacon who, according to the Book of Acts, was stoned to death; he is widely regarded as the first martyr (or "protomartyr") of the Christian Church. In English, Stephen is most commonly pronounced as ' (). The name, in both the forms Stephen and Steven, is often shortened to Steve or Stevie. The spelling as Stephen can also be pronounced which is from the Greek original version, Stephanos. In English, the female version of the name is Stephanie. Many surnames are derived from the first name, including Stephens, Stevens, Stephenson, and Stevenson, all of which mean "Stephen's (son)". In modern times the name has sometimes been given with intentionally non-standard spelling, such as Stevan or Stevon. A common variant of the name used in English is Stephan ; related names that have found some curr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jeroen Van Den Hoven
Jeroen van den Hoven (born 1957 in Rotterdam) is a Dutch ethicist and a philosophy professor at Delft University of Technology. He specializes in ethics of information technology. Work Van den Hoven has written and worked with a range of scholars including Seumas Miller, Thomas Pogge, Martha Nussbaum and John Weckert. Currently he is Scientific Director of the Delft Design for Values Institute, editor in chief of '' Ethics and Information Technology,'' and the founding Scientific Director of the 3TU.Centre for Ethics and Technology (2007-2013). Van den Hoven is also founding Chair of the CEPE conference (Computer Ethics Philosophical Enquiry), a permanent member of the European Group on Ethics (EGE) to the European Commission. Awards * In 2009, he won the World Technology Award for Ethics as well as the IFIP prize for ICT and Society for his work in Ethics and ICT. * In 2017 he was knighted in the Order of the Netherlands Lion The Order of the Netherlands Lion, also kno ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
There's Plenty Of Room At The Bottom
"There's Plenty of Room at the Bottom: An Invitation to Enter a New Field of Physics" was a lecture given by physicist Richard Feynman at the annual American Physical Society meeting at Caltech on December 29, 1959. Feynman considered the possibility of direct manipulation of individual atoms as a more robust form of synthetic chemistry than those used at the time. Although versions of the talk were reprinted in a few popular magazines, it went largely unnoticed. It did not inspire the conceptual beginnings of the field of nanotechnology. Beginning in the 1980s, nanotechnology advocates cited it to establish the scientific credibility of their work. Conception Feynman considered some ramifications of a general ability to manipulate matter on an atomic scale. He was particularly interested in the possibilities of denser computer circuitry and microscopes that could see things much smaller than is possible with scanning electron microscopes. These ideas were later realized by the u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surely You're Joking, Mr
"Surely" is a 1995 single by British pop group Five Star. The single was a U.S. only release, available in the UK as an import. Although it missed the ''Billboard'' Hot 100 chart, it peaked at number 125 in October of that year (see 1995 in music This is a list of notable events in music that took place in the year 1995. Specific locations *1995 in British music * 1995 in Norwegian music Specific genres * 1995 in classical music *1995 in country music * 1995 in heavy metal music * 1 ...). The song includes a rap by Junior P. This was the first time Five Star had used a rapper on one of their songs. Track listing #Surely (Radio Mix) #Surely (Sure Funk) #Surely (Dub Mix) #Surely (Instrumental) #Surely (Album Version featuring Junior P) #Surely (Club Jam Mix featuring Junior P) References {{Five Star 1995 singles Five Star songs Songs written by Delroy Pearson Songs written by Doris Pearson ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |